 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Integration of Biopolyesters and Natural Fibers in Structural Composites: An Innovative Approach for Sustainable Materials
1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University of Mataram, Mataram, 83125, Indonesia
2 Department Research Center for Biomass and Bioproducts, National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN), Jl. Raya Bogor Km 46, Cibinong, Bogor, 16911, Indonesia
* Corresponding Author: Nasmi Herlina Sari. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Valorization of Lignocellulosic Biomass for Functional Materials)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2025, 13(8), 1521-1546. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2025.02024-0058
Received 13 December 2024; Accepted 25 February 2025; Issue published 22 August 2025
Abstract
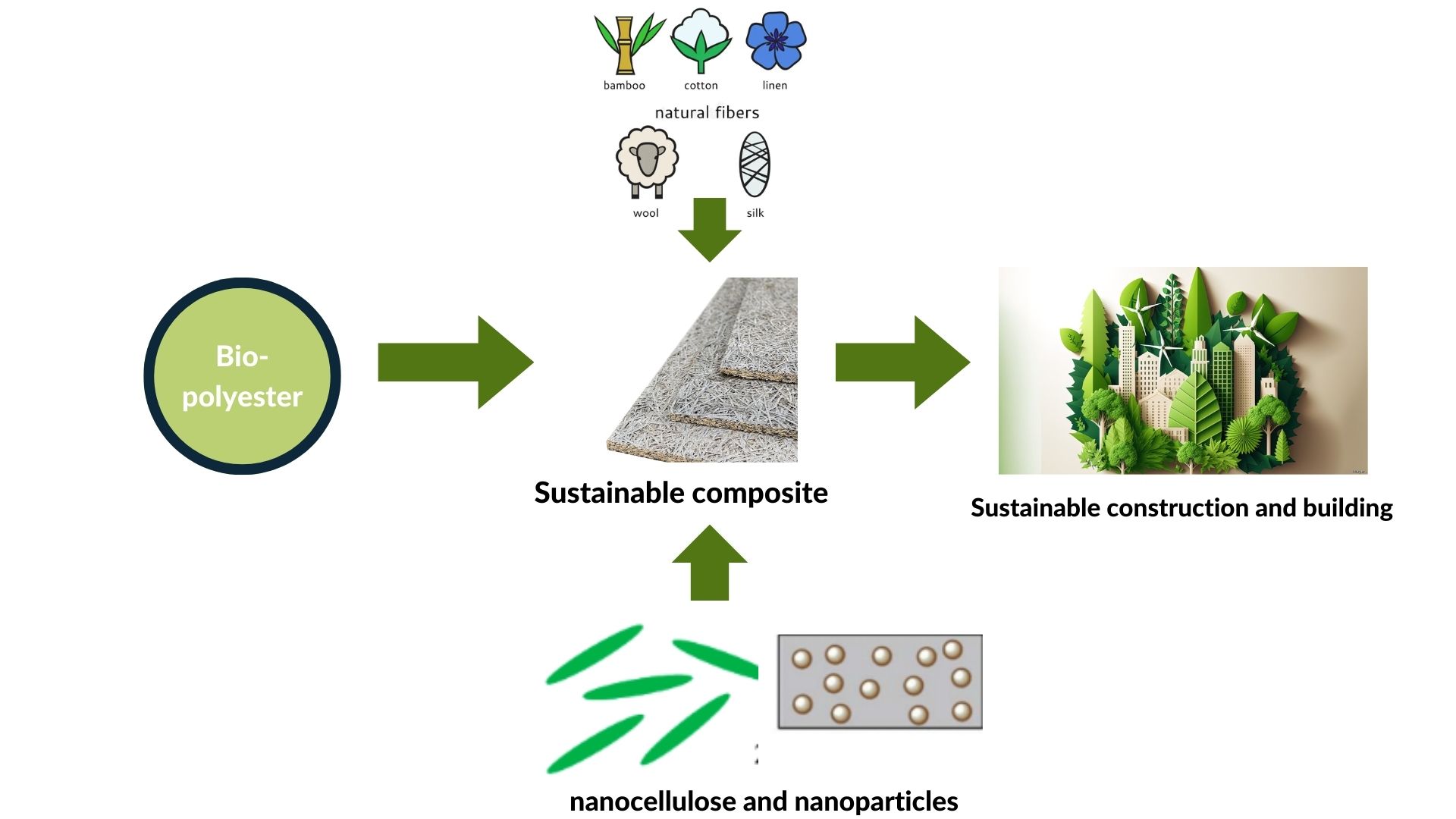
Composites made from biopolymers and natural fibers are gaining popularity as alternative sustainable structural materials. Biopolyesters including polylactic acid (PLA), polybutylene succinate (PBS), and polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA), when mixed with natural fibers such as kenaf, hemp, and jute, provide an environmentally acceptable alternative to traditional fossil-based materials. This article examines current research on developments in the integration of biopolymers with natural fibers, with a focus on enhancing mechanical, thermal, and sustainability. Innovative approaches to surface treatment of natural fibers, such as biological and chemical treatments, have demonstrated enhanced adhesion with biopolymer matrices, increasing attributes such as tensile strength and rigidity. Furthermore, nano filling technologies such as nanocellulose and nanoparticles have improved the attributes of multifunctional composites, including heat conductivity and moisture resistance. According to performance analysis, biopolymer-natural fiber-based composites may compete with synthetic composites in construction applications, particularly in lightweight buildings and automobiles. However, significant issues such as degradation in humid settings and long-term endurance must be solved. To support a circular economy, solutions involve the development of moisture-resistant polymers and composite recycling technology. This article examines current advancements and identifies problems and opportunities to provide insight into the future direction of more inventive and sustainable biocomposites, and also the dangers they pose to green technology and industrial materials. These findings are significant in terms of the development of building materials which are not only competitive but also contribute to global sustainability.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools