 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
MiR-520f-3p inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colorectal cancer cells by targeting Yes-associated protein 1
1 Department of Gastroenterology, The First Clinical Medical College of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, 030001, China
2 The First Clinical Medical School, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, 030001, China
* Corresponding Author: Jinchun Liu,
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Non-Coding RNAs in the Regulation of Human Cancers)
BIOCELL 2023, 47(8), 1803-1810. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.029516
Received 23 February 2023; Accepted 02 April 2023; Issue published 28 August 2023
Abstract
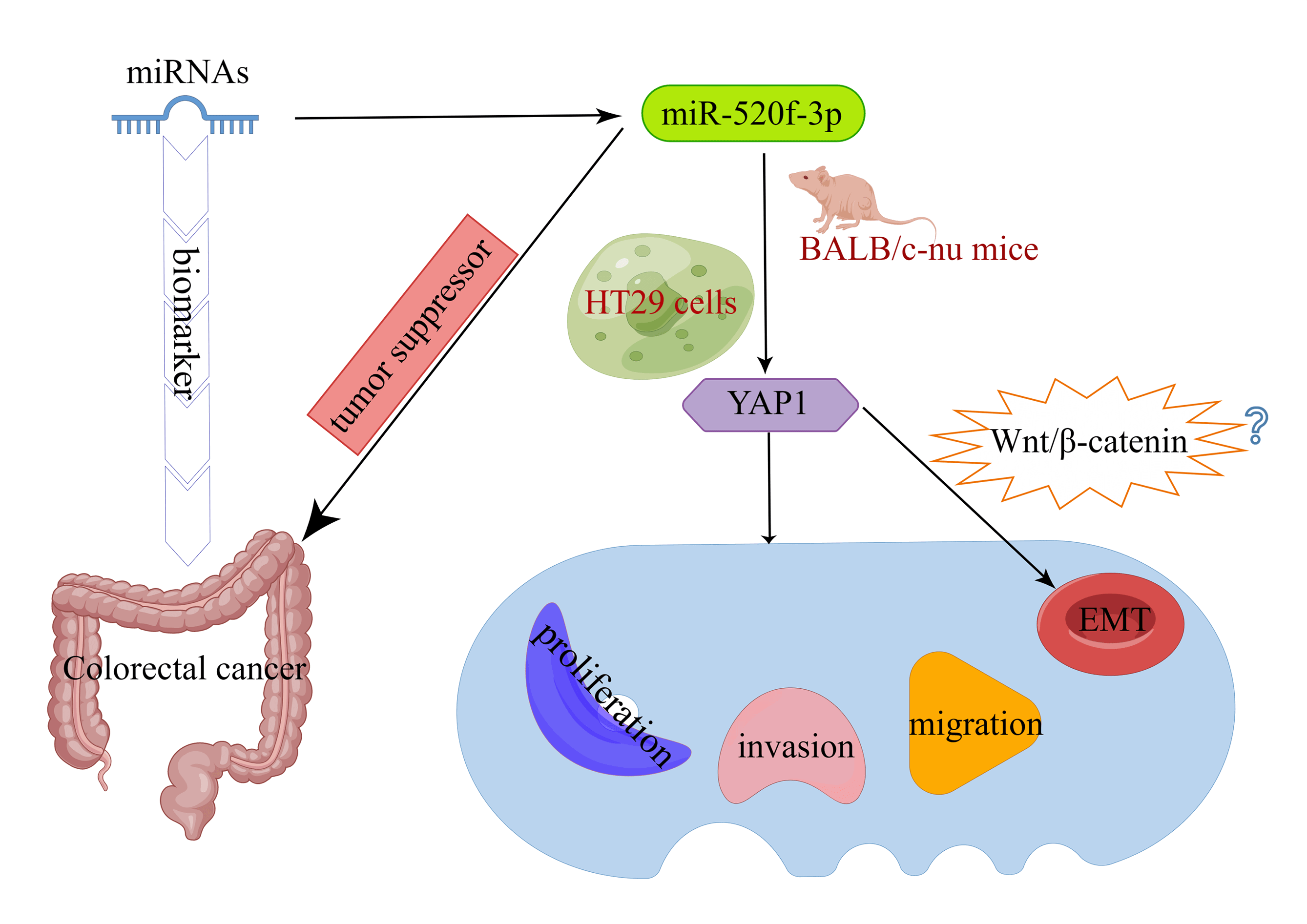
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common malignancies. Early diagnosis is the key to effective treatment of CRC. Since microRNAs (miRNAs) can be used as biomarkers of CRC, the objective of this work was to examine the effect of miR-520f-3p, which targets YAP1 (Yes-associated protein 1), on the ability of CRC cells to proliferate, invade, migrate, and undergo epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Methods: A miR-520f-3p mimic was used to overexpress miR-520f-3p in HT29 cells. To establish the tumor-bearing mouse model, transfected HT29 cells were subcutaneously implanted into BALB/c-nu nude mice, and YAP1 and miR-520f-3p levels were determined using qRT‒PCR. The viability, invasion ability, and migration ability of cells were evaluated by CCK-8, Transwell, and wound healing assays. Apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry and TUNEL assays. The regulatory link between miR-520f-3p and the YAP1 gene was examined by dual-luciferase reporter assay. Tumor tissues with positive Ki-67 expression were identified by immunohistochemistry. Vimentin, E-cadherin, and YAP1 expression were evaluated by western blotting. Results: MiR-520f-3p overexpression could inhibit proliferation, invasion, migration, and EMT and induce apoptosis in HT29 cells. YAP1 was found as a target of miR-520f-3p. The inhibitory effects of miR-520f-3p on proliferation, invasion, migration, and EMT may be reversed by overexpressing YAP1. In tumor-bearing mice, miR- 520f-3p overexpression reduced the Ki-67 level, increased apoptosis, and prevented tumor development and spread. Conclusion: By targeting YAP1, miR-520f-3p may be capable of suppressing CRC cell proliferation, invasion, migration, and EMT, providing a novel therapeutic target for the disease.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools