 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Deep Learning and Federated Learning in Human Activity Recognition with Sensor Data: A Comprehensive Review
Faculty of Computer Science and Information Technology, University Putra Malaysia (UPM), Serdang, 43400, Malaysia
* Corresponding Author: Farhad Mortezapour Shiri. Email:
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2025, 145(2), 1389-1485. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2025.071858
Received 13 August 2025; Accepted 06 October 2025; Issue published 26 November 2025
Abstract
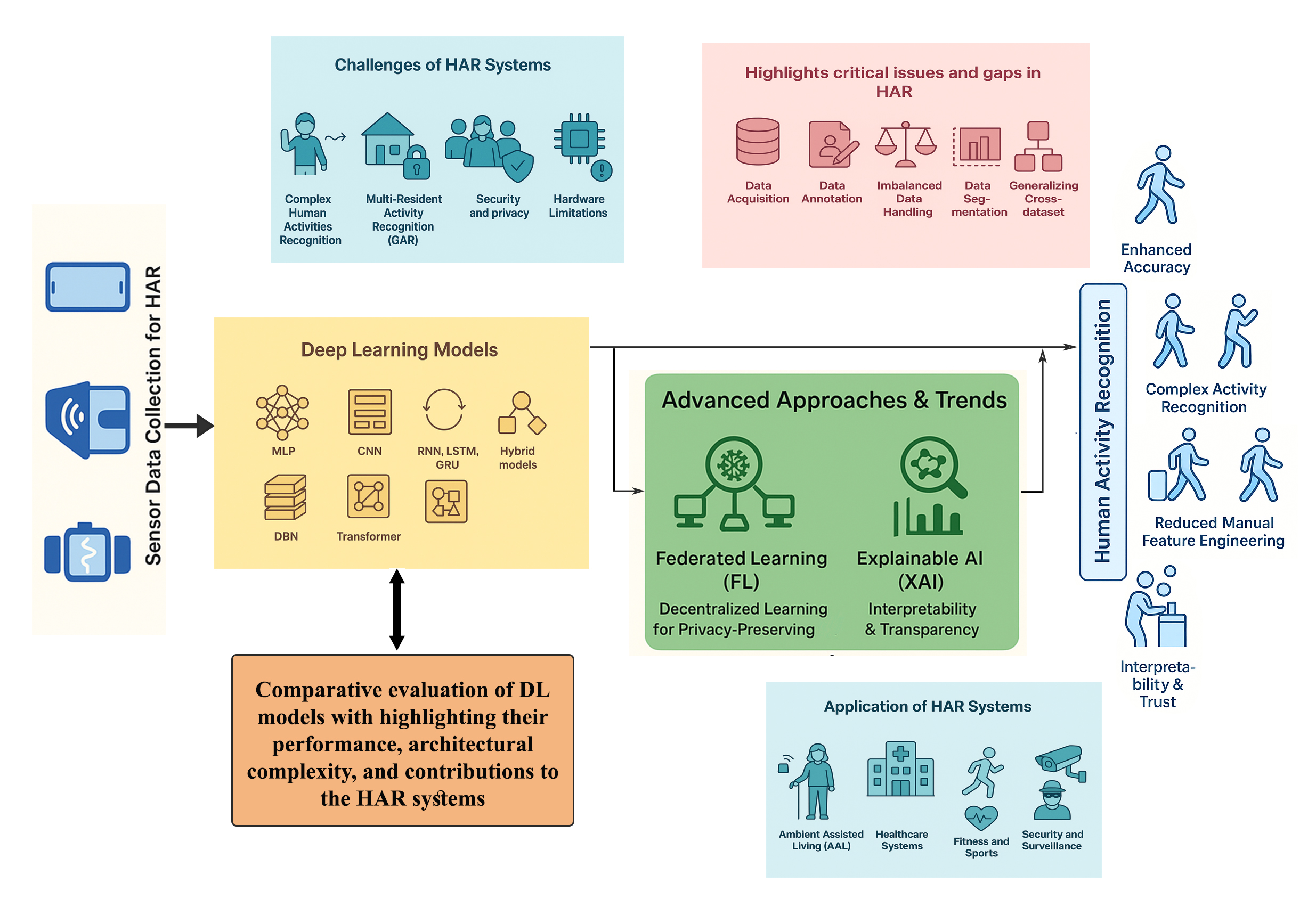
Human Activity Recognition (HAR) represents a rapidly advancing research domain, propelled by continuous developments in sensor technologies and the Internet of Things (IoT). Deep learning has become the dominant paradigm in sensor-based HAR systems, offering significant advantages over traditional machine learning methods by eliminating manual feature extraction, enhancing recognition accuracy for complex activities, and enabling the exploitation of unlabeled data through generative models. This paper provides a comprehensive review of recent advancements and emerging trends in deep learning models developed for sensor-based human activity recognition (HAR) systems. We begin with an overview of fundamental HAR concepts in sensor-driven contexts, followed by a systematic categorization and summary of existing research. Our survey encompasses a wide range of deep learning approaches, including Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLP), Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN), Long Short-Term Memory networks (LSTM), Gated Recurrent Units (GRU), Transformers, Deep Belief Networks (DBN), and hybrid architectures. A comparative evaluation of these models is provided, highlighting their performance, architectural complexity, and contributions to the field. Beyond Centralized deep learning models, we examine the role of Federated Learning (FL) in HAR, highlighting current applications and research directions. Finally, we discuss the growing importance of Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) in sensor-based HAR, reviewing recent studies that integrate interpretability methods to enhance transparency and trustworthiness in deep learning-based HAR systems.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools