 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Enhancing Rice Straw Fibers for Pulp Films Using DES and Streptomyces rochei Synergy
1 Institute of Agricultural Resources and Environment, Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Nanjing, 210014, China
2 Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center for Solid Organic Waste Resource Utilization, Nanjing, 225000, China
3 Key Laboratory of Saline-Alkali Soil Improvement and Utilization (Coastal Saline-Alkali Lands), Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Nanjing, 225000, China
4 College of Materials Science and Engineering, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, 210037, China
5 Key Laboratory of New Materials and Facilities for Rural Renewable Energy, MOA of China, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, 450002, China
* Corresponding Authors: Enhui Sun. Email: ; Mingjie Guan. Email:
Journal of Renewable Materials 2025, 13(9), 1803-1817. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0059
Received 14 March 2025; Accepted 18 July 2025; Issue published 22 September 2025
Abstract
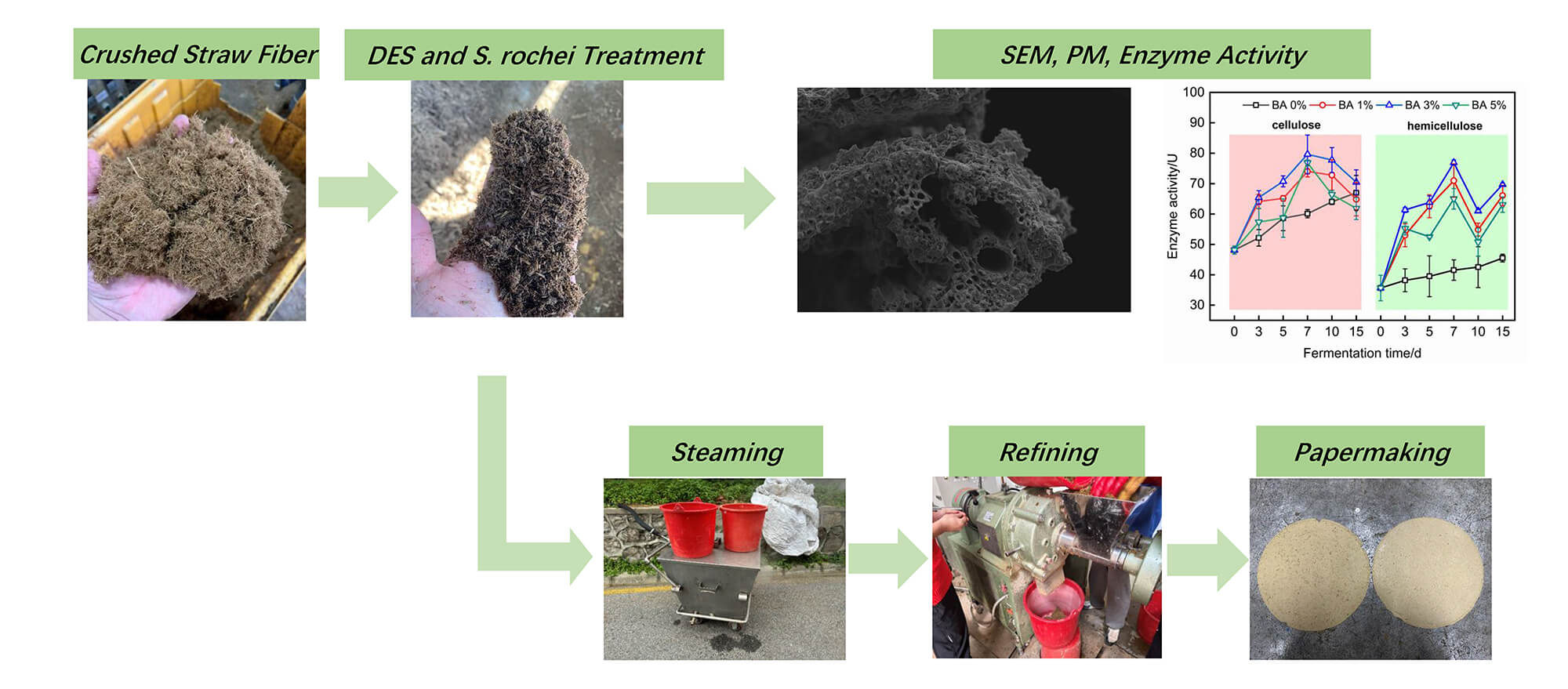
Long-time fermentation has always been one of the reasons restricting the development of straw biological pulping. This study aimed to develop a novel straw pulp film with shortened solid-state fermentation time with less than 20% mass loss rate by bio-pulping synergistic treatment of straw fibers with deep eutectic solvent (DES) and Streptomyces rochei (S. rochei). Results illustrated that at 3% S. rochei concentration with 7-day fermentation, both cellulose and hemicellulose enzyme activities of the treated rice straw fiber reached peak values with a fiber mass loss rate of 17.01%. Microstructural morphology revealed that S. rochei colonization initiated on straw surfaces and progressively penetrated internal structures, resulting in surface loosening and distinct disruption of cell wall tissues within vascular bundles in transverse sections. The treated rice straw strip indicated a maximum tensile strength of 46.22 MPa for (Bacteria) BA 3% at day 7, attributed to optimized synergistic effects of microfibril angle (MFA) and cellulose/hemicellulose relative content ratio. The modified straw pulp film exhibited significant enhancement in the tensile index (44.9% increase), burst index (10.3% increase), and tear index (60% increase) compared to untreated groups. This work demonstrated the important role of DES and S. rochei bio-pulping synergistic treatment in improving rice straw pulp performance, suggesting an eco-friendly, novel, and efficient biomass pretreatment technology for potential application prospects in sustainable agricultural mulching materials.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools