 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
MPPa-PDT induced apoptosis and autophagy through JNK and p38 MAPK signaling pathways in A549 cells
Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Xiaogan Hospital Affiliated to Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Xiaogan, 432000, China
* Corresponding Author: ZHANLING WU. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Navigating the Interplay of Cancer, Autophagy, ER Stress, Cell Cycle and Apoptosis: Mechanisms, Therapies, and Future Directions)
BIOCELL 2024, 48(11), 1603-1612. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2024.054364
Received 26 May 2024; Accepted 27 August 2024; Issue published 07 November 2024
Abstract
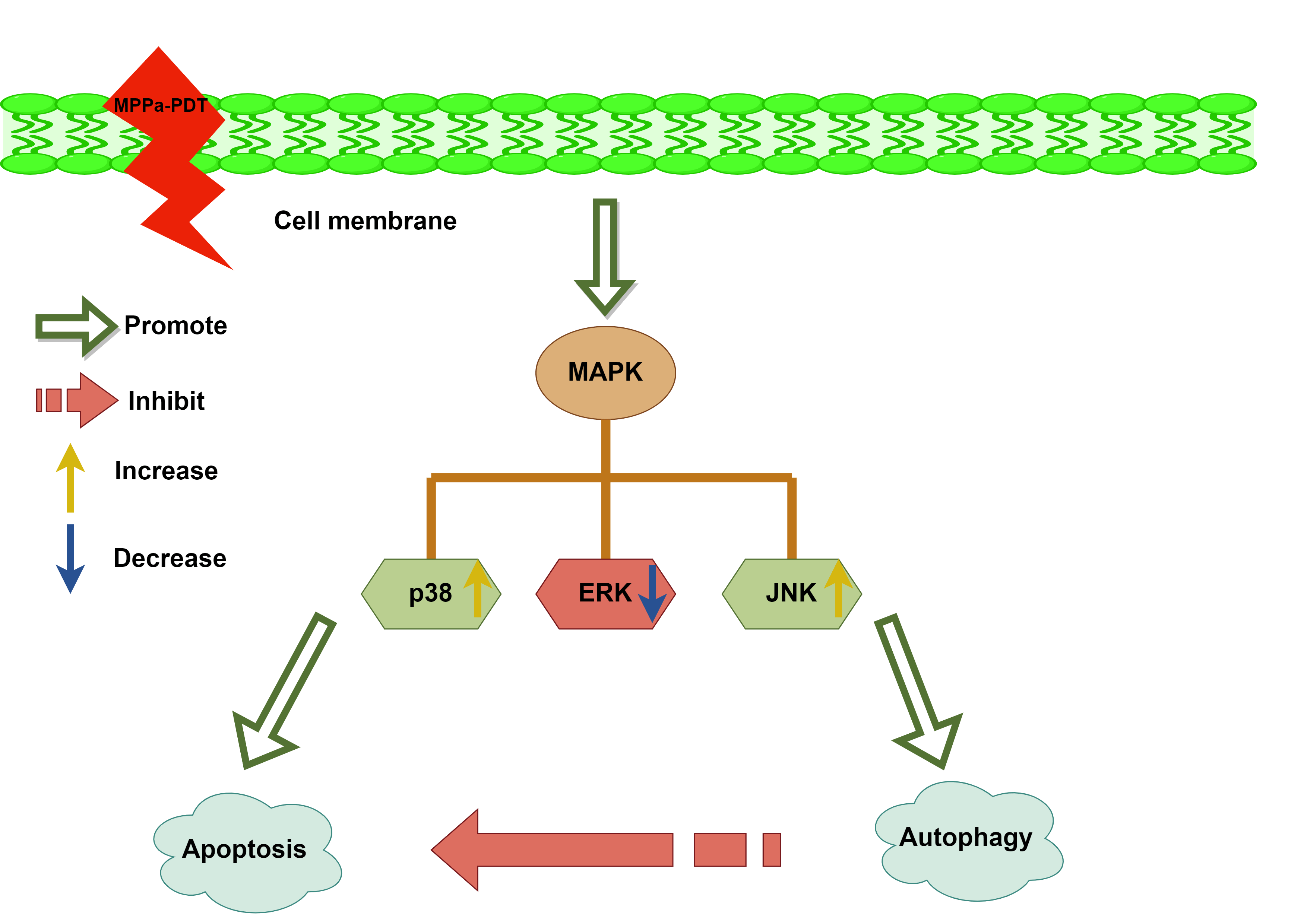
Objectives: The antitumor effects of pyropheophorbide-α methyl ester-mediated photodynamic therapy (MPPa-PDT) were observed in several cancers. The objective of this investigation was to examine the antineoplastic efficacy of MPPa-PDT acting on lung carcinoma A549 cells and further elaborate mechanisms. Methods: The viability of A549 cells was examined with cell counting kit-8 after MPPa-PDT disposal. Hoechst 33342 staining, monodansylcadaverine (MDC) staining, and transmission electron microscopy were employed to observe apoptotic bodies and autophagic vesicles. Flow cytometry with Annexin V/propidium iodide (PI) labeling objectively assessed cell death. The expression of associated proteins, including Caspase-3, Beclin-1, LC-3II, and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) families concluding c-jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK), p38 MAPK, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK) were identified by Western blotting. Results: Prolonged exposure to MPPa-PDT gradually decreased lung cancer A549 cell viability. Apoptosis and autophagy activity were higher in the MPPa-PDT cohort in comparison to the control group. Meanwhile, autophagy inhibition enhanced cell-killing efficacy apparently. Besides, the JNK and p38 MAPK pathways were implicated in MPPa-PDT-triggered apoptosis and autophagy. Conclusions: This study demonstrated that JNK and p38 MAPK were engaged in MPPa-PDT-mediated apoptosis and autophagy in lung carcinoma A549 cells.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools