 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Efficient Application to Remove Arsenic and Antimony from the Water Environment Using Renewable Carbon-Based Materials: A Review
1 Institute for Interdisciplinary and Innovate Research, Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, Xi’an, 710055, China
2 School of Environmental and Municipal Engineering, Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, Xi’an, 710055, China
3 Department of Chemistry and Chemical Processing Technologies, Bahçe Vocational School, Osmaniye Korkut Ata University, Osmaniye, 80000, Türkiye
4 International Research Centre of Nanotechnology for Himalayan Sustainability (IRCNHS), Shoolini University, Solan, 173229, India
* Corresponding Authors: Hui Shi. Email: ; Tao Liu. Email:
# These authors contributed equally to thiswork
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Advances in Biochar and Carbon-Based Materials Characteristics and Environment Applications)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2025, 13(6), 1103-1137. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2025.02024-0043
Received 21 November 2024; Accepted 05 February 2025; Issue published 23 June 2025
Abstract
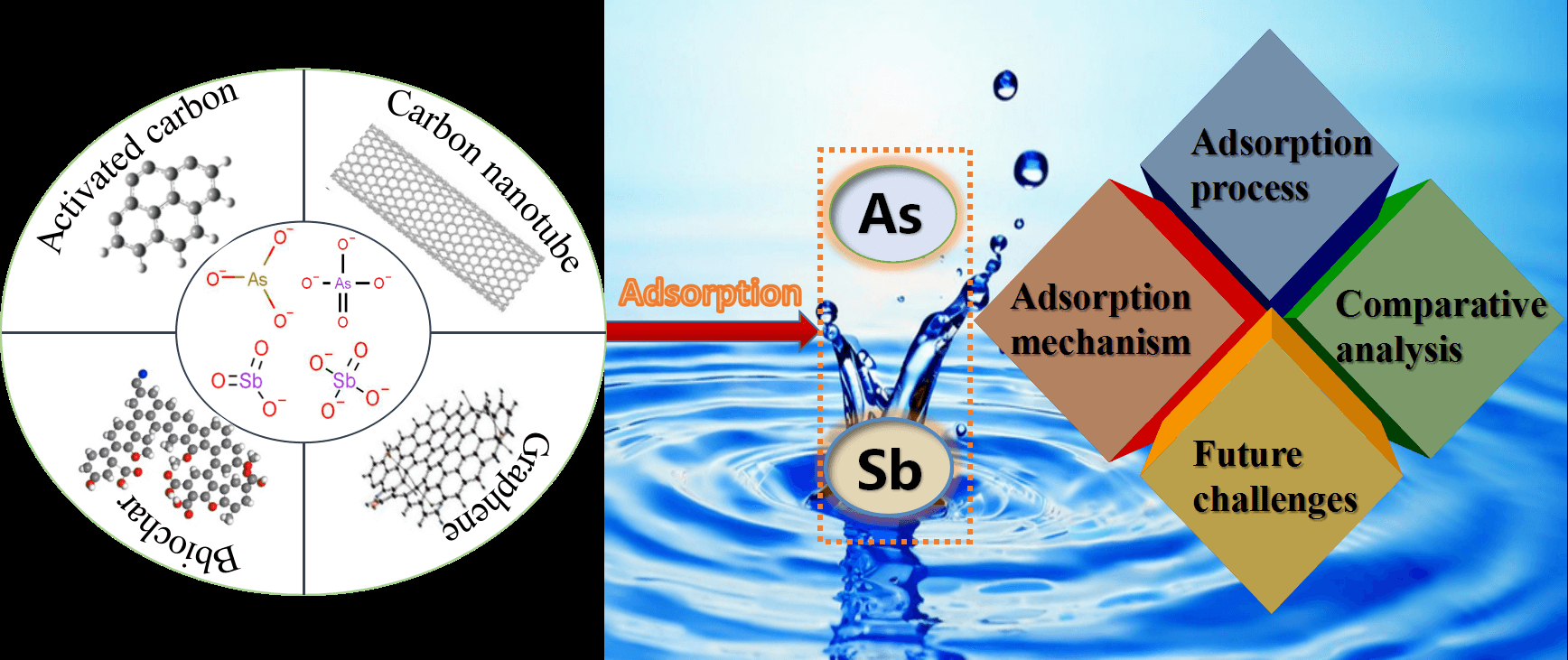
With the rapid development of industry, the environmental problems caused by heavy metal arsenic and antimony are becoming increasingly serious. Therefore, it is urgent to solve the problem of arsenic and antimony pollution in the water environment. Renewable carbon-based materials, as a kind of adsorbent widely used in wastewater treatment, have been the focus of scholars’ research for many years. In this review, the preparation methods, characteristics, and applications of renewable carbon-based materials (biochar, activated carbon, carbon nanotubes, and graphene) for the removal of arsenic and antimony are described in detail. Based on adsorption kinetics, isothermal adsorption, temperature, pH, and coexisting ions, we discuss the process of adsorption of arsenic and antimony by renewable carbon-based materials, explore the mechanism of adsorption of anions in water by renewable carbon-based materials, and comparatively analyze the differences in adsorption performance of arsenic and antimony by different renewable carbon-based materials. Compared with biochar, activated carbon, carbon nanotube, and graphene renewable materials loaded with iron-manganese oxides have better removal effects on arsenic and antimony wastewater. Extensive research data shows that biochar, as a renewable material, is recommended, followed by activated carbon. Both are recommended because of their excellent adsorption properties and low production costs. Finally, the prospects and challenges of the application of renewable carbon-based materials in wastewater treatment are discussed, and the directions and development trends of future research are pointed out, which provide references and insights for further promoting the application of renewable carbon-based materials in wastewater treatment.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools