 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Solar Radiation Estimation Based on a New Combined Approach of Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) and Genetic Algorithms (GA) in South Algeria
1 Material Sciences Department, Faculty of Material Sciences, Mathematics and Computer Science, Laboratory of Sustainable Development and Computer Science (LSDCS) University of Adrar, Adrar, 01000, Algeria
2 Department of Civil Engineering, University of Sistan and Baluchestan, Zahedan, 98167-45845, Iran
3 Laboratory of Computer, Production and Maintenance Engineering (LGIPM), University of Lorraine, Chieulles, 57070, France
4 Laboratory of Energy Environment and Information System (LEEIS), University of Adrar, Adrar, 01000, Algeria
* Corresponding Author: Djeldjli Halima. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Advances in Ensemble Framework of Meta-heuristics and Machine Learning: Methods and Applications)
Computers, Materials & Continua 2024, 79(3), 4725-4740. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmc.2024.051002
Received 25 February 2024; Accepted 12 April 2024; Issue published 20 June 2024
Abstract
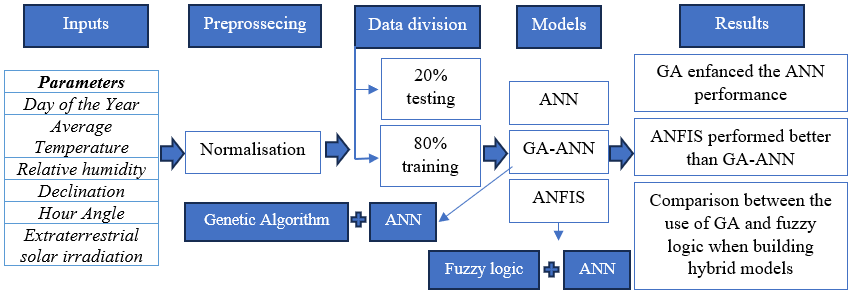
When designing solar systems and assessing the effectiveness of their many uses, estimating sun irradiance is a crucial first step. This study examined three approaches (ANN, GA-ANN, and ANFIS) for estimating daily global solar radiation (GSR) in the south of Algeria: Adrar, Ouargla, and Bechar. The proposed hybrid GA-ANN model, based on genetic algorithm-based optimization, was developed to improve the ANN model. The GA-ANN and ANFIS models performed better than the standalone ANN-based model, with GA-ANN being better suited for forecasting in all sites, and it performed the best with the best values in the testing phase of Coefficient of Determination (R = 0.9005), Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE = 8.40%), and Relative Root Mean Square Error (rRMSE = 12.56%). Nevertheless, the ANFIS model outperformed the GA-ANN model in forecasting daily GSR, with the best values of indicators when testing the model being R = 0.9374, MAPE = 7.78%, and rRMSE = 10.54%. Generally, we may conclude that the initial ANN stand-alone model performance when forecasting solar radiation has been improved, and the results obtained after injecting the genetic algorithm into the ANN to optimize its weights were satisfactory. The model can be used to forecast daily GSR in dry climates and other climates and may also be helpful in selecting solar energy system installations and sizes.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools