 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Contents of Cymbocarpum widemannii and Their Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, DNA Damaging Activities
1 Department of Biology, Faculty of Art and Science, Siirt University, Siirt, 56100, Türkiye
2 Department of Agricultural Biotechnology, Faculty of Agriculture, Siirt University, Siirt, 56100, Türkiye
3 Department of Crop and Animal Production, Kurtalan Vocational School, Siirt University, Siirt, 56100, Türkiye
4 Department of Food Engineering, Faculty of Engineering and Architecture, Siirt University, Siirt, 56100, Türkiye
* Corresponding Author: Behcet Inal. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Functional Plant Extracts and Bioactive Metabolites)
Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany 2025, 94(3), 781-791. https://doi.org/10.32604/phyton.2025.062171
Received 11 December 2024; Accepted 20 February 2025; Issue published 31 March 2025
Abstract
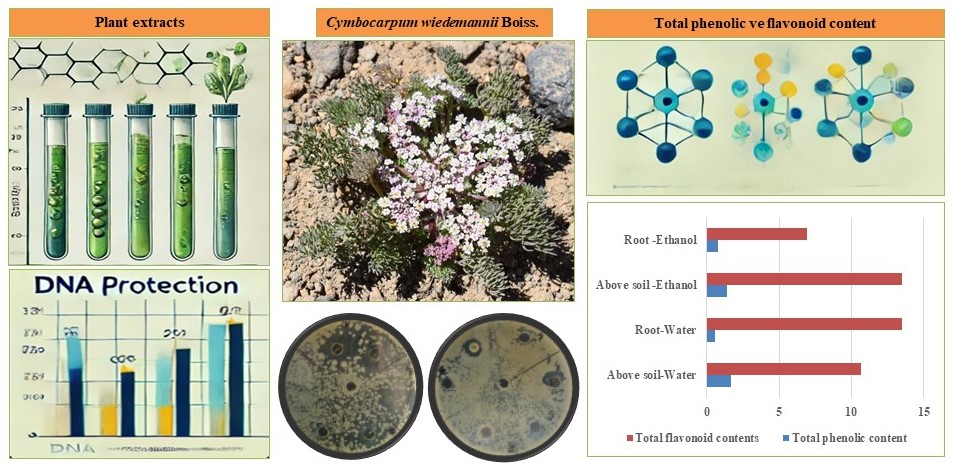
The use of conventional herbal medicines is a rapidly expanding phenomenon in developed nations. For instance, 30%–50% of all drug use in China is attributed to traditional herbal preparations. Current study evaluated the antioxidant (DPPH, FRAP), total phenolic and flavonoid content, antibacterial activity, and DNA damage protective potential of aqueous and methanolic extracts obtained from the aerial parts and roots of Cymbocarpum wiedemannii Boiss., an endemic plant in Turkey. In antioxidant analyses, the methanolic extract of the aerial parts showed the highest %DPPH (73.38) and IC50 (3.46 mg/mL) values. The FRAP analysis revealed the highest iron-reducing capacity in the methanolic extract of the aerial parts (108.10 ± 0.11 mg FeSO4/mL). The aqueous extract of the aerial parts exhibited the highest total phenolic content (1.69 ± 0.02 mg gallic acid/mL), while the methanolic extract of the aerial parts had the highest total flavonoid content (13.53 ± 0.09 mg rutin/mL). Antibacterial activity tests showed no significant effect at a concentration of 1 mg/mL for the samples. DNA protective effects were tested on pBR322 plasmid DNA, demonstrating that both aerial and root extracts could protect DNA from Fenton reaction-induced damage. In conclusion, C. wiedemannii exhibits potential bioactive properties, particularly in terms of its antioxidant and DNA protective effects.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools