 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Structure, function, and mechanism of the TNFAIP8 (TIPE) family of proteins in cancer and inflammation
1 School of Pharmacy & Clinical Pharmacy, School of Integrative Pharmacy, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou, 510006, China
2 Department of Biomedical Sciences Laboratory, Affiliated Dongyang Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Dongyang, 322100, China
3 The Second People’s Hospital of China Three Gorges University, Yichang, 443000, China
4 Guangdong Province Key Laboratory for Biotechnology Drug Candidates, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou, 510006, China
5 Key Specialty of Clinical Pharmacy, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou, 510080, China
* Corresponding Authors: Song Liu, ; Huiqun Tian,
# These authors contributed equally to this article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Frontiers in cancer: tumor microenvironment)
BIOCELL 2023, 47(10), 2217-2232. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.030233
Received 28 March 2023; Accepted 28 June 2023; Issue published 08 November 2023
Abstract
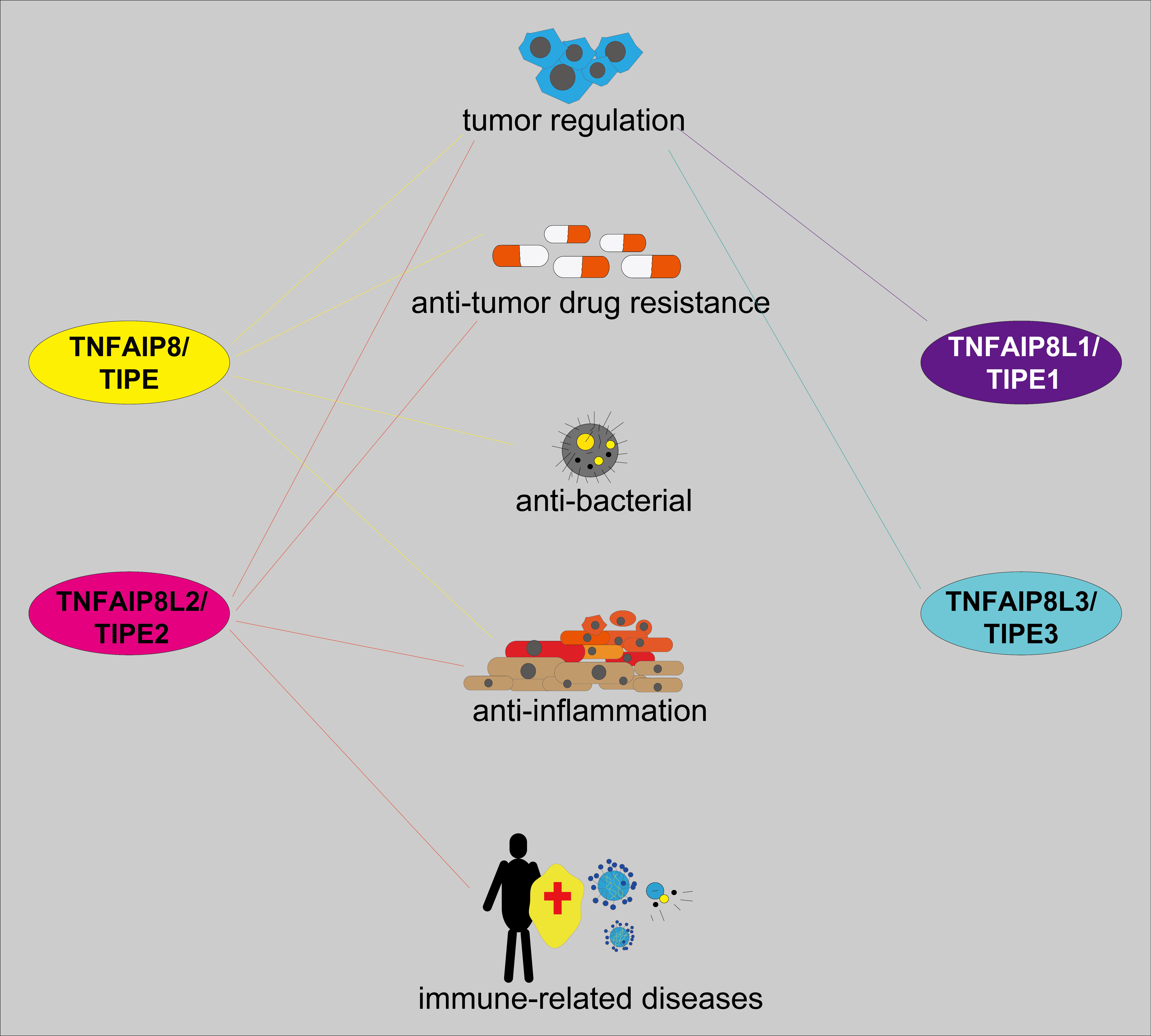
The multiple roles of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α-inducible protein 8 (TNFAIP8), also named TIPE family of proteins have been shown in tumor and inflammation progression and regulation of cellular autophagy and apoptosis. In this review, we found that the TIPE family showed highly homologous sequences and conserved functional domains, such as the death effector domain (DED)-like domain but displayed different roles and mechanisms in different biological activities. For example, while TIPE is primarily associated with tumor progression and antitumor drug resistance, TIPE1 suppresses tumor progression in most instances. TIPE2 has multiple roles in tumor progression regulation, and antitumor drug resistance. Moreover, TIPE2 was also involved in inflammatory response regulation, tumor typing, and staging. A few studies reported that TIPE3 was engaged in tumor development by activating the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) signaling pathway. The structure, function, and mechanism of the TIPE family in cancer and inflammation have been summarized in this review. This might serve as a reference for further research on the TIPE family and shed new light on the crosstalk among antitumor responses, inflammation, and immunology.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools