 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Gallic acid suppresses esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression and enhances cisplatin chemosensitivity through IL-6/STAT3/Notch pathway
College of Biological Sciences and Technology, YiLi Normal University, Yining, 835000, China
* Corresponding Author: YANLI REN. Email:
# These two authors contributed equally to this work
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Signaling Pathway Crosstalk in Malignant Tumors: Molecular Targets and Combinatorial Therapeutics)
Oncology Research 2025, 33(6), 1473-1484. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2025.060151
Received 25 October 2024; Accepted 16 January 2025; Issue published 29 May 2025
Abstract
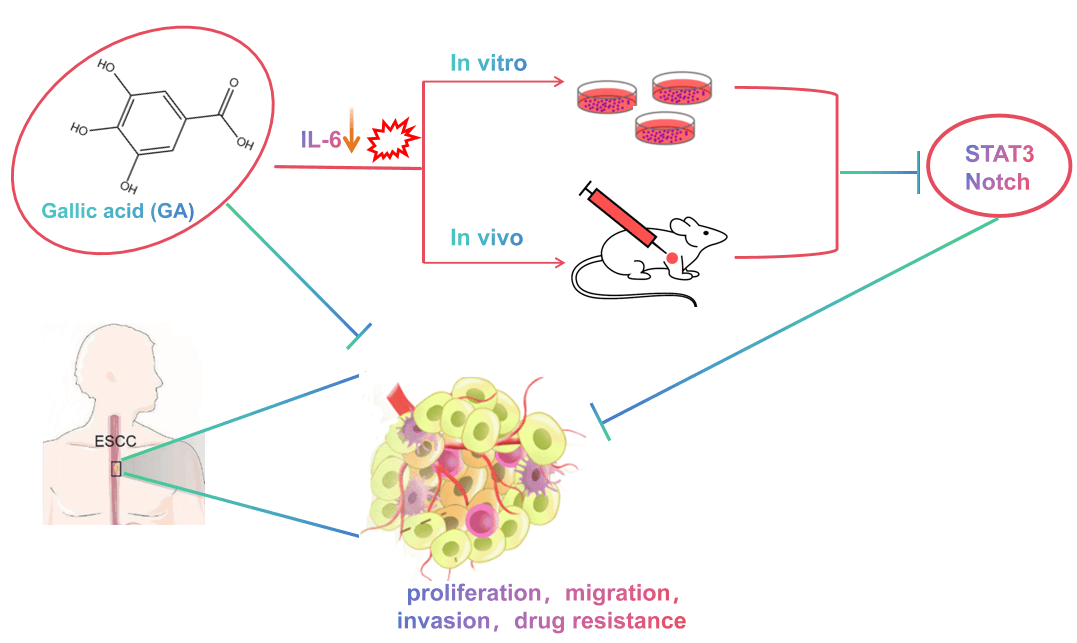
Background: Gallic acid (GA), a plant-derived polyphenol, possesses diverse biological functions such as reducing inflammation and against tumors. Currently, the influence of GA on the resistance of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cells to cisplatin (DDP) is not well understood. Methods: Cell counting kit-8 assay examined how GA affected KYSE30 and TE-1 cell viability. 5-Ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine and TdT-mediated dUTP Nick-End labeling staining detected cell proliferation and apoptosis. Clone formation assay, flow cytometry, Carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester fluorescent probes, and Transwell assay determined cell biological properties, and 2′,7′-Dichlorofluorescin diacetate (DCFH-DA) fluorescent probes detected oxidative stress levels. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3)/Notch pathway protein levels after GA and/or Interleukin-6 (IL-6) intervention were examined through Western blot. Furthermore, a model for subcutaneous graft tumors was established in nude mice. Results: GA exerted suppressive effects on cell proliferation, and caused apoptosis of KYSE30 and TE-1 cells. IL-6 intervention activated the STAT3/Notch pathway and promoted the malignant biological properties of ESCC cells. In contrast, GA attenuated the effects of IL-6, while STAT3 or Notch inhibitor further enhanced the effects of GA, suggesting that GA inhibited the IL-6/STAT3/Notch pathway. Not only that, GA promoted oxidative stress and enhanced cell sensitivity to DDP both in vitro and in vivo. Conclusion: GA suppresses the malignant progression of ESCC and enhances cell sensitivity to DDP by hindering the IL-6/STAT3/Notch pathway.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools