 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Human-Derived Low-Molecular-Weight Protamine (hLMWP) Conjugates Enhance Skin Cell Penetration and Physiological Activity
1 Department of Biocosmetics, Dongshin University, 185, Gunjae-ro, Naju, 58245, Jeonnam, Republic of Korea
2 Medicinal Nano-Material Research Institute, BIO-FD&C Co., Ltd., 106, Sandan-gil, Hwasun, 58141, Jeonnam, Republic of Korea
* Corresponding Author: Kyung Mok Park. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Understanding Cellular Mechanisms in Wound Healing During Therapeutic Interventions)
BIOCELL 2025, 49(8), 1435-1448. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2025.065199
Received 06 March 2025; Accepted 04 July 2025; Issue published 29 August 2025
Abstract
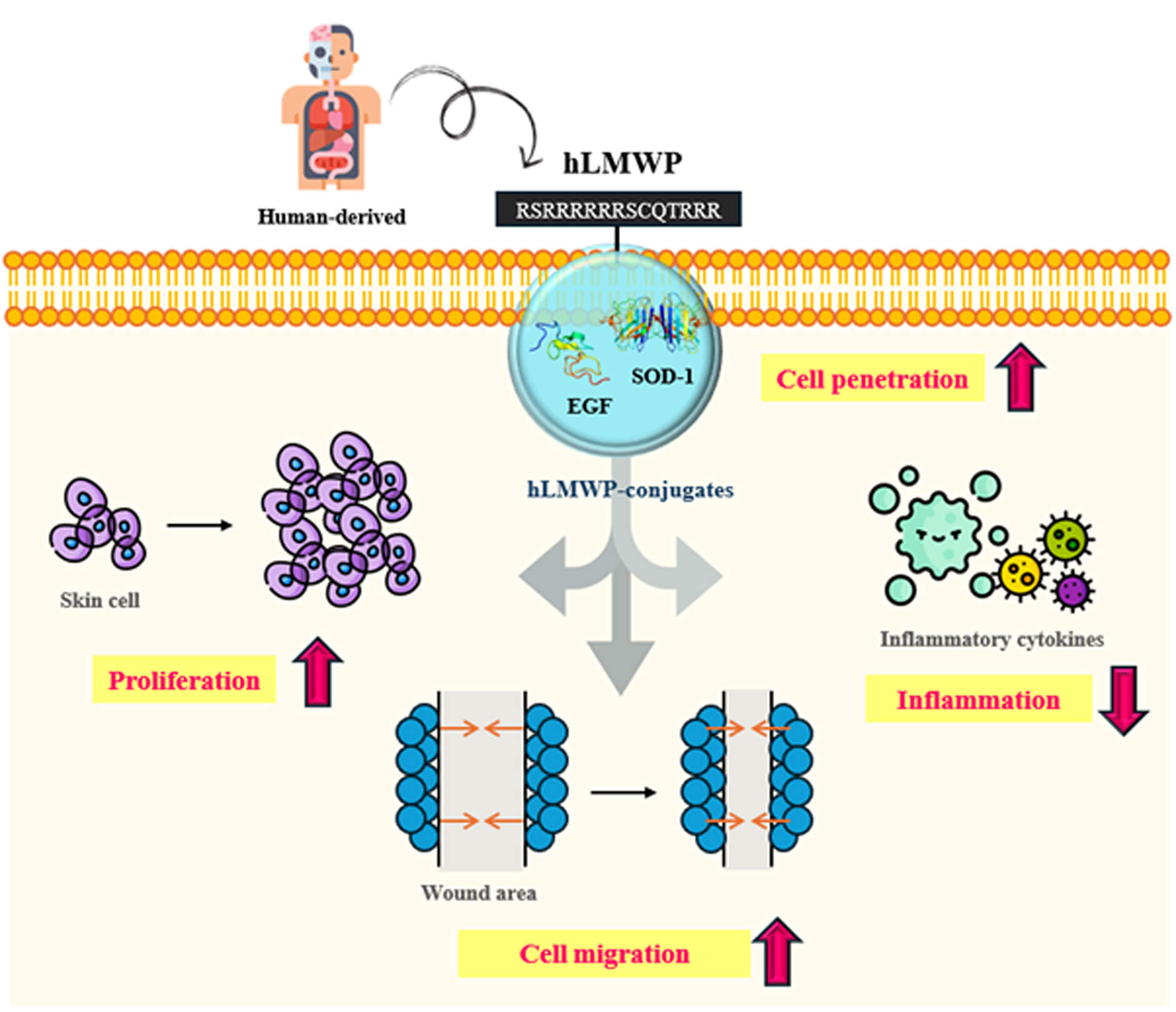
Background: The efficient transdermal delivery of biologically active molecules remains a major challenge because of the structural barrier of the stratum corneum, which limits the penetration of large or hydrophilic molecules. Low-molecular-weight protamine (LMWP) has a structure similar to that of the HIV TAT protein-derived peptide and is a representative cell-penetrating peptide (CPP) used to increase cell permeability. However, protamine has been reported to have many toxicities and side effects. Objectives: We developed human-derived low-molecular-weight protamine (hLMWP), which is based on fish-derived LMWP but designed using human protein sequences to improve safety and functionality. As it is derived from human proteins, it may reduce side effects and immune rejection during long-term or repeated administration. Additionally, we confirmed in our preliminary study that hLMWP enhances permeability compared to LMWP. In this study, we evaluated physiological activities and skin cell penetration of hLMWP conjugates to assess the potential applications of hLMWP. Methods: cDNA sequences for hLMWP-EGF (His) and hLMWP-SOD-1 (His) were synthesized by connecting hLMWP (RSRRRRRRSCQTRRR) to the N-terminus of Epidermal growth factor (EGF) and Superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD-1), respectively, with a 6 His-tag added to the C-terminus. The constructs were cloned into a pET-41b(+) expression vector and expressed in E. coli BL21-CodonPlus (DE3)-RIL cells. Expressed proteins were purified using a nickel column and eluted with imidazole buffer. Protein purity was confirmed by SDS-PAGE, and concentrations were quantified using a BCA assay. To evaluate the functional properties of these hLMWP-protein conjugates, a series of in vitro assays were conducted using keratinocyte and macrophage cell lines. These included assessments of permeability, proliferation, wound healing, and anti-inflammatory activity. Results: The results demonstrated that hLMWP-EGF and hLMWP-SOD-1 exhibited superior biological activities, including increased cell proliferation, wound healing, and anti-inflammatory effects, compared to EGF and SOD-1. Moreover, hLMWP-EGF and hLMWP-SOD-1 significantly enhanced the skin permeability of both EGF and SOD-1, as shown by Franz diffusion cell assay and immunofluorescence analysis. Conclusion: Our findings demonstrate that hLMWP significantly enhances skin permeability and biological activity of functional proteins such as EGF and SOD-1 while maintaining safety. This suggests its potential for application in transdermal drug delivery, regenerative medicine, and cosmeceutical formulations.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools