 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Curcumin inhibits colorectal cancer development by blocking the YAP/TAZ signaling axis
1 Department of Pharmacy, Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Shantou University School of Medicine, Shantou, China
2 Department of Pharmacy, Shantou University Mental Health Center, Shantou, China
3 Static Distribution Center, Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Shantou University School of Medicine, Shantou, China
* Corresponding Authors: MINGHAO ZHENG. Email: ; JIAOLING CHEN. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Herbal Active Ingredients: Potential for the Prevention and Treatment of Cancer)
BIOCELL 2024, 48(3), 443-451. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.029188
Received 06 February 2023; Accepted 08 May 2023; Issue published 15 March 2024
Abstract
Background: Curcumin is a plant polyphenol with antitumor properties and inhibits the development of colorectal cancer (CRC). However, as the molecular mechanism associated is still unclear, our study aimed to explore the underlying molecular mechanisms by which curcumin inhibits CRC. Methods: HT29 and SW480 cells were treated with curcumin or/and Doxycycline (DOX), and cell viability, colony forming ability, migration and invasion were confirmed by cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8), colony forming, Transwell assays. And Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP) and PDZ-binding motif (TAZ) signaling-related genes or proteins were analyzed using reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR), western blot, and immunofluorescence assays. Then nude mice xenograft tumor model was constructed, YAP and Ki67 expressions were tested by immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining. Results: In our study, we proved that curcumin significantly inhibited the CRC cell viability, cell migration, and cell invasion abilities. In addition, curcumin inhibited YAP and Transcriptional coactivator with TAZ or the YAP/TAZ signaling axis in CRC cells. Further, in the nude mice model, curcumin treatment significantly decreased the size and weight of xenotransplant tumors. Conclusion: Therefore, curcumin significantly inhibited CRC development and invasion by regulating the YAP/TAZ signaling axis.Graphic Abstract
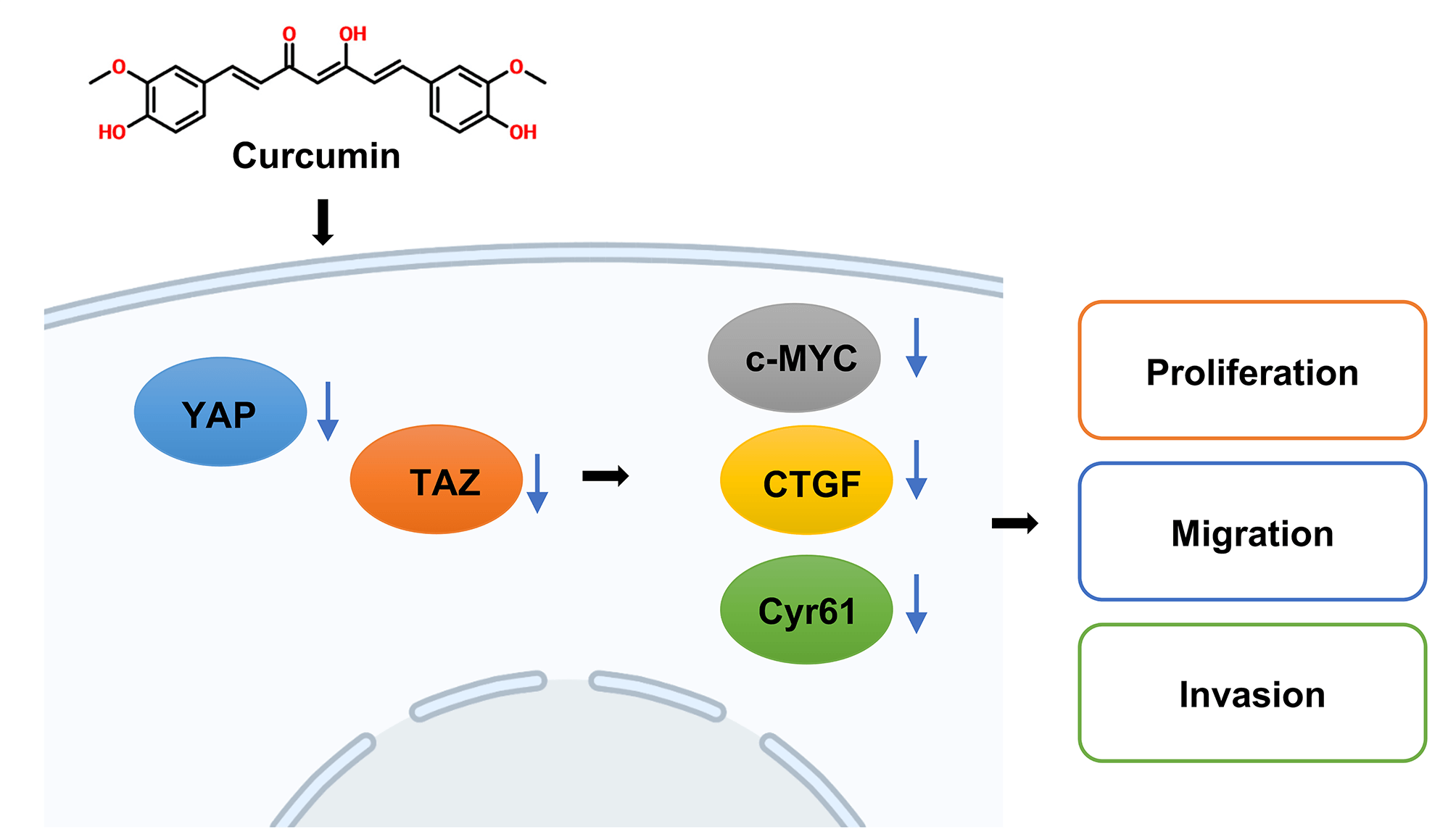
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools