 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Boosting Structural and Dielectric Properties of Polyvinyl Alcohol/Starch/Carboxymethyl Cellulose Films with Iron-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Advanced Applications
1 Department of Chemistry, College of Education for Pure Sciences (Ibn Al-Haitham), University of Baghdad, Baghdad, 10053, Iraq
2 Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science, King Khalid University, Abha, 61421, Saudi Arabia
3 Egyptian Drug Authority (EDA) formerly National Organization for Drug Control and Research (NODCAR), Giza, 29, Egypt
4 Cellulose and Paper Department, National Research Centre, Dokki, Giza, 12622, Egypt
5 Photochemistry Department, National Research Centre, Dokki, Giza, 12622, Egypt
* Corresponding Author: Ahmed M. Khalil. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Advances on Renewable Materials)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2025, 13(7), 1459-1473. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0046
Received 25 February 2025; Accepted 18 April 2025; Issue published 22 July 2025
Abstract
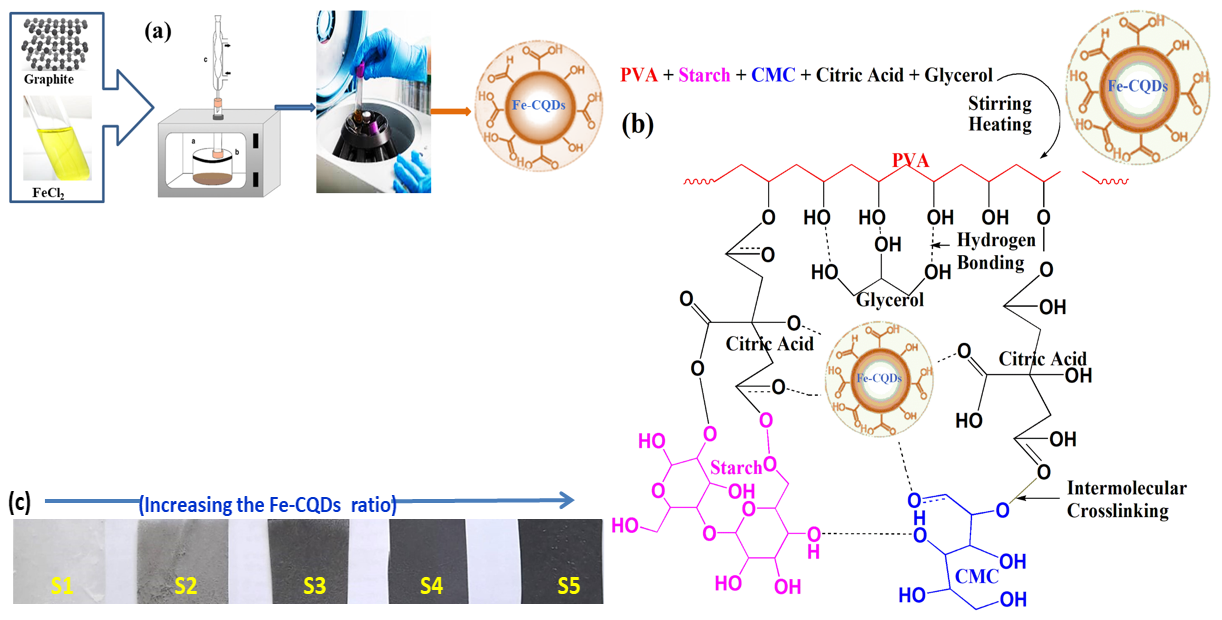
In this study, the casting process is used to fabricate modified polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), starch (S), and carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) polymer blend films (PVA/S/CMC) loaded with various concentrations of iron-doped carbon quantum dots (Fe-CQDs) and denoted as (PVA/S/CMC@Fe-CQDs). A one-step microwave strategy was employed as a facile method to prepare Fe-CQDs. Through a series of characterization techniques, fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, x-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) have been used to show the successful integration of Fe-CQDs into the PVA/S/CMC matrix. Loading the synthesized Fe-CQDs to the polymeric matrix significantly enhanced the mechanical properties of the films represented in the tensile strength, Young’s modulus, and hardness. However, the elongation decreased noticeably upon increasing the iron-doped carbon dots. The surface wettability was also studied by measuring the contact angle of the prepared films. The findings showed a noticeable elevation in these measurements by increasing the Fe-CQDs content, declaring the role of a hydrophobic character in these nanoparticles when introduced into a hydrophilic polymeric system. The dielectric characteristics of the reinforced polymer composite films were evaluated. These results revealed that the ac-conductivity of the investigated films was boosted with increasing Fe-CQDs’ ratio and frequency. The PVA/S/CMC@Fe-CQDs films possess substantial potential for efficient energy storage applications.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools