 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Enhancing Mechanical Properties of Biobased Polyurethane Composites Using Birch Flour and Diatomite Fillers
1 Center of Chemical Engineering, ITMO University, Kronverkskiy pr. 49, Saint-Petersburg, 197101, Russia
2 Institute of Macromolecular Compounds, Branch of Petersburg Nuclear Physics Institute Named by B.P. Konstantinov of National Research Centre «Kurchatov Institute», Bolshoi pr. 31, Saint-Petersburg, 199004, Russia
* Corresponding Author: Vjacheslav V. Zuev. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Eco-friendly Wood-Based Composites: Design, Manufacturing, Properties and Applications – Ⅱ)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2025, 13(10), 2043-2058. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0079
Received 25 March 2025; Accepted 25 May 2025; Issue published 22 October 2025
Abstract
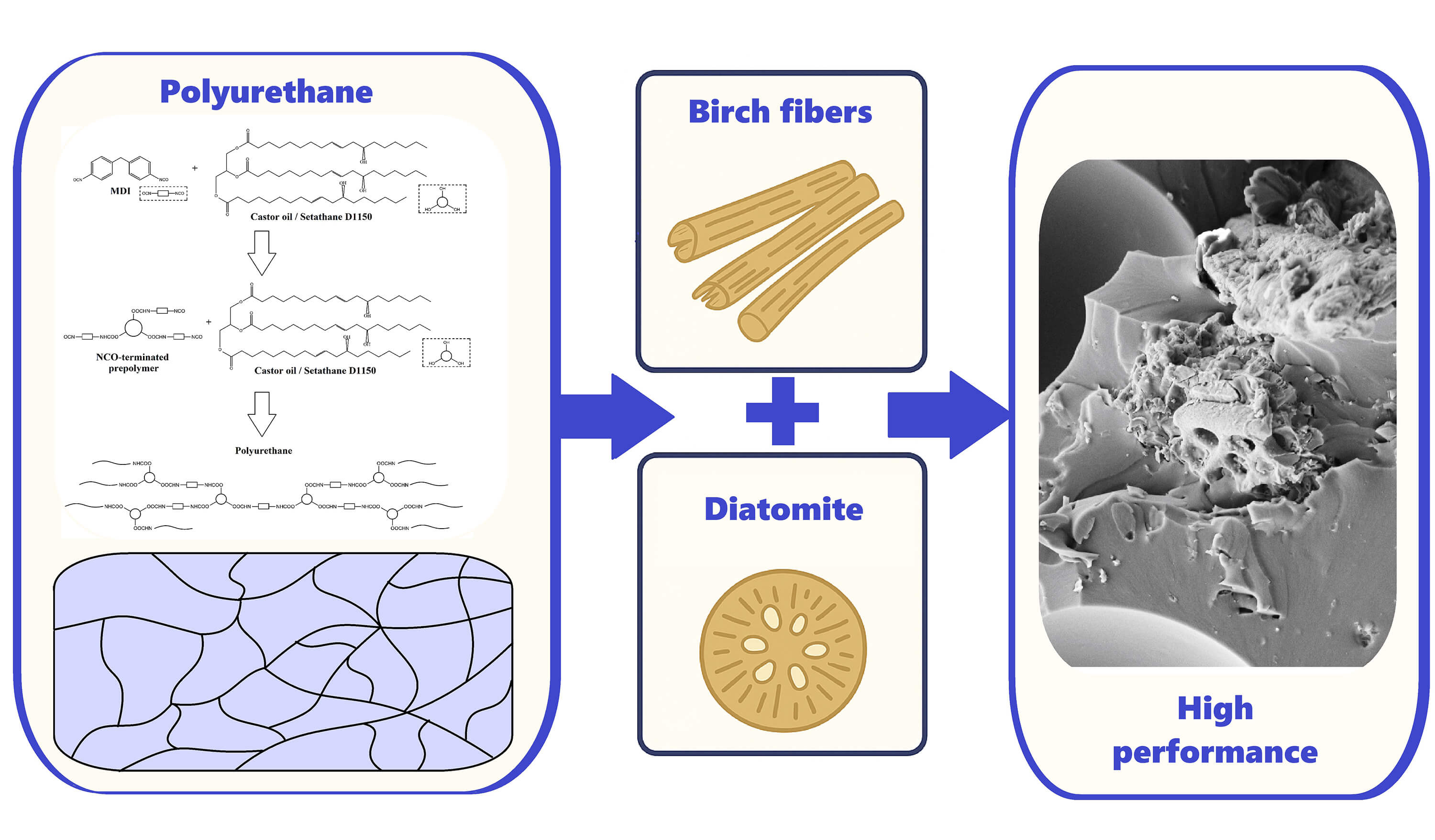
In this study, the polyurethanes (PU) were synthesized from 4,4′-methylene diphenyl diisocyanate and biobased ethoxylated castor oil or one mixture of ethoxylated and neat castor oil by direct mixing method. Utilization of ethoxylated castor oil increases the tensile strength of PU up to 2.75 times (from 3.2 to 8.8 MPa), compared to PU based on neat castor oil. The PU composites filled with birch flour, diatomite, and their mixture were prepared using a homemade dissolver with a cutter-shaped attachment at a speed of 1500 r min−1. The tensile strength of PU composites filled with birch flour increases up to two time at loading 5–30 wt.%. Application of combined birch flour/diatomite additives has similar effect. The tensile strength of PU composites based on one to one mixture of ethoxylated and neat castor oil and filled with birch flour or combined birch flour/diatomite additives increases sharply up to 16–17 fold (up to 18.1 MPa). The birch flour and diatomite well soaked polymer matrix. The main factor determining mechanical performance is the morphology of PU samples and composites. Formation of ordered lamella-like structure of the amorphous phase of PU matrix leads to an increase in mechanical performance and glass transition temperatures. The formation of a disordered unstructured soft phase of starting PU leads to a decline of these functional properties.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material FileCite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools