 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
ELK3-ID4 axis governs the metastatic features of triple negative breast cancer
Department of Biomedical Science, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea
* Corresponding Author: KYUNG-SOON PARK. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Cancer Metastasis)
Oncology Research 2024, 32(1), 127-138. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2023.042945
Received 17 June 2023; Accepted 08 September 2023; Issue published 15 November 2023
Abstract
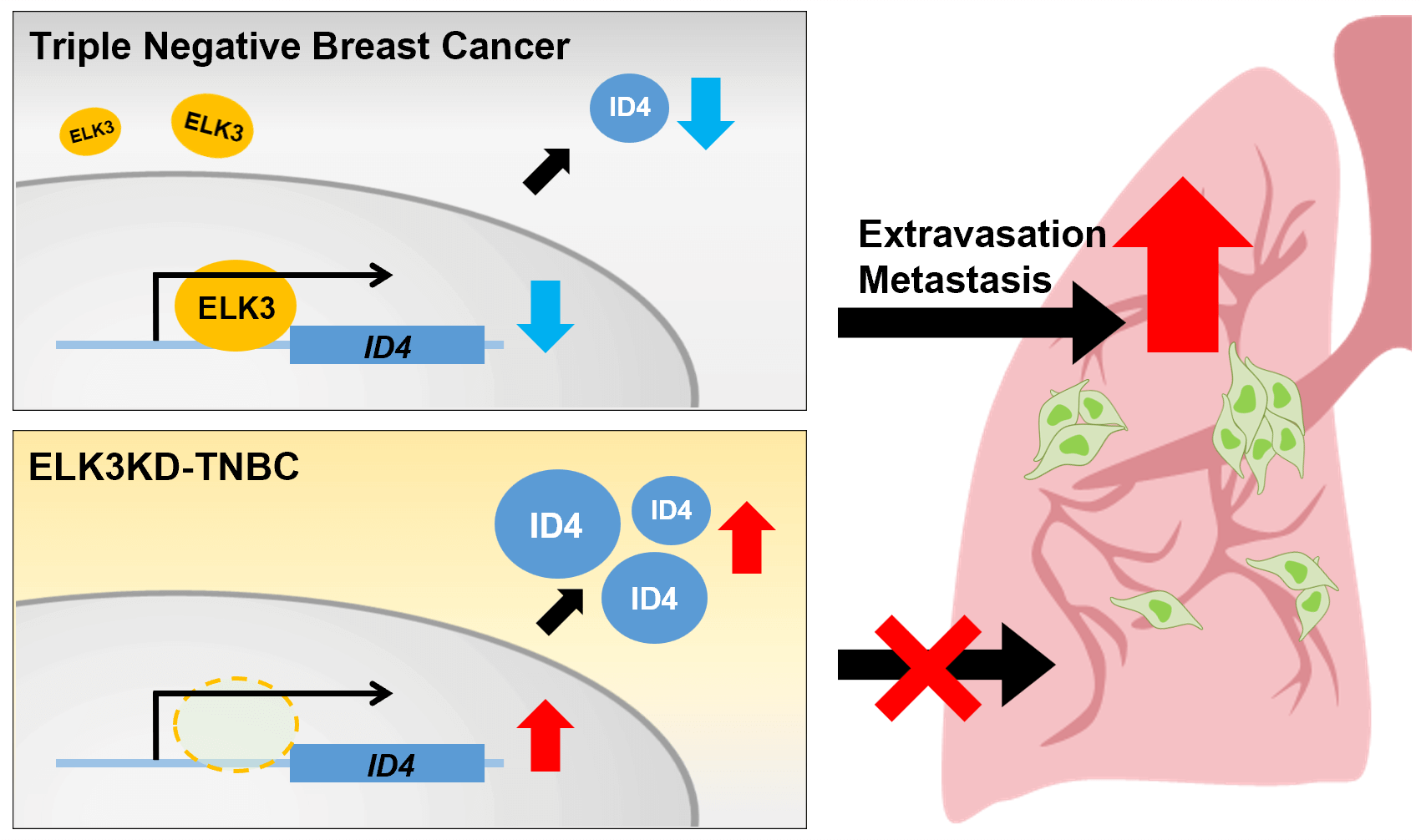
Purpose: Cancer cell metastasis is a multistep process, and the mechanism underlying extravasation remains unclear. ELK3 is a transcription factor that plays a crucial role in regulating various cellular processes, including cancer metastasis. Based on the finding that ELK3 promotes the metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), we investigated whether ELK3 regulates the extravasation of TNBC by forming the ELK3-ID4 axis. ID4 functions as a transcriptional regulator that interacts with other transcription factors, inhibiting their activity and subsequently influencing various biological processes associated with cell differentiation, survival, growth, and metastasis. Methods: We assessed the correlation between the expression of ELK3 and that of ID4 in TNBCs using bioinformatics analyses, QRT-PCR, western blot analysis, luciferase reporter assays, and chromatin immunoprecipitation. Migration, adhesion, invasion, and lung metastasis assays were employed to determine whether the ELK3-ID4 axis regulates the metastatic features of TNBC. Results: We found that ELK3 binds directly to a binding motif close to the ID4 promoter to repress promoter activity. The expression of E-cadherin in TNBC was regulated by the ELK3-ID4 axis. In vitro and in vivo analyses showed that inhibiting ID4 expression in ELK3-knockdown MDA-MB-231 (ELK3KD) cells restored the ability to extravasate and metastasize. Conclusion: The results indicate that the ELK3 regulates ID4 promoter activity, and that the ELK3-ID4 axis regulates the metastatic characteristics of TNBC cells. Additionally, the data suggest that the ELK3-ID4 axis regulates metastasis of TNBCs by modulating expression of E-cadherin.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools