 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Optimal Operation of Virtual Power Plants Based on Revenue Distribution and Risk Contribution
School of Electrical Engineering, Shenyang Institute of Engineering, Shenyang, 110136, China
* Corresponding Author: Wenyao Sun. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Grid Integration of Intermittent Renewable Energy Resources: Technologies, Policies, and Operational Strategies)
Energy Engineering 2026, 123(1), 17 https://doi.org/10.32604/ee.2025.069603
Received 26 June 2025; Accepted 21 August 2025; Issue published 27 December 2025
Abstract
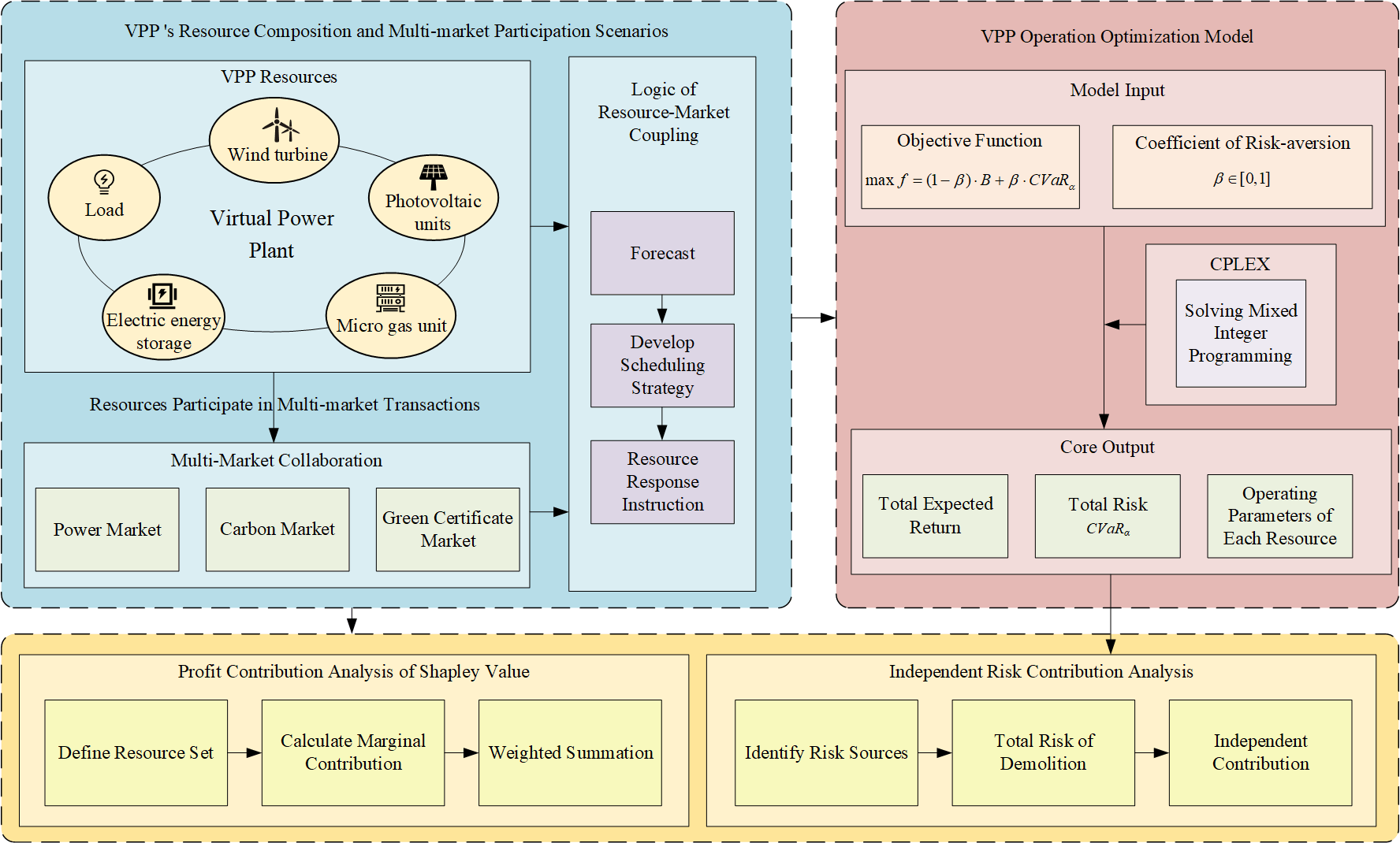
Virtual power plant (VPP) integrates a variety of distributed renewable energy and energy storage to participate in electricity market transactions, promote the consumption of renewable energy, and improve economic efficiency. In this paper, aiming at the uncertainty of distributed wind power and photovoltaic output, considering the coupling relationship between power, carbon trading, and green card market, the optimal operation model and bidding scheme of VPP in spot market, carbon trading market, and green card market are established. On this basis, through the Shapley value and independent risk contribution theory in cooperative game theory, the quantitative analysis of the total income and risk contribution of various distributed resources in the virtual power plant is realized. Moreover, the scheduling strategies of virtual power plants under different risk preferences are systematically compared, and the feasibility and accuracy of the combination of Shapley value and independent risk contribution theory in ensuring fair income distribution and reasonable risk assessment are emphasized. A comprehensive solution for virtual power plants in the multi-market environment is constructed, which integrates operation strategy, income distribution mechanism, and risk control system into a unified analysis framework. Through the simulation of multi-scenario examples, the CPLEX solver in MATLAB software is used to optimize the model. The proposed joint optimization scheme can increase the profit of VPP participating in carbon trading and green certificate market by 29%. The total revenue of distributed resources managed by VPP is 9% higher than that of individual participation.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2026 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2026 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools