 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
UCHL5 inhibits U251 glioma cell proliferation and tumor growth via stabilizing and deubiquitinating PTEN
1 Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Regional Immunity and Diseases, Department of Neurosurgery, Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital, The first Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, Shenzhen University Medical School, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, 518055, China
2 Institute of Biological Therapy, Department of Immunology, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, 518055, China
3 Department of Neurosurgery, Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, 310058, China
* Corresponding Author: WEILIN CHEN. Email:
# These authors contributed equally to this work
BIOCELL 2023, 47(12), 2617-2625. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.042476
Received 31 May 2023; Accepted 23 October 2023; Issue published 27 December 2023
Abstract
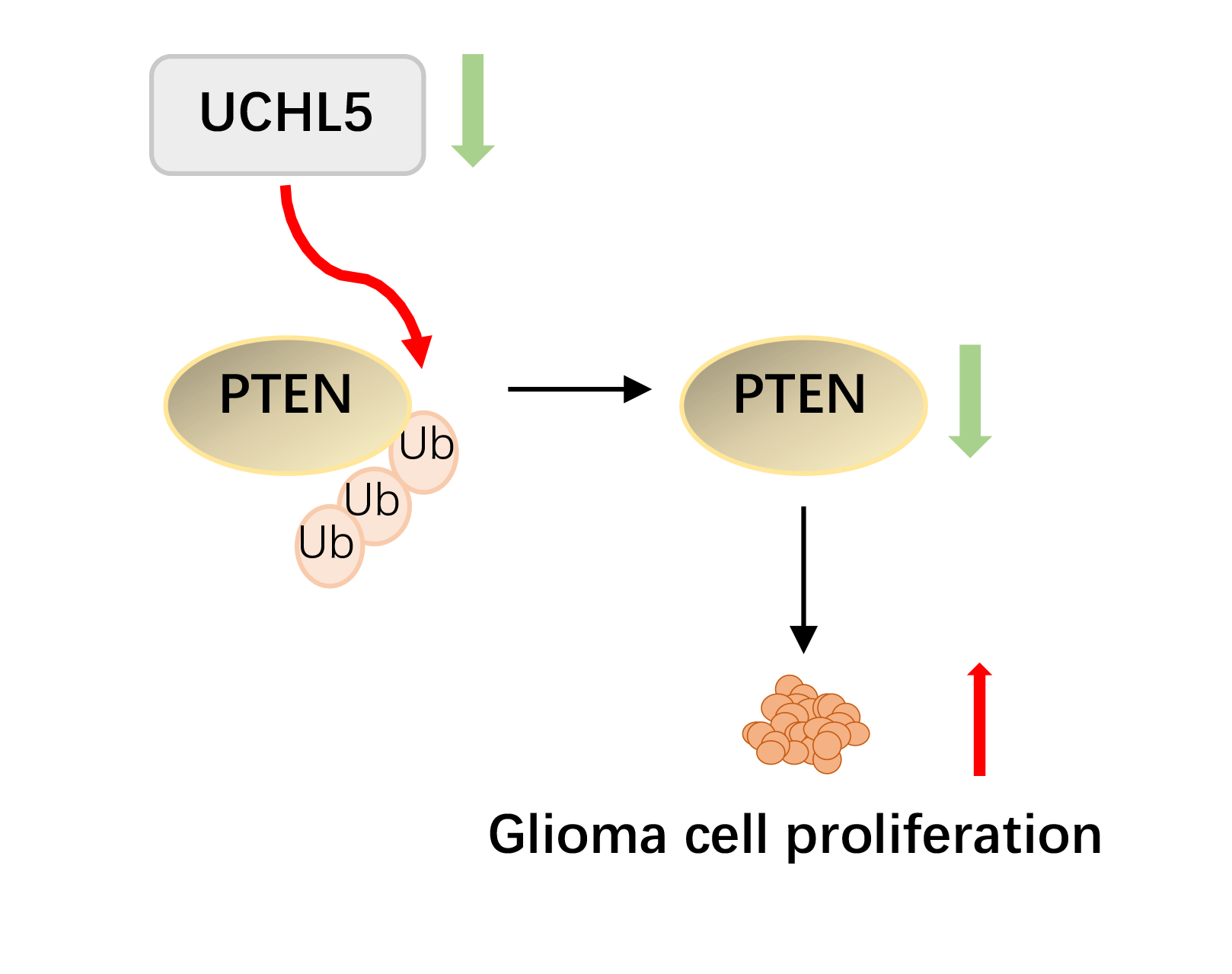
Background: Glioma is the most common primary brain tumor. Exploration of new tumorigenesis mechanism of glioma is critical to determine more effective treatment targets as well as to develop effective prognosis methods that can enhance the treatment efficacy. We previously demonstrated that the deubiquitinase biquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase L5 (UCHL5) was downregulated in human glioma. However, the effect and mechanism of UCHL5 on the proliferation of glioma cells remains unknown. Methods: Transfection of siRNA was used to knockdown the expression of UCHL5 in U251 cells. The 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5 diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, Edu assay, and colony formation assay were employed to identify the effect of UCHL5 on the proliferation of U251 glioma cells. Western blotting and quantitative real-time PCR were carried out to detect the interaction of UCHL5 and PTEN. The effect of UCHL5 on the growth of glioma in vivo was evaluated in nude mice. Then Immunohistochemistry (IHC) were performed to analysis the expression of UCHL5 and PTEN in human glioma tissues. Results: Here, we have reported that silencing of UCHL5 could promote the proliferation of U251 glioma cells through MTT assay, Edu assay, and colony formation assay. Mechanically, we revealed that UCHL5 stabilizes the phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) expression by deubiquitination, thereby inhibiting cell proliferation in U251 cells. Tumor xenograft experiments further demonstrated that silencing the UCHL5 expression could accelerate U251 cell growth in vivo. Finally, in human glioma tissue microarray, the positive correlation between UCHL5 and PTEN expression was confirmed through IHC assay. Conclusion: UCHL5 restrains the proliferation of U251 glioma cells by stabilizing and deubiquitinating PTEN. Our findings provide ideas for developing enhanced targeted PTEN therapy for patients with glioma.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools