 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
A Comparative Review of the Experimental Mitigation Methods of the S-Shaped Diffusers in the Aeroengine Intakes
1 College of Engineering Technologies, University of Hilla, Hilla, Babylon, 51001, Iraq
2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, College of Engineering, University of Kerbala, Karbala, 56001, Iraq
3 Department of Electromechanical Engineering, University of Technology-Iraq, Baghdad, 10066, Iraq
* Corresponding Authors: Hussain H. Al-Kayiem. Email: ,
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancements in Energy Resources and Their Processes, Systems, Materials and Policies for Affordable Energy Sustainability)
Energy Engineering 2026, 123(2), 3 https://doi.org/10.32604/ee.2025.073303
Received 15 September 2025; Accepted 28 November 2025; Issue published 27 January 2026
Abstract
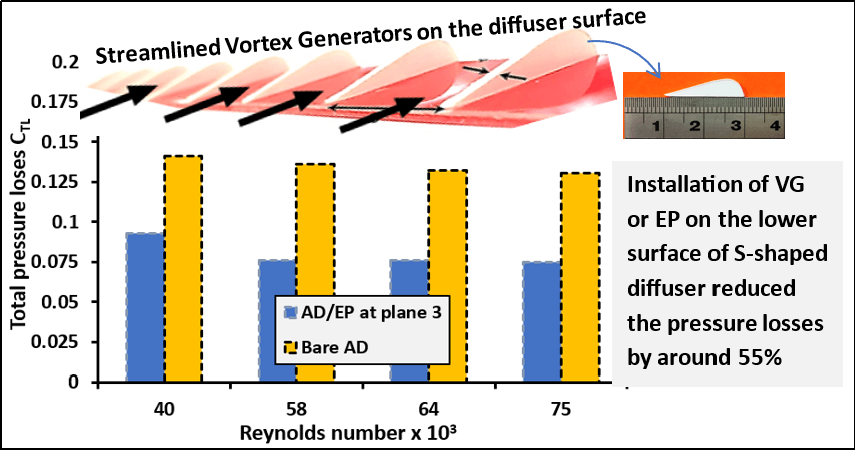
Gas Turbines are among the most important energy systems for aviation and thermal-based power generation. The performance of gas turbine intakes with S-shaped diffusers is vulnerable to flow separation, reversal flow, and pressure distortion, mainly in aggressive S-shaped diffusers. Several methods, including vortex generators and energy promoters, have been proposed and investigated both experimentally and numerically. This paper compiles a review of experimental investigations that have been performed and reported to mitigate flow separation and restore system performance. The operational principles, classifications, design geometries, and performance parameters of S-shaped diffusers are presented to facilitate the analysis and understanding of the influence of each mitigation method on flow enhancement in S-shaped diffusers. The influencing design parameters on the performance of the S-shaped diffuser and the findings achieved by various experimental investigations are discussed and compared. The review concludes that reducing the intake length reduces the size and weight of the gas turbine, leading to a higher power-to-weight ratio. However, the main challenge in shortening the S-shaped diffusers is the flow separation in the high-curvature section, which must be prevented to maintain high performance. Prevention can be achieved through flow control methods, which are categorized into passive and aggressive methods. The static pressure recovery coefficient, total pressure loss coefficient, ideal static pressure coefficient, distortion coefficient, and skin friction coefficient are the primary performance evaluation and comparison parameters between the experimentally investigated mitigation methods. The new trend in S-shaped diffuser studies includes the integration of computational and data-driven methods.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2026 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2026 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools