 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Exploring Efficiency of Silicon Carbide for Next Generation of Alkali & Alkaline Earth Metals-Ion Batteries Using Quantum Mechanic Method
1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering and Architecture, Kastamonu University, Kastamonu, 37150, Turkey
2 Department of Chemical Engineering, CT.C., Islamic Azad University, Tehran, 1496969191, Iran
* Corresponding Author: Fatemeh Mollaamin. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Analytics on Energy Systems)
Energy Engineering 2025, 122(12), 4971-4986. https://doi.org/10.32604/ee.2025.069945
Received 03 July 2025; Accepted 24 October 2025; Issue published 27 November 2025
Abstract
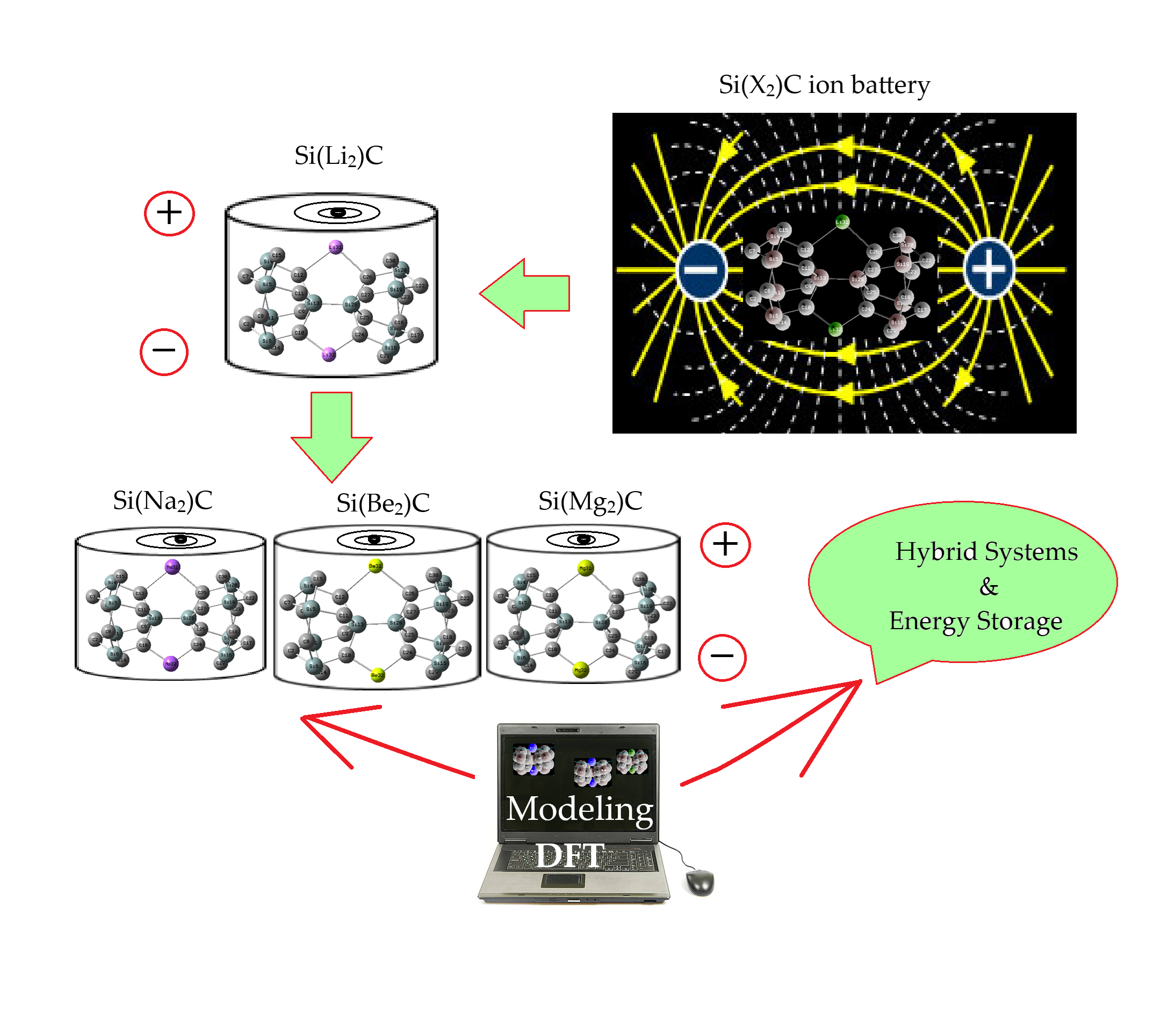
Delving alternative high-performance anodes for lithium-ion batteries have always attracted scientist attention. A wide-bandgap semiconductor with excellent mechanical properties, “silicon carbide (SiC)”, has been introduced as the anode electrode. Two-dimensional SiC has special hybridization which can build it as an appropriate substitution for graphene. Energy storage technologies are keys in the extension and function of electric devices. To keep up with steady innovations in saving energy technologies, it is essential to progress corresponding practical strategies. In this research article, SiC has been designed and characterized as an anode electrode for lithium (Li), sodium (Na), beryllium (Be), and magnesium (Mg) ion batteries, forming SiLi2C, SiNa2C, SiBe2C, and SiMg2C nanoclusters. A comprehensive study of energy-saving by SiLi2C, SiNa2C, SiBe2C, and SiMg2C complexes was conducted using computational methods, accompanied by analysis of charge density differences (CDD), total density of states (TDOS), and localized orbital locator (LOL) for hybrid clusters of SiLi2C, SiNa2C, SiBe2C, and SiMg2C. Functionalizing lithium, sodium, beryllium, and magnesium can shift the negative charge distribution of carbon toward electron-acceptor states in SiLi2C, SiNa2C, SiBe2C, and SiMg2C nanoclusters. Higher Si/C content can increase battery capacity via SiLi2C, SiNa2C, SiBe2C, and SiMg2C nanoclusters during the energy storage process and improve rate performance by enhancing electrical conductivity. Besides, silicon carbide anode material may improve cycling consistency by mitigating electrode degradation, and it augments capacity owing to higher surface capacitance.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools