 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Scaffold proteins of cancer signaling networks: The paradigm of FK506 binding protein 51 (FKBP51) supporting tumor intrinsic properties and immune escape
1 Department of Molecular Medicine and Medical Biotechnology, University of Naples Federico II, Naples, 80131, Italy
2 Dipartimento di Diagnostica per Immagini e Neuroradiologia, Fondazione Policlinico Universitario “A.Gemelli” IRCCS, Università Cattolica S. Cuore, Rome, Italy
* Corresponding Authors: SIMONA ROMANO. Email: ; MARIA FIAMMETTA ROMANO. Email:
Oncology Research 2023, 31(4), 423-436. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2023.028392
Received 15 December 2022; Accepted 10 March 2023; Issue published 25 June 2023
Abstract
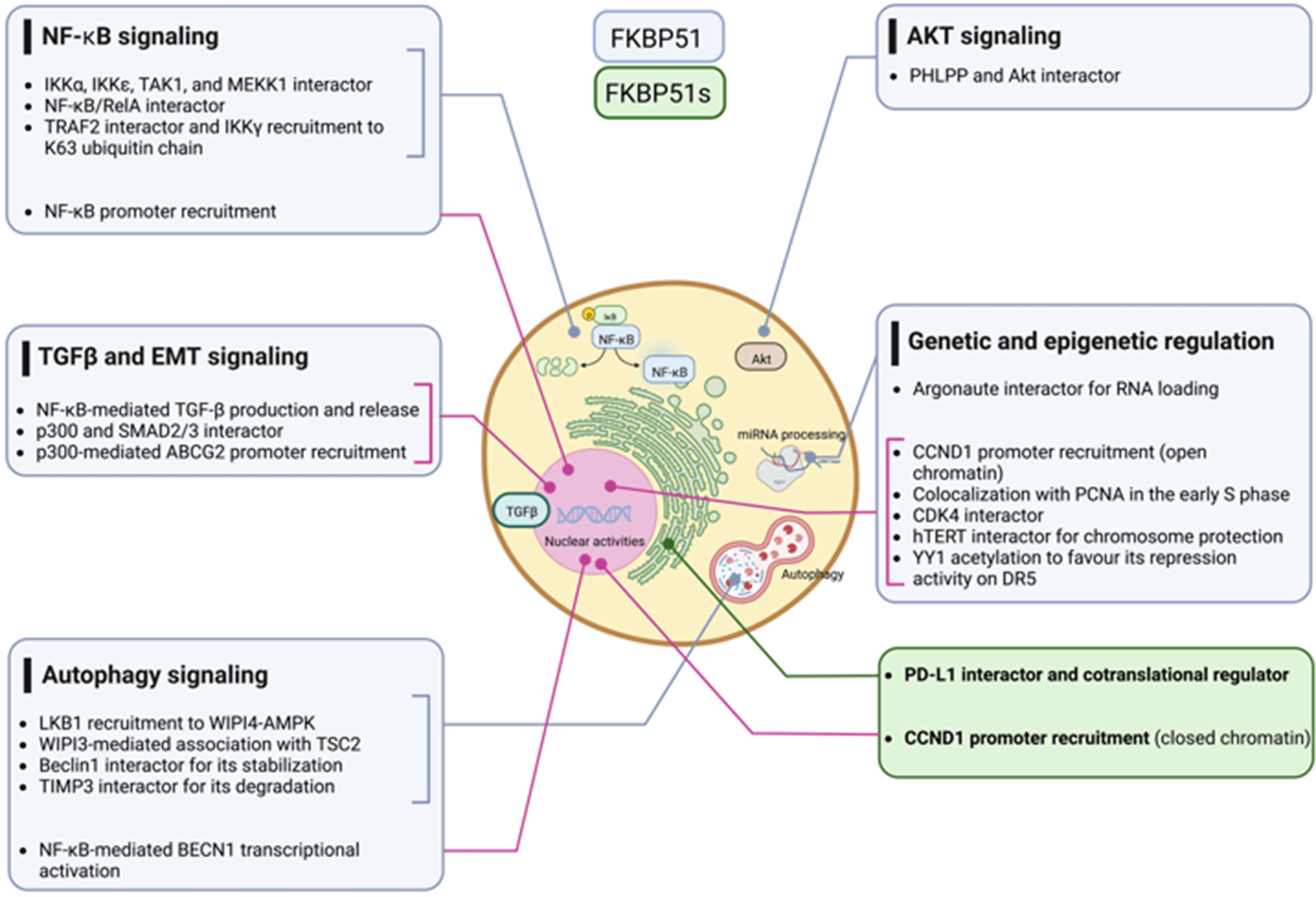
Scaffold proteins are crucial regulators of signaling networks, and their abnormal expression may favor the development of tumors. Among the scaffold proteins, immunophilin covers a unique role as ‘protein-philin’ (Greek ‘philin’ = friend) that interacts with proteins to guide their proper assembly. The growing list of human syndromes associated with the immunophilin defect underscores the biological relevance of these proteins that are largely opportunistically exploited by cancer cells to support and enable the tumor’s intrinsic properties. Among the members of the immunophilin family, the FKBP5 gene was the only one identified to have a splicing variant. Cancer cells impose unique demands on the splicing machinery, thus acquiring a particular susceptibility to splicing inhibitors. This review article aims to overview the current knowledge of the FKBP5 gene functions in human cancer, illustrating how cancer cells exploit the scaffolding function of canonical FKBP51 to foster signaling networks that support their intrinsic tumor properties and the spliced FKBP51s to gain the capacity to evade the immune system.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools