 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Experimental and Neural Network Modeling of the Thermal Behavior of an Agricultural Greenhouse Integrated with a Phase Change Material (CaCl2·6H2O)
1 Unité de Recherche Appliquée en Energies Renouvelables, URAER, Centre de Développement des Energies Renouvelables, CDER, Ghardaïa, 47133, Algeria
2 Laboratoire d’Instrumentation, Faculté de Génie Electrique, Université des Sciences et de la Technologie Houari Boumediene, BP 32, El-Alia, Bab-Ezzouar, Alger, 16111, Algeria
3 Department of Energy and Power Engineering, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081, China
4 Solar Energy Research Institute, Yunnan Normal University, Kunming, 650500, China
5 Zhengzhou Research Institute, Beijing Institute of Technology, Zhengzhou, 450000, China
* Corresponding Author: Abdelouahab Benseddik. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Advance and Development in Solar Energy)
Energy Engineering 2025, 122(12), 5021-5037. https://doi.org/10.32604/ee.2025.072991
Received 08 September 2025; Accepted 17 October 2025; Issue published 27 November 2025
Abstract
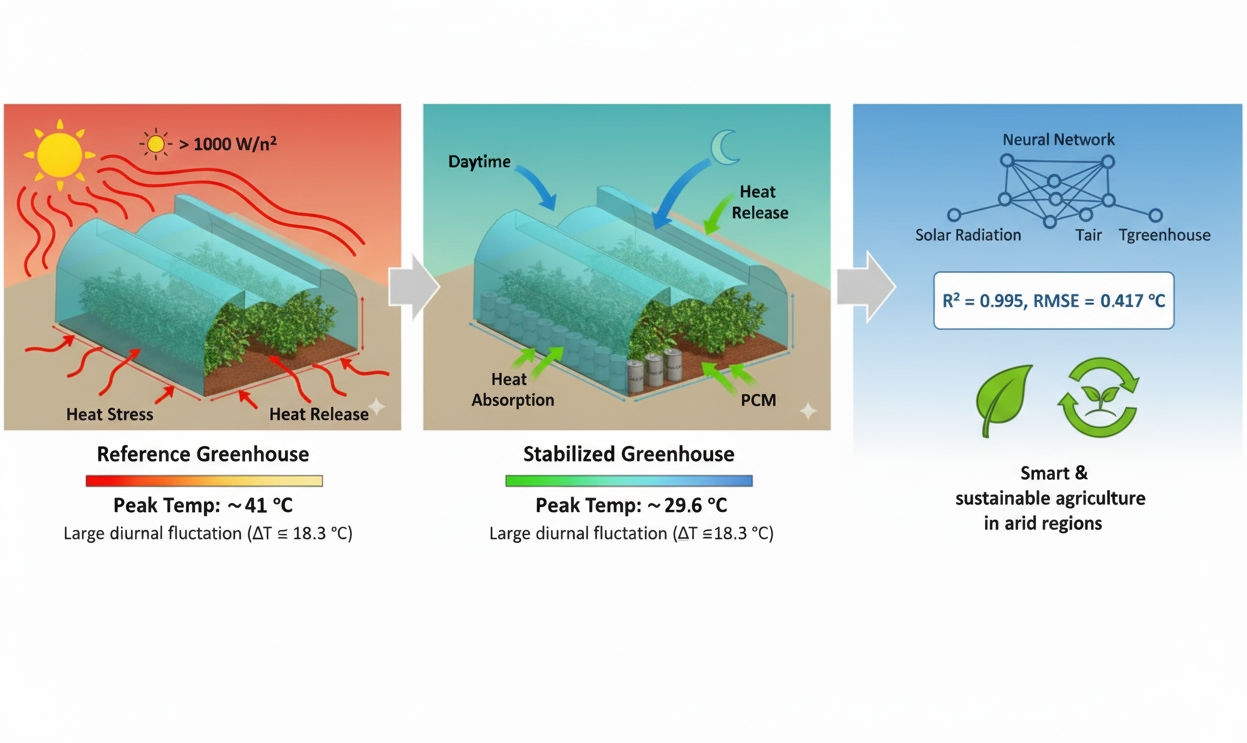
In Saharan climates, greenhouses face extreme diurnal temperature fluctuations that generate thermal stress, reduce crop productivity, and hinder sustainable agricultural practices. Passive thermal storage using Phase Change Materials (PCM) is a promising solution to stabilize microclimatic conditions. This study aims to evaluate experimentally and numerically the effectiveness of PCM integration for moderating greenhouse temperature fluctuations under Saharan climatic conditions. Two identical greenhouse prototypes were constructed in Ghardaïa, Algeria: a reference greenhouse and a PCM-integrated greenhouse using calcium chloride hexahydrate (CaCl2·6H2O). Thermal performance was assessed during a five-day experimental period (7–11 May 2025) under severe ambient conditions. To complement this, a Nonlinear Auto-Regressive with eXogenous inputs (NARX) neural network model was developed and trained using a larger dataset (7–25 May 2025) to predict greenhouse thermal dynamics. The PCM greenhouse reduced peak daytime air temperature by an average of 8.14°C and decreased the diurnal temperature amplitude by 53.6% compared to the reference greenhouse. The NARX model achieved high predictive accuracy (R2 = 0.990, RMSE = 0.425°C, MAE = 0.223°C, MBE = 0.008°C), capturing both sensible and latent heat transfer mechanisms, including PCM melting and solidification. The combined experimental and predictive modeling results confirm the potential of PCM integration as an effective passive thermal regulation strategy for greenhouses in arid regions. This approach enhances microclimatic stability, improves energy efficiency, and supports the sustainability of protected agriculture under extreme climatic conditions.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools