 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
An Investigation on the Thermal-Hydraulics Performance of a Bubble Column Reactor Fitted with Tube Bundle under Different Gas Sparger Configurations
1 College of Mechanical and Electronic Engineering, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou, 350002, China
2 Fujian Key Laboratory of Agricultural Information Sensing Technology, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou, 350002, China
* Corresponding Author: Changliang Han. Email:
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer 2025, 23(4), 1103-1128. https://doi.org/10.32604/fhmt.2025.068181
Received 22 May 2025; Accepted 25 June 2025; Issue published 29 August 2025
Abstract
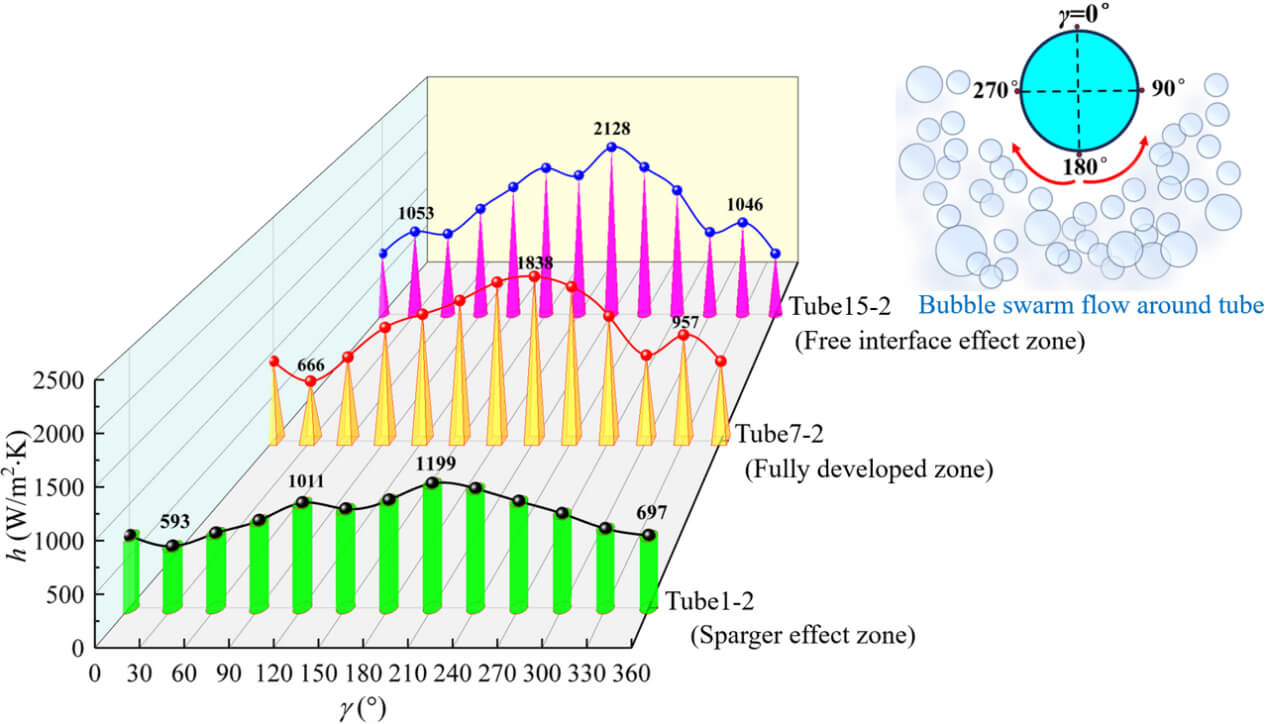
Bubble column reactors fitted with tube bundles (BCR TB) belong to common heat transfer equipment in the field of chemical engineering, yet the complicated thermal-hydraulics performance of BCR TB has not been deeply revealed. To fill this gap, the present study proposes a novel variable bubble size modeling approach based on the Euler-Euler two-fluid framework, which is coupled with the population balance model considering comprehensive interphase forces. On the basis of verifying numerical reliability using experimental data, the mechanism of bubble swarm flow around the tube bundle and the effects of gas sparger configurations on the thermal-hydraulics performance of BCR TB are investigated. Results indicate that the entire tube bundle can be divided into three distinct zones, namely the sparger effect zone, fully developed zone and interface effect zone in view of the local mixture-to-wall heat transfer coefficient. The maximum peak value of the mixture-to-wall heat transfer coefficient always appears at 210° of heat exchange tubes. When the orifice diameter is 4 mm, the axial gradient of gas holdup is relatively large due to more intense shearing and fragmentation effects. Interestingly, the fractions of medium-sized and large-sized bubbles are not sensitive to orifice angle. Both the mixture-to-wall heat transfer coefficient and the friction factor decrease initially and then increase when the installation height increases. Under the optimized gas sparger structure configuration, the mixture-to-wall heat transfer coefficient increases by 10.23%, accompanied by the reduction of pressure drop by 8.14%, ultimately attaining a system energy conversion efficiency of 97.88% and performance evaluation criterion of 1.087. Finally, a new dimensionless and semi-theoretical Nusselt correlation incorporating a structural correction factor with an average absolute deviation of 5.15% is developed. The findings can offer useful guidance for the optimal design of BCR TB.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools