 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Artem N. Kotov*, Aleksandr A. Starostin, Aleksandr L. Gurashkin
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2026.074926
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Heat and Mass Transfer on A Small Temporal and Spatial Scale)
Abstract Dynamic methods for creating a superheated state of liquids and tracking their decay are presented. These methods allow relaxation characteristics of short-lived metastable states to be investigated across a wide range of temperatures and pressures. The relaxation of a medium is studied by a “probe” action after a short “pump” pulse. The concentration of the pump pulse in time and space allows the synchronization and localization of means for recording fast-flowing processes. Our aim was to carry out a brief review of methods for studying pulsed thermal processes in a superheated liquid based on the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Anandhi C.1, Narsu Sivakumar1,*, Revathi Devi M.2
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2026.075232
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Heat and Mass Transfer: Integrating Numerical Methods with Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Data-Driven Approaches)
Abstract This work explores a Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) flow in a triangular cavity with a thermally insulated baffle. Enclosure’s inclined wall is hotter, whereas the vertical border is adiabatic and the bottom is cooler. The study aims to clarify how geometric changes affect thermal performance and offers new perspectives on how to improve heat dissipation mechanisms. A COMSOL Multiphysics version 6.2 has been used to solve numerical solutions. Streamlines and thermal distributions are examined systematically in order to understand how the unique geometry and baffle size of triangular cavities can influence the fluid flow. This influence can More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
M. I. Hernández-López1, E. V. Macias-Melo2, F. N. Demesa-López1, J. Serrano-Arellano1,*
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2026.076455
Abstract The accumulation of carbon monoxide
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Wei Dong1, Xuqing Feng2, Taoxiang Mei2, Xiang Li2, Zhenzong He2,3,*
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2026.075846
Abstract The proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) and the hydrogen hybrid power system are studied by the fuzzy-PID (FPID) control method and the fuzzy-PID control method by Artificial Bee Colony algorithm (ABC-FPID), respectively. The results reveal that compared with the FPID control method, the temperature overshoot of the PEMFC stack under the ABC-FPID control method is decreased by 0.6%. Moreover, the circulating water flow rate within the full operating envelope (about 3 min) is reduced by 19.46 L, which means the ABC-FPID control method is more effective in regulating the stack temperature. Then, the ABC-FPID… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Guohai Jia1, Yongjia Ma1, Yuanyuan Li2, Yuling Cheng2, Dan Huang2,*
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2026.076516
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Innovations in Drying Technologies: Bridging Industrial, Environmental, and Energy Efficiency Challenges)
Abstract Microwave vacuum drying (MVD) is a promising technique for enhancing drying efficiency and product quality in ginger processing. In this study, the effects of microwave power, vacuum degree, and slice thickness on the MVD behavior of ginger slices were systematically investigated. The drying performance of MVD was also compared with hot-air drying (HAD) and microwave drying (MD). The results showed that increasing microwave power and vacuum degree, together with reducing slice thickness, significantly accelerated moisture removal, with microwave power being the dominant factor. Under comparable conditions, MVD required only one-sixth of the drying time of… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zebing Chen1, Yang Wang1, Hong Wu1, Wenbin Zhao1, Jinjun Yan1, Luyao Peng2, Yugang Zhao2, Zilong Wang2, Kang Li2,*, Saleh S. Meibodi3, Mohammad Moosazadeh4, Soheil Mohtaram2,*
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2026.077274
Abstract Energy storage batteries require strict thermal management due to temperature sensitivity, operating optimally within a narrow thermal range. Simultaneously, control rooms demand stable and comfortable ambient conditions for staff staying long-term. Conventional temperature control systems typically employ isolated solutions, resulting in functional fragmentation and inefficient resource utilization. To address these challenges, this study proposes and implements an integrated R290 secondary loop heat pump air-conditioning system designed to simultaneously manage the thermal environments of both energy storage batteries and control rooms. By adopting a secondary-loop coupling architecture, all thermal regulation is achieved indirectly via indirect heat… More >
Graphic Abstract
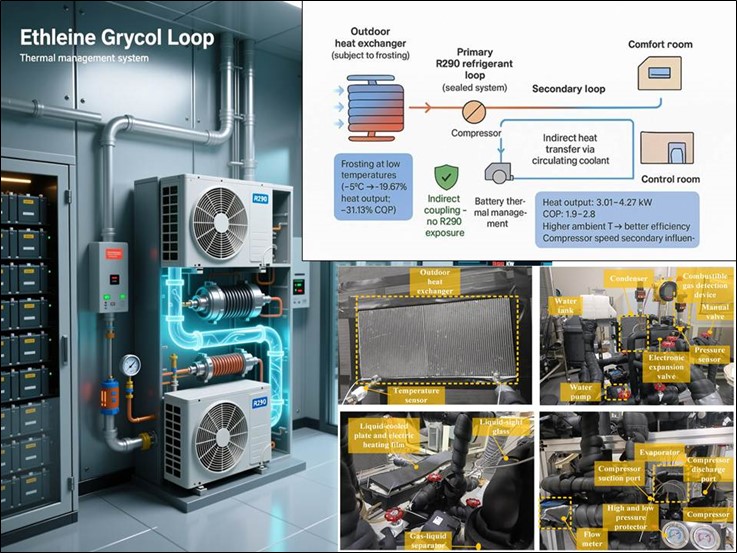
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
M. A. Vega Navarrete1,*, P. J. Argumedo Teuffer1, C. M. Rodríguez Román1, L. E. Marrón Ramírez2, E. A. Islas Narvaez1
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2026.076095
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Innovative Cooling Systems: Design, Optimization, and Applications)
Abstract This article presents an adaptive intelligent control strategy applied to a lumped-parameter evaporator model, i.e., a simplified dynamic representation treating the evaporator as a single thermal node with uniform temperature distribution, suitable for control design due to its balance between physical fidelity and computational simplicity. The controller uses a wavelet-based neural proportional, integral, derivative (PID) controller with IIR filtering (infinite impulse response). The dynamic model captures the essential heat and mass transfer phenomena through a nonlinear energy balance, where the cooling capacity “
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yumeng Li, Fuyong Su*
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2026.076007
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Heat Exchanger Design, Performance, and Applications)
Abstract Based on the Fluent numerical simulation method, this study systematically analyzed the structural parameters of the spiral tube heat exchanger and the influence of the external baffle on its heat transfer performance. The results show that when the equivalent diameter of the spiral tube increased from 16.68 to 21.23 mm, its surface heat transfer coefficient decreased from 22,040 to 17,230 W/m2·K, and the outlet air temperature dropped from 822.3 to 807.3 K. However, the pressure loss decreased from 2.692 to 0.958 kPa. which reveals the contradiction between the heat transfer efficiency and the flow resistance. By More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Bin Li1,2, Liying Gao1,2,*, Yong Li3, Kun Zhu1,2, Zhenling Fu1,2, Shifan Xu1,2, Mohan Li1,2
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2026.075814
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Enhancement Technologies for Fluid Heat and Mass Transfer)
Abstract Cyclone separators are highly efficient gas-solid separation that operate on the centrifugal force and play an indispensable role in industries such as chemical engineering, environmental protection, and power generation. They exhibit excellent reliability, particularly under demanding conditions such as high temperatures and elevated particle concentrations. However, a persistent trade-off between separation efficiency and pressure drop has limited further performance improvements. To address this, optimization of cyclone separators has become a major research focus. This article systematically reviews recent advances, first by examining the mechanisms through which key structural parameters, such as inlet geometry, exhaust pipe… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Jin Huang1, Zihao Tang1, Tingting Wu1, Hualiang Li2, Yanxin Hu1,*
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2026.075643
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Innovations in Drying Technologies: Bridging Industrial, Environmental, and Energy Efficiency Challenges)
Abstract In order to explore the effects of CaO, lignite dust and sawdust on the drying characteristics of municipal sludge at different concentrations, a three-factor three-level regression experiment was carried out based on the results of thermogravimetric experiment and single factor experiment. By fitting three common mathematical models, the Page model with the highest fitting degree was selected to determine the most suitable mathematical model to describe the municipal sludge drying process. In addition, the Box-Behnken design principle in the response surface method was used to analyze the interaction of three factors on the drying characteristics… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
M. Faizan1, Syed Sohaib Zafar2, Farhan Ali1, Umair Khan3,4, Aurang Zaib5, Najiyah Safwa Khashi’ie6,*
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2026.075018
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Heat and Mass Transfer in Nanofluid Boundary Layers: Modeling, Simulation, and Applications)
Abstract The purpose of the present investigation is to explore the implications of Cross fluid in a Darcy-Forchheimer porous medium due to the tri-hybrid nanofluid past a porous cylinder. Thermal radiation, heat generation, thermal convection, solutal convective and chemical reaction have been encountered in this analysis. Entropy generation has been accounted for under the fluidic friction, heat rate analysis, and porosity analysis. Three different nanoparticles of multiwall carbon nanotube (
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Luca Giammichele*, Valerio D’Alessandro, Matteo Falone, Renato Ricci
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2026.072535
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Heat and Mass Transfer Applications in Engineering and Biomedical Systems: New Developments)
Abstract The airborne diffusion of saliva droplets during respiratory activities is one of the major factors in the spread of infections. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the use of protective face masks was essential to reduce the risk of infection and spread of SARS-CoV-2. The face mask is able to significantly reduce the saliva droplet emission in front of the person. However, the use of masks also produces a particle leakage towards the back of the person, which could increase the infection risk of people behind the subject. Most of the experimental investigations applied invasive and/or complex… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Lei Xing1, Haonan Huang2, Mingyang Sun2, Dongyue Jiang2,*, Qiang He1,*
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2026.075774
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Enhancement Technologies for Fluid Heat and Mass Transfer)
Abstract In response to the actual demands of the energy storage type organic Rankine power generation cycle, this study proposes a new type of jacketed shell and tube heat exchanger with integrated cold storage and heat exchange. N-tedecane is selected as the phase change material for cold storage, low-temperature water as the cold source, and R134a as the heat source. The phase change material for cold storage is filled inside the jacket tube of the heat exchanger. Cold fluid is introduced into the inner tube to cause the phase change material to condense and store cold.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Taher Maatallah1,*, Nagmeldeen A. M. Hassanain1, Gaydaa Al Zohbi2, Farooq Saeed1, Muhammad Saleem1, Nassir Hariri1, Mohamed Elsharawy3, Tapas Kumar Mallick1,4, Fahad Gallab Al-Amri1
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2026.075763
Abstract High-concentration photovoltaic (HCPV) systems present significant thermal management challenges due to the intense heat fluxes generated under concentrated solar irradiation, especially in arid environments. Effective heat dissipation is critical to prevent performance degradation and structural failure. This study investigates the thermal performance and design optimization of an enhanced HCPV module, integrating numerical, analytical, and experimental methods. A coupled optical-thermal-electrical model was developed to simulate ray tracing, heat transfer, and temperature-dependent electrical behaviour, with predictions validated under real-world desert conditions. Compared to a baseline commercial module operating at 106°C, the optimized design achieved a peak temperature More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yida Shen1, Bin Dong2, Quan Ma1, Chao Dang1,*, Congjian Li2,*, Guojian Ren3, Shaozhan Wang1,2, Xiaozhe Sun1, Yong Ding4
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.077096
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Microscale Fluid Flow, Heat Transfer, and Phase Change)
Abstract This article explores the application of Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) in solving supersonic flow problems within a Laval nozzle, proposing innovative methods by integrating physical constraints and neural network optimization techniques. The main innovations of this study include the construction of a novel neural network architecture with shortcut connections to enhance the prediction of overall flow trends and local fluctuations, thereby improving convergence speed, reducing computational costs, and increasing the accuracy of flow field reconstruction. Additionally, this study designs a PINNs framework that incorporates specific physical knowledge (SPK) to improve model stability, generalization, and accuracy, More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ahmed Ghazy*
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.076192
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Heat and Mass Transfer for Enhanced Solar Desalination Technologies)
Abstract In this study, the covers of the conventional double slope solar distiller (CDSSD) were replaced with a glass air heater and a glass air-cooled condenser. Ambient air was circulated through the air heater and air-cooled condenser to recover unavoidable heat losses in air heating as an auxiliary product. The thermal performance of the double slope solar distiller integrated with an air heater and an air-cooled condenser (DSSD-AH-ACC) was mathematically evaluated under real weather conditions and varying air flows. The results showed that increasing air flow through the air heater and air-cooled condenser improved the efficiency More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Hao Zhu1,2, Xi Chen1,2,*, Pengcheng Qu1,2, Yifan Zhu1,2, Haoyi Wang1,2, Yingxia Qi1,2
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2026.076127
Abstract Pulse tube cryocoolers are widely employed in cryogenic systems, where gas contamination has become a critical factor limiting both performance and service life. To further investigate the condensation behavior of contaminants, this study develops a two-dimensional axisymmetric model of a linear-type cryocooler to simulate the transport and deposition processes of trace CO2, evaluating the impact of contamination on system pressure drop under various operating conditions. Results indicate that CO2 diffusion is primarily driven by concentration gradients. The CO2 deposition rate increases markedly at low temperatures and high concentrations, with over 90% of deposition occurring in the cold-end… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Luling Li1, Minghui Li2, Zhengxiang Xu2, Haofeng Lin2, Xuemei Lang2, Peiming Li1, Hengrong Zhang1,*, Dongxu Ji3,*, Jian Liu1, Jianhui Liu1, Guang Yang1, Shuanshi Fan2,*
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2026.075692
Abstract This study addresses the energy-intensive challenge of small-scale biogas upgrading by optimizing a chemical absorption process employing methyl diethanolamine (MDEA). Focusing on a typical distributed application of 300 Nm3/d, we developed an integrated simulation-optimization framework using Aspen HYSYS 14.0 to systematically evaluate the effects of critical operating parameters—absorption pressure, MDEA concentration, flow rate, temperature, number of trays, and reboiler duty—on methane purity and energy consumption. The key finding is the identification of an optimal parameter set: absorption pressure of 1200 kPa, MDEA concentration of 20 mol%, lean flow rate of 2.5 kmol/h, temperature of 298.15 K,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ratan Kumar Chanda1, Rakesh Bhowmick2, Giulio Lorenzini3,*, Rabindra Nath Mondal1,*
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.075311
Abstract Due to ample engineering and industrial applications involving electrically conducting fluids, such as in magnetic flow control devices, thermal magnetic systems, magnetic filtration and separation, and fluid transport in curved rotating channels, the present study examines the impacts of pressure-induced instability characteristics and chaotic nature of Magneto-hydrodynamic fluid flow in a rotating curved square duct (CSD), incorporating Hall and ion-slip currents. The rotational speed (ΩT) around the vertical axis of the duct is constant while a variable transverse magnetic field is applied perpendicular to the fluid. The numerical solutions are obtained through the spectral method as a… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Linkang Wang1, Bowei Xie2,3,4,*, Zhiqiang Liu1, Lijing Yi2,3,4, Mu Du2,3,4,*
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2026.076486
Abstract The Local Surface Plasma Resonance (LSPR) of spherical metal particles is typically only observed within the visible spectrum. This inherent property renders modulation through alterations in radius or material challenging, significantly constraining its practical applications. In this work, we propose a super-elliptic gold nanoparticle model that allows for the continuous modulation of particle geometry from spherical to star-like shapes using a single roundness parameter (e). Unlike conventional nanorods or discrete nanostars, this geometry provides a unified framework to investigate the evolution of multipole resonances. The radiation characteristics of super elliptic gold nanoparticles in the range of… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Geqiang Li1,2, Kai Wang1, Juntao Liu3, Zhengyang Han1,2, Shuai Wang1,2,*, Donglin Li1,2
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.075249
Abstract To explore the distribution law of the temperature field in the motor pump and the influence of the fan-shaped DC channel with spoiler in the pump housing on its heat dissipation performance. This study takes the arc-gear type hydraulic motor pump as the research object. In COMSOL, a coupled heat transfer simulation model of the motor pump’s fluid-solid coupling is established, and the internal temperature field characteristics are analyzed. To improve the heat dissipation effect of the motor pump, it is proposed to arrange spoiler in the fan-shaped DC channel of the pump housing to… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yendoubouame Lare1,2,*, Koffi Sagna1,2, Amah Séna d’Almeida3
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.074506
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Heat and Mass Transfer on A Small Temporal and Spatial Scale)
Abstract This study presents a numerical investigation of the transient relaxation dynamics of a near-critical CO2 droplet immersed in a warmer supercritical environment composed of the same fluid. Three thermodynamic regimes were analysed: quasi-critical (
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Muhammad Waheed Azam1,*, Uzair Sajjad2,*, Faisal Maqbool3, Giovani Sempirini4
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.074690
Abstract Heat exchangers play a crucial role in thermal energy systems, with their performance directly impacting efficiency, cost, and environmental impact. A powerful technique for performance improvement can be given by passive enhancement strategies, which are characterized by their dependability and minimal external power requirements. This comprehensive review critically assesses recent advancements in such passive methods to evaluate their heat transfer mechanisms, performance characteristics, and practical implementation challenges. Our methodology involves a systematic and comprehensive analysis of various heat transfer enhancement techniques, including surface modifications, extended surfaces, swirl flow devices, and tube inserts. This approach synthesizes… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Wei Dong1, Baoqi Guo2, Weiwei Zhao2, Hui Jian2, Zhenzong He2,*
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.075848
Abstract This study explores the design of a tapered cathode flow channel in a proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC), leveraging artificial intelligence and multi-objective optimization techniques to attain an optimal configuration. First, the influence of the channel height ratio and mass flow rate on PEMFC performance was systematically examined. The results reveal that decreasing the height ratio and increasing the mass flow rate lead to reduction in the standard deviation of current density, accompanied by a monotonic rise in pressure drop. The average current density initially rises before exhibiting a slight decline. Subsequently, a surrogate… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Josmell Alva Alcántara1, Elder Mendoza Orbegoso1, Nattan Roberto Caetano2, Luis Julca Verástegui1, Juan Bengoa Seminario1, Jimmy Silvera Otañe1, Yvan Leiva Calvanapón1, Giulio Lorenzini3,*
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.074995
Abstract The continuous improvement of solar thermal technologies is essential to meet the growing demand for sustainable heat generation and to support global decarbonization efforts. This study presents the design, implementation, and validation of a real-time monitoring framework based on the Internet of Things (IoT) and cloud computing to enhance the thermal performance of evacuated tube solar water heaters (ETSWHs). A commercial system and a custom-built prototype were instrumented with Industry 4.0 technologies, including platinum resistance temperature detectors (PT100), solar irradiance and wind speed sensors, a programmable logic controller (PLC), a SCADA interface, and a cloud-connected… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
E. V. Macias-Melo1, P. R. Torres-Hernández2, K. M. Aguilar-Castro1, I. Hernández-Pérez1, P. García-Alamilla3, C. E. Torres-Aguilar1, M. I. Hernández-López4, S. Medina García4, J. Serrano-Arellano4,*
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.074900
Abstract This study presents the design, construction, and thermal evaluation of a solar-powered cocoa roaster based on a Parabolic Cylinder Collector (PCC) with dual-axis solar tracking. The system integrates three functional subsystems: the cylindrical-parabolic reflecting surface, the stainless-steel absorber tube, and a microcontroller-based tracking mechanism. The prototype enables continuous acquisition of key thermal variables (solar irradiance, ambient temperature, absorber surface temperature, and bean temperature), allowing a detailed characterization of heat transfer processes during roasting. Roasting experiments were conducted at controlled durations of 40, 55, and 70 min between 10:00 and 14:00 h. Maximum roasting temperatures of… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Kai Song1, Lishan Feng1, Shugang Duan1, Weilong Zhao2, Haikun Zheng3,*
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.074404
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Microscale Fluid Flow, Heat Transfer, and Phase Change)
Abstract This study experimentally investigates the influence of surface wettability on the frosting characteristics of three types of corrugated structures (Types A, B, and C) under controlled low-temperature conditions. The experiments were conducted in a constant-temperature bath at a cold surface temperature of –5°C, relative humidity of 90%, and ambient air temperature of 10°C. The results reveal that the variation trends of frost morphology, frost mass, and frost layer thickness are generally consistent across surfaces with different wettability. Among the tested surfaces, frost crystal formation and complete surface coverage occurred latest on the superhydrophobic surface (CA =… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zheming Cheng1,*, Xinping OuYang2, Leren Tao2, Zihao Wang2, Ke Sun2
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.074325
Abstract Energy shortage has become one of the most concerning issues in the world today, and improving energy utilization efficiency is a key area of research for experts and scholars worldwide. Small-diameter heat exchangers offer advantages such as reduced material usage, lower refrigerant charge, and compact structure. However, they also face challenges, including increased refrigerant pressure drop and smaller heat transfer area inside the tubes. This paper combines the advantages and disadvantages of both small and large-diameter tubes and proposes a combined-diameter heat exchanger, consisting of large and small diameters, for use in the indoor units… More >