 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Research on Electric Vehicle Charging Optimization Strategy Based on Improved Crossformer for Carbon Emission Factor Prediction
1 Marketing Service Center of State Grid Jibei Electric Power Co, Ltd., Xicheng District, Beijing, 100051, China
2 School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, North China Electric Power University, Changping District, Beijing, 102206, China
* Corresponding Author: Zixuan Meng. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence-Driven Collaborative Optimization of Electric Vehicle, Charging Station and Grid: Challenges and Opportunities)
Energy Engineering 2026, 123(1), 15 https://doi.org/10.32604/ee.2025.069576
Received 26 June 2025; Accepted 13 October 2025; Issue published 27 December 2025
Abstract
To achieve low-carbon regulation of electric vehicle (EV) charging loads under the “dual carbon” goals, this paper proposes a coordinated scheduling strategy that integrates dynamic carbon factor prediction and multi-objective optimization. First, a dual-convolution enhanced improved Crossformer prediction model is constructed, which employs parallel 1 × 1 global and 3 × 3 local convolution modules (Integrated Convolution Block, ICB) for multi-scale feature extraction, combined with an Adaptive Spectral Block (ASB) to enhance time-series fluctuation modeling. Based on high-precision predictions, a carbon-electricity cost joint optimization model is further designed to balance economic, environmental, and grid-friendly objectives. The model’s superiority was validated through a case study using real-world data from a renewable-heavy grid. Simulation results show that the proposed multi-objective strategy demonstrated a superior balance compared to baseline and benchmark models, achieving a 15.8% reduction in carbon emissions and a 5.2% reduction in economic costs, while still providing a substantial 22.2% reduction in the peak-valley difference. Its balanced performance significantly outperformed both a single-objective strategy and a state-of-the-art Model Predictive Control (MPC) benchmark, highlighting the advantage of a global optimization approach. This study provides theoretical and technical pathways for dynamic carbon factor-driven EV charging optimization.Graphic Abstract
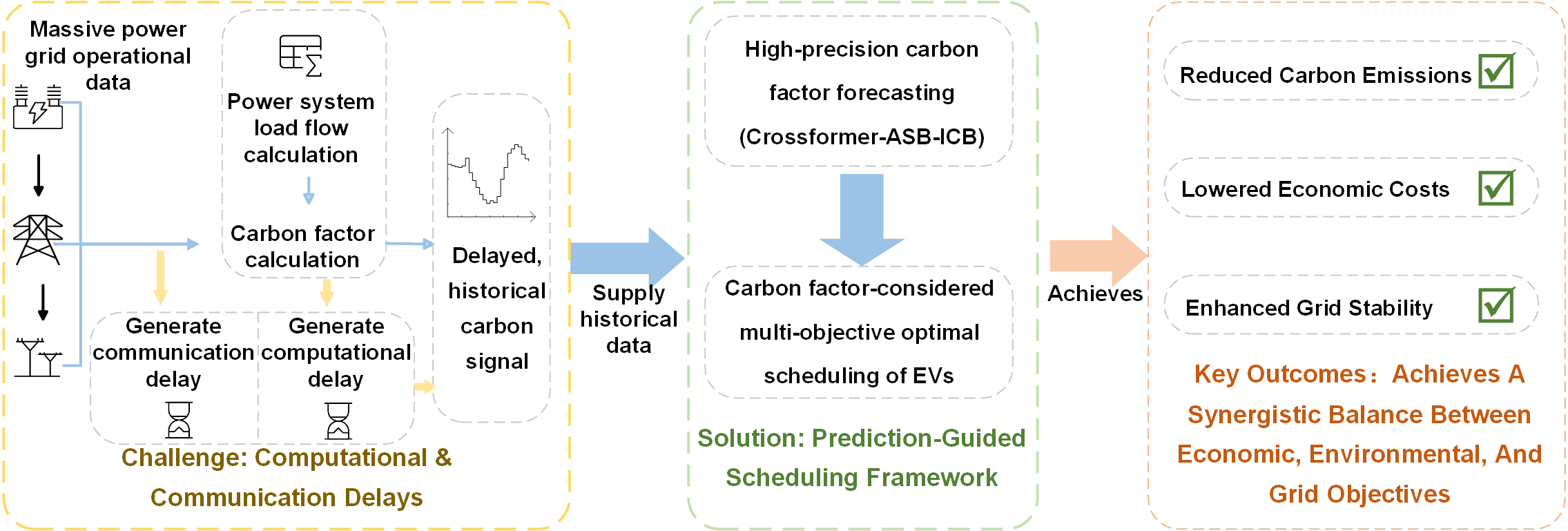
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2026 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2026 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools