 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Preparation and Characterization of Biobased Dehydroabietyl Polyethylene Glycol Glycidyl Ether-Grafted Hydroxyethyl Cellulose with High Emulsifying Property
School of Chemical and Chemistry, Yancheng Institute of Technology, Yancheng, 224051, China
* Corresponding Authors: Xujuan Huang. Email: ; Zhaosheng Cai. Email:
Journal of Renewable Materials 2024, 12(1), 103-117. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2023.029424
Received 18 February 2023; Accepted 20 March 2023; Issue published 23 January 2024
Abstract
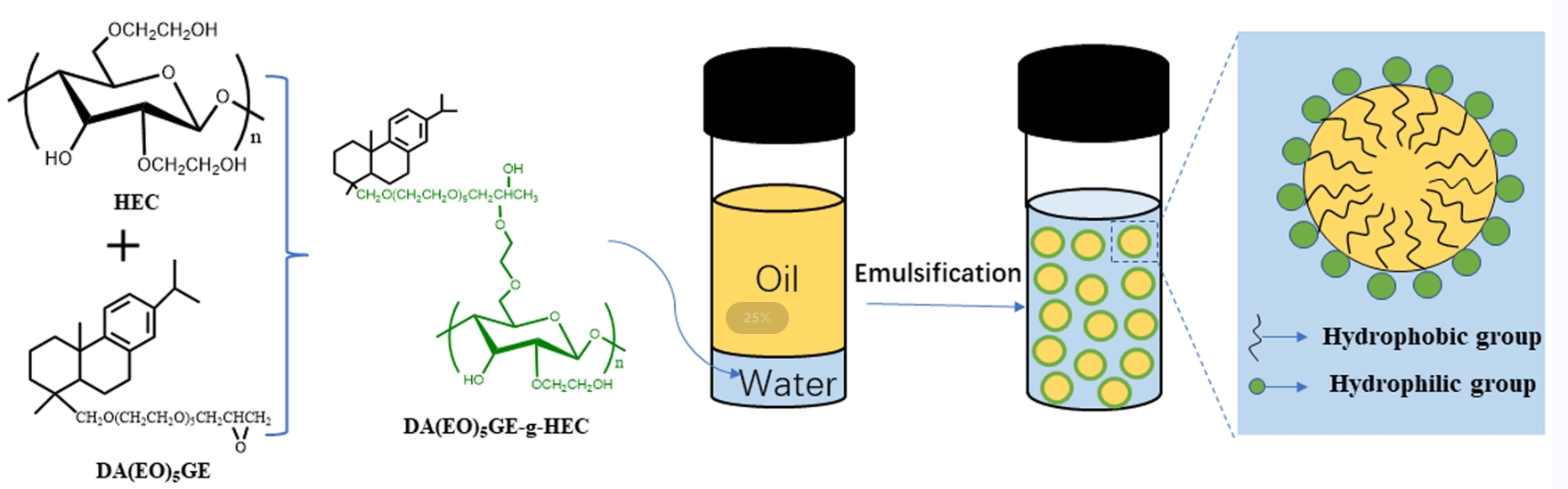
Dehydroabietyl polyethylene glycol glycidyl ether-grafted hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC) polymer surfactant (DA(EO)5GE-g-HEC) was prepared using ring-opening polymerization with biobased rosin and hydroxyethyl cellulose as feedstocks. Dehydroabietyl polyethylene glycol glycidyl ether (DA(EO)5GE) was formed by condensation of dehydroabietyl alcohol polyoxyethylene ether (Rosin derivative: DA(EO)5H) and epichlorohydrin. The grafting degree of DA(EO)5GE-g-HEC was manipulated by adjusting the mass ratio of HEC and DA(EO)5GE and confirmed by EA. According to the formula, when m(HEC)/m(DA(EO)2GE) was 1:1~1:5, the grafting rate of DA(EO)5GE in DA(EO)5GE-g-HEC varied from 34.43% to 38.33%. The surface activity and foam properties of DA(EO)5GE-g-HEC aqueous solution were studied. The results showed that with the increase in grafting rate, the critical micellar concentration (CMC) in aqueous solution changed from 1.28 to 0.96 g/L. The results of the thermogravimetric analysis showed that the temperature range of the main stage of mass loss of DA(EO)5GE-g-HEC was 310°C~410°C, and the thermal decomposition processes of the samples with five mass ratios were similar. An oil in water emulsion was prepared by choosing cyclohexane as the oil phase and DA(EO)5GE-g-HEC as the emulsifier. The effect of DA(EO)5GE-g-HEC mass fraction on emulsion particle size and stability was analyzed. The results suggested that when the oil-water ratio was 8:2 with 0.4% emulsifier, the emulsion droplets were the smallest in terms of particle size and were the most stable. The rheological test results showed that the apparent viscosity decreased with the increase in shear rate and showed a typical elastic gel phenomenon.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools