 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Cellular Knockdown of SELENOM Promotes Apoptosis Induction in Human Glioblastoma (A-172) Cells via Redox Imbalance
Institute of Cell Biophysics of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Federal Research Center “Pushchino Scientific Center for Biological Research of the Russian Academy of Sciences”, Pushchino, 142290, Russia
* Corresponding Author: Egor A. Turovsky. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: MitoROS: Exploring Mitochondria and Oxidative Stress)
BIOCELL 2026, 50(2), 10 https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2025.073728
Received 24 September 2025; Accepted 21 November 2025; Issue published 14 February 2026
Abstract
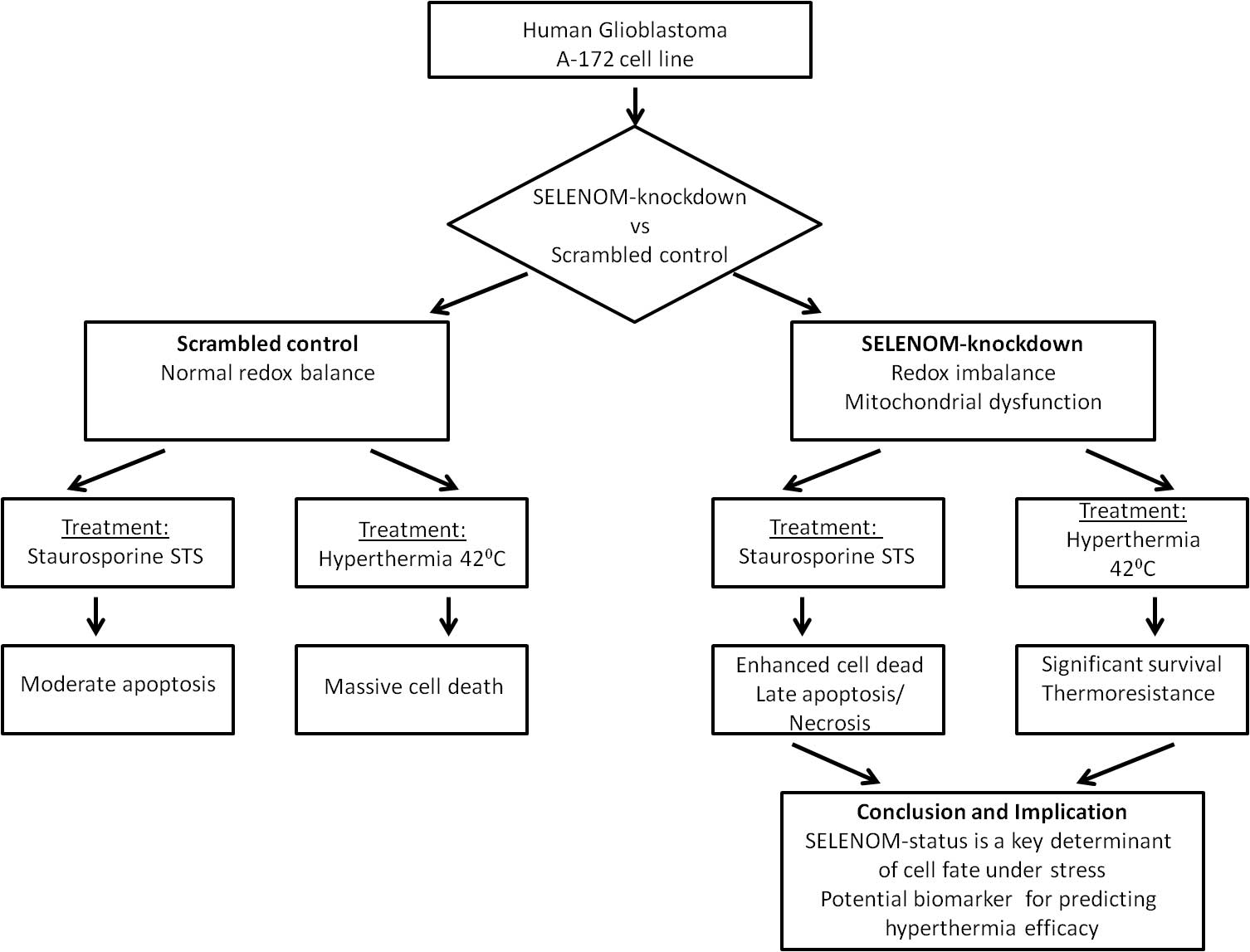
Objectives: Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is highly resistant to apoptosis. This study investigates the role of Selenoprotein M (SELENOM), a redox-regulating protein, in the response of human glioblastoma A-172 cells to staurosporine (STS) and hyperthermia. Methods: A stable SELENOM-knockdown (SELENOM-KD) cell line was created. We measured reactive oxygen species (ROS), mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm), cell death, and apoptotic gene expression. Results: SELENOM-KD increased basal ROS levels and induced mitochondrial dysfunction. It sensitized cells to STS-induced apoptosis, enhancing the upregulation of pro-apoptotic genes. Conversely, under hyperthermia (42°C), SELENOM-KD cells exhibited significant thermoresistance, with 52% survival vs. 99% death in controls, associated with suppressed pro-apoptotic signaling. Conclusions: SELENOM is a critical redox and mitochondrial regulator in GBM. Its loss produces a context-dependent effect on cell fate: sensitizing to chemical apoptosis while conferring resistance to hyperthermia. SELENOM expression is a promising predictive biomarker for stratifying GBM patients for hyperthermia-based therapies.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material FileCite This Article
 Copyright © 2026 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2026 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools