 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CSRNP1 Promotes Apoptosis and Mitochondrial Dysfunction via ROS-Mediated JNK/p38 MAPK Pathway Activation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
1 Department of Gastroenterology, Yangpu Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai, 200090, China
2 Center for Clinical Research and Translational Medicine, Yangpu Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai, 200090, China
3 Department of Surgical Room, Yangpu Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai, 200090, China
4 Department of General Surgery, Yangpu Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai, 200090, China
5 Department of Hepatic-Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery, Shanghai Fourth People’s Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai, 200434, China
* Corresponding Authors: Kai Lu. Email: ; Wenchao Wang. Email:
; Maoling Zhu. Email:
# These authors contributed equally to this work
§ The primary corresponding author
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Molecular Targets and Combinatorial Therapeutics of Liver Cancer)
Oncology Research 2026, 34(1), 17 https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2025.068737
Received 05 June 2025; Accepted 03 September 2025; Issue published 30 December 2025
Abstract
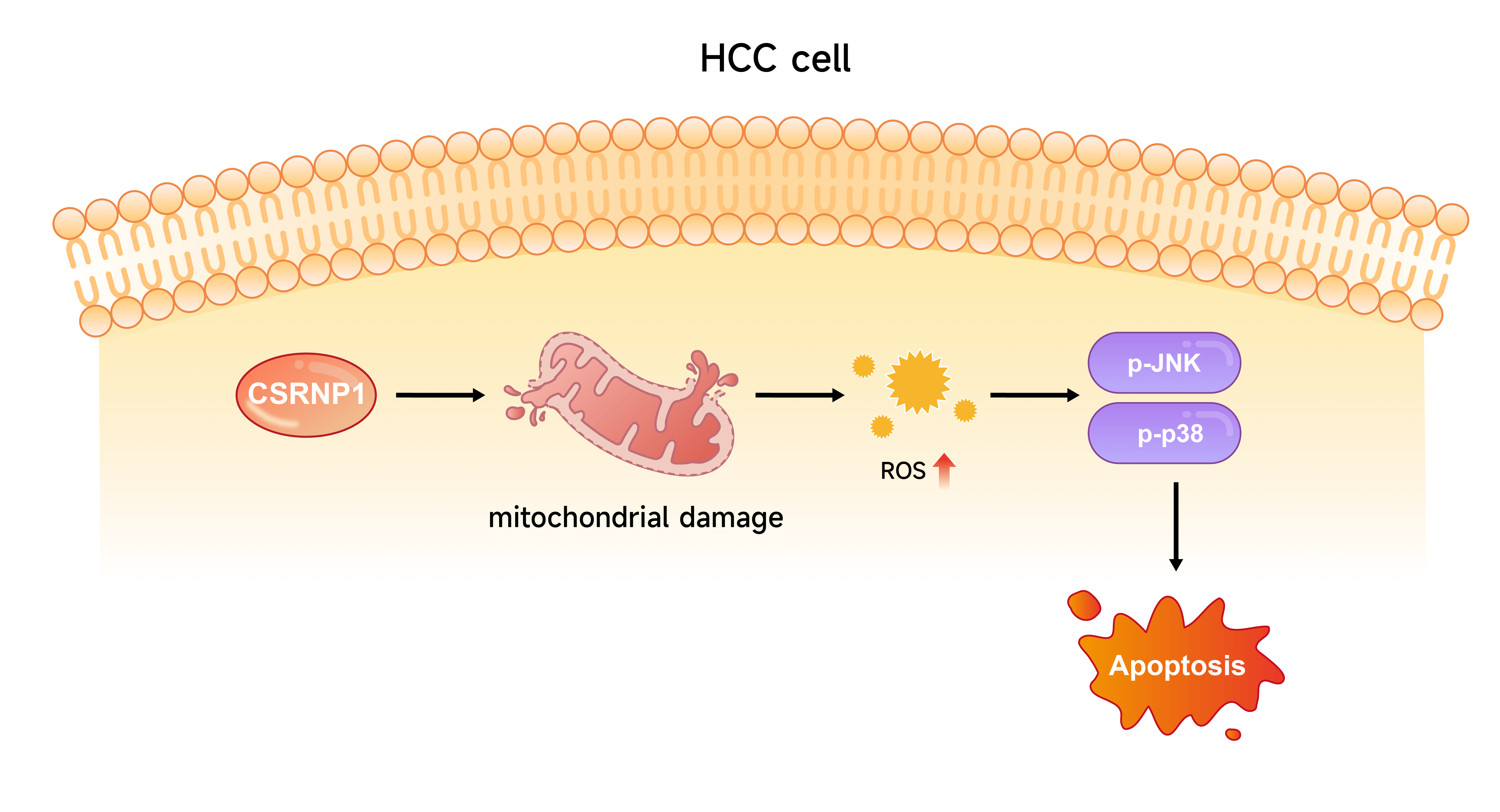
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide. This study aimed to identify key genes involved in HCC development and elucidate their molecular mechanisms, with a particular focus on mitochondrial function and apoptosis. Methods: Differential expression analyses were performed across three datasets—The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA)-Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma (LIHC), GSE36076, and GSE95698—to identify overlapping differentially expressed genes (DEGs). A prognostic risk model was then constructed. Cysteine/serine-rich nuclear protein 1 (CSRNP1) expression levels in HCC cell lines were assessed via western blot (WB) and quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). The effects of CSRNP1 knockdown or overexpression on cell proliferation, migration, and apoptosis were evaluated using cell counting-8 (CCK-8) assays, Transwell assays, and flow cytometry. Mitochondrial ultrastructure was examined by transmission electron microscopy, and intracellular and mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (mROS) levels were measured using specific fluorescent probes. WB was used to assess activation of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, and pathway dependence was examined using the ROS scavenger N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) and the JNK inhibitor SP600125. Results: A six-gene prognostic model was established, comprising downregulated genes (NR4A1 and CSRNP1) and upregulated genes (CENPQ, YAE1, FANCF, and POC5) in HCC. Functional experiments revealed that CSRNP1 knockdown promoted the proliferation of HCC cells and suppressed their apoptosis. Conversely, CSRNP1 overexpression impaired mitochondrial integrity, increased both mitochondrial and cytoplasmic ROS levels, and activated the JNK/p38 MAPK pathway. Notably, treatment with NAC or SP600125 attenuated CSRNP1-induced MAPK activation and apoptosis. Conclusion: CSRNP1 is a novel prognostic biomarker and tumor suppressor in HCC. It exerts anti-tumor effects by inducing oxidative stress and activating the JNK/p38 MAPK pathway in a ROS-dependent manner. These findings suggest that CSRNP1 may serve as a potential therapeutic target in the management of HCC.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material FileCite This Article
 Copyright © 2026 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2026 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools