 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Synthesis and Properties of Rosin-Based Composite Acrylamide Hydrogels
Jiangsu Co-Innovation Center of Efficient Processing and Utilization of Forest Resources, Jiangsu Provincial Key Laboratory for the Chemistry and Utilization of Agro–Forest Biomass, College of Chemical Engineering, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, 210037, China
* Corresponding Authors: Muhua Chen. Email: ; Xu Xu. Email:
Journal of Renewable Materials 2023, 11(2), 853-865. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2022.022901
Received 31 March 2022; Accepted 06 May 2022; Issue published 22 September 2022
Abstract
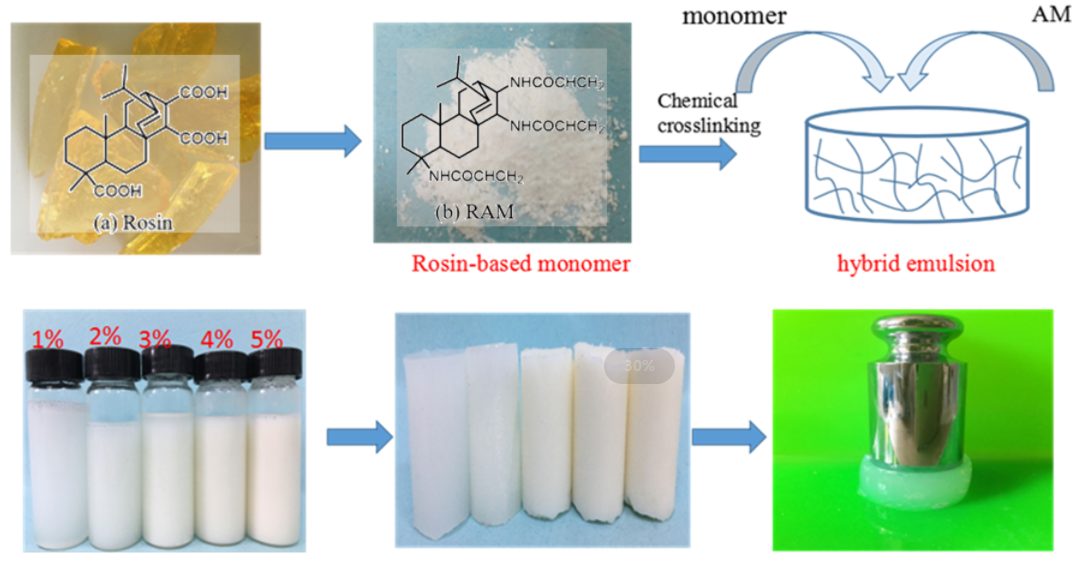
Hydrogels have been widely applied in agricultural drought-resistance, pollution regulation, drug delivery and so on. Acrylamide (AM) is usually used as raw material to synthesize acrylamide hydrogels. However, inherently low mechanical strength greatly limits their applications in some special areas. Therefore, it is necessary to choose suitable functional monomers to optimize acrylamide hydrogels and improve their mechanical performances. In this paper, a novel acrylamide monomer modified by rosin was synthesized, and then polyacrylamide/rosin-based acrylamide (RAM) composite hydrogels were prepared via free radical polymerization using potassium persulfate as initiator, N, N′-methylene-bisacrylamide (MBA) as a crosslinker. The influence of RAM monomer was investigated in detail. The chemical structure, pore structure, swelling properties, thermal performances and mechanical properties of composite hydrogels were characterized by Fourier Transform Infrared spectrometer (FT-IR), thermogravimetric analysis (TG), scanning electron microscope (SEM), and universal testing, respectively. The results showed that the thermal stability and mechanical property of RAM hydrogels were improved significantly. The compressive strength of RAM hydrogels was increased to 3.5 times than that of AM hydrogels, and the tensile strength was 5.1 times compared with AM hydrogels as well. Moreover, RAM hydrogels exhibited a faster initial swelling rate due to the new pore structure formed after introducing the RAM monomer.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools