 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
A Multi-Block Material Balance Framework for Connectivity Evaluation and Optimization of Water-Drive Gas Reservoirs
1 Key Laboratory of Drilling and Production Engineering for Oil and Gas, Wuhan, China
2 School of Petroleum Engineering, Yangtze University, Wuhan, China
3 Western Research Institute, Yangtze University, Karamay, China
4 PetroChina Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration & Development, Beijing, China
* Corresponding Author: Yuyang Liu. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Fluid and Thermal Dynamics in the Development of Unconventional Resources III)
Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2026, 22(1), 3 https://doi.org/10.32604/fdmp.2026.075865
Received 10 November 2025; Accepted 26 January 2026; Issue published 06 February 2026
Abstract
Carbonate gas reservoirs are often characterized by strong heterogeneity, complex inter-well connectivity, extensive edge or bottom water, and unbalanced production, challenges that are also common in many heterogeneous gas reservoirs with intricate storage and flow behavior. To address these issues within a unified, data-driven framework, this study develops a multi-block material balance model that accounts for inter-block flow and aquifer influx, and is applicable to a wide range of reservoir types. The model incorporates inter-well and well-group conductive connectivity together with pseudo–steady-state aquifer support. The governing equations are solved using a Newton–Raphson scheme, while particle swarm optimization is employed to estimate formation pressures, inter-well connectivity, and effective aquifer volumes. An unbalanced exploitation factor, UEF, is introduced to quantify production imbalance and to guide development optimization. Validation using a synthetic reservoir model demonstrates that the approach accurately reproduces pressure evolution, crossflow behavior, and water influx. Application to a representative case (the Longwangmiao) field further confirms its robustness under highly heterogeneous conditions, achieving a 12.9% reduction in UEF through optimized production allocation.Graphic Abstract
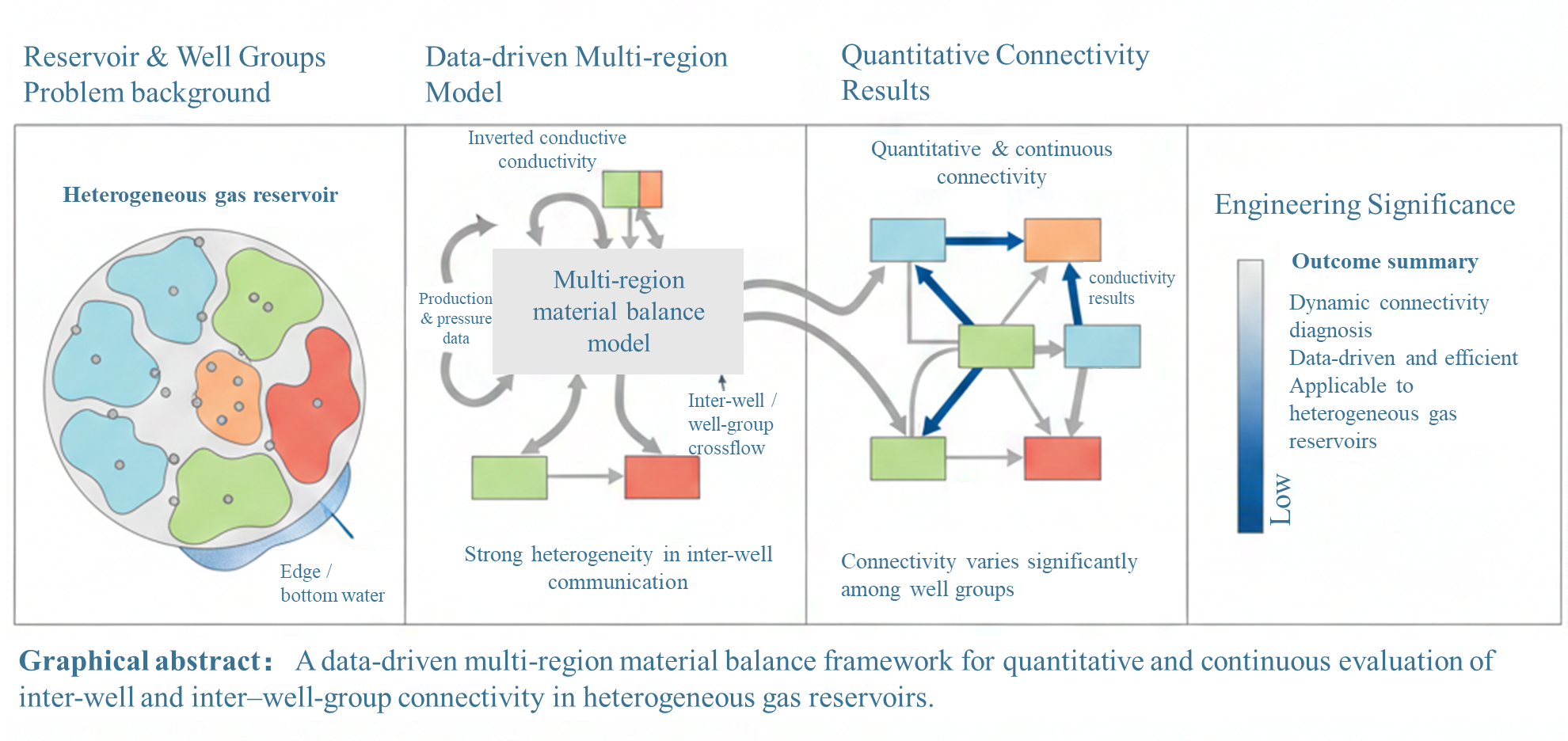
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2026 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2026 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools