 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Design and Development of a Small-Scale Green Hydrogen Vehicle: Hydrogen Consumption Analysis under Varying Loads for Zero-Emission Transport
1 Research Centre for Sustainable Technologies, Faculty of Engineering, Computing and Science, Swinburne University of Technology, Jalan Simpang Tiga, Kuching, 93350, Sarawak, Malaysia
2 College of Engineering, Faculty of Computing, Engineering and the Built Environment, Birmingham City University, Birmingham, B4 7XG, UK
* Corresponding Author: Hadi Nabipour Afrouzi. Email:
Energy Engineering 2025, 122(5), 1789-1804. https://doi.org/10.32604/ee.2025.060124
Received 24 October 2024; Accepted 28 February 2025; Issue published 25 April 2025
Abstract
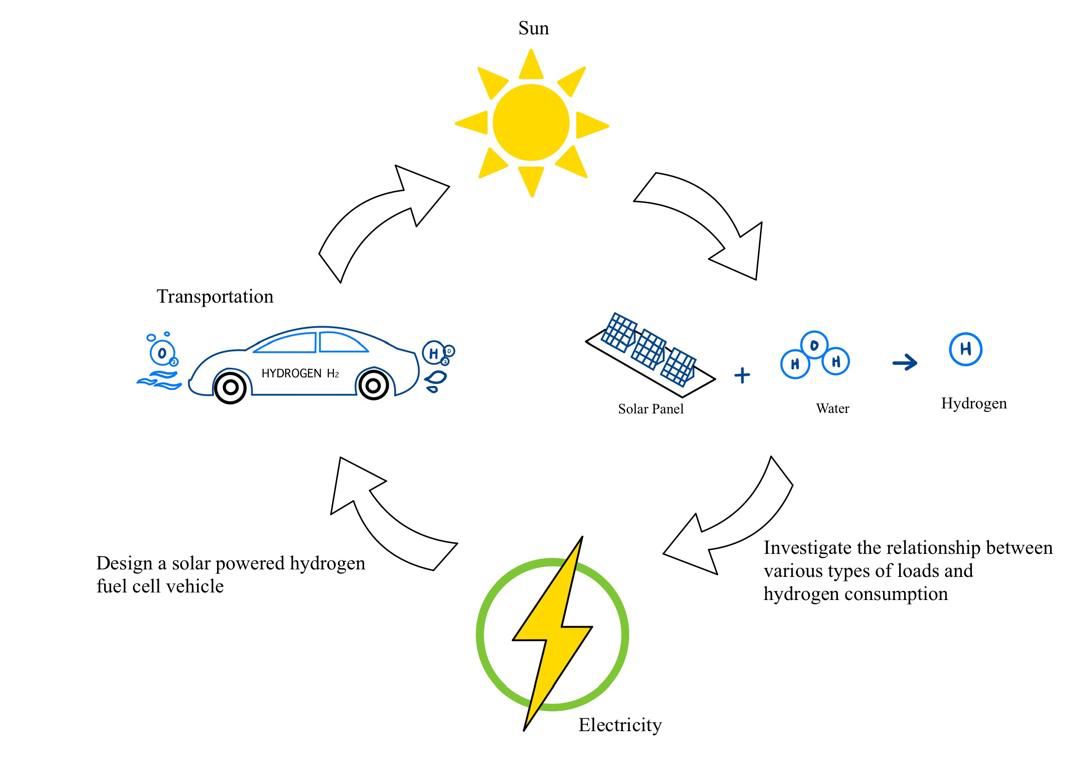
With growing interest in its potential applications across both stationary and transportation sectors, hydrogen has emerged as a promising alternative for environmentally responsible power generation. By replacing traditional fuels, hydrogen can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions in the transportation sector. This study focuses on the design and downsizing of a green hydrogen fuel cell car, aiming to scale the concept for larger vehicles. Key components, including fuel cells, electrolysers, and solar panels, were evaluated through extensive laboratory testing. The findings reveal that variations in sunlight impact the solar panel’s hydrogen production rate, with differences of approximately 4.9% attributed to changes in time and date. Analysis of consumption rates showed that a 17.4% increase in current consumption leads to a significant reduction in operational time. Further testing under varying loads demonstrated that higher current demands, such as those from a DC motor, accelerate hydrogen depletion, whereas lower currents extend operational duration. These results underscore the importance of maximizing solar energy efficiency, reducing reliance on conventional energy sources, and regulating consumption rates to optimize fuel cell performance. Since hydrogen is produced using renewable energy, fuel cell technology is virtually emission-free. Additionally, the study highlights the viability of powering vehicles with renewable energy, emphasizing the potential of green hydrogen fuel cell technology as a sustainable transportation solution.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools