 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Competitive Sequestration of miR-1183 by lncRNA DDX11-AS1 Drives Gliomagenesis through E2F7 Activation
1 Department of Neurosurgery, Shenzhen Hospital, Southern Medical University, Shenzhen, 518100, China
2 The Third School of Clinical Medicine, Southern Medical University, Shenzhen, 518100, China
3 Department of Neurosurgery, Shenzhen Yantian District People’s Hospital, Shenzhen, 518100, China
4 Department of Neurosurgery, Longgang Central Hospital of Shenzhen, Shenzhen, 518100, China
5 Department of Pathology, Longgang Central Hospital of Shenzhen, Shenzhen, 518100, China
* Corresponding Authors: Jianbo Yu. Email: ; Jie Mao. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Novel Targets and Biomarkers in Solid Tumors)
Oncology Research 2025, 33(10), 3023-3040. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2025.065380
Received 11 March 2025; Accepted 25 July 2025; Issue published 26 September 2025
Abstract
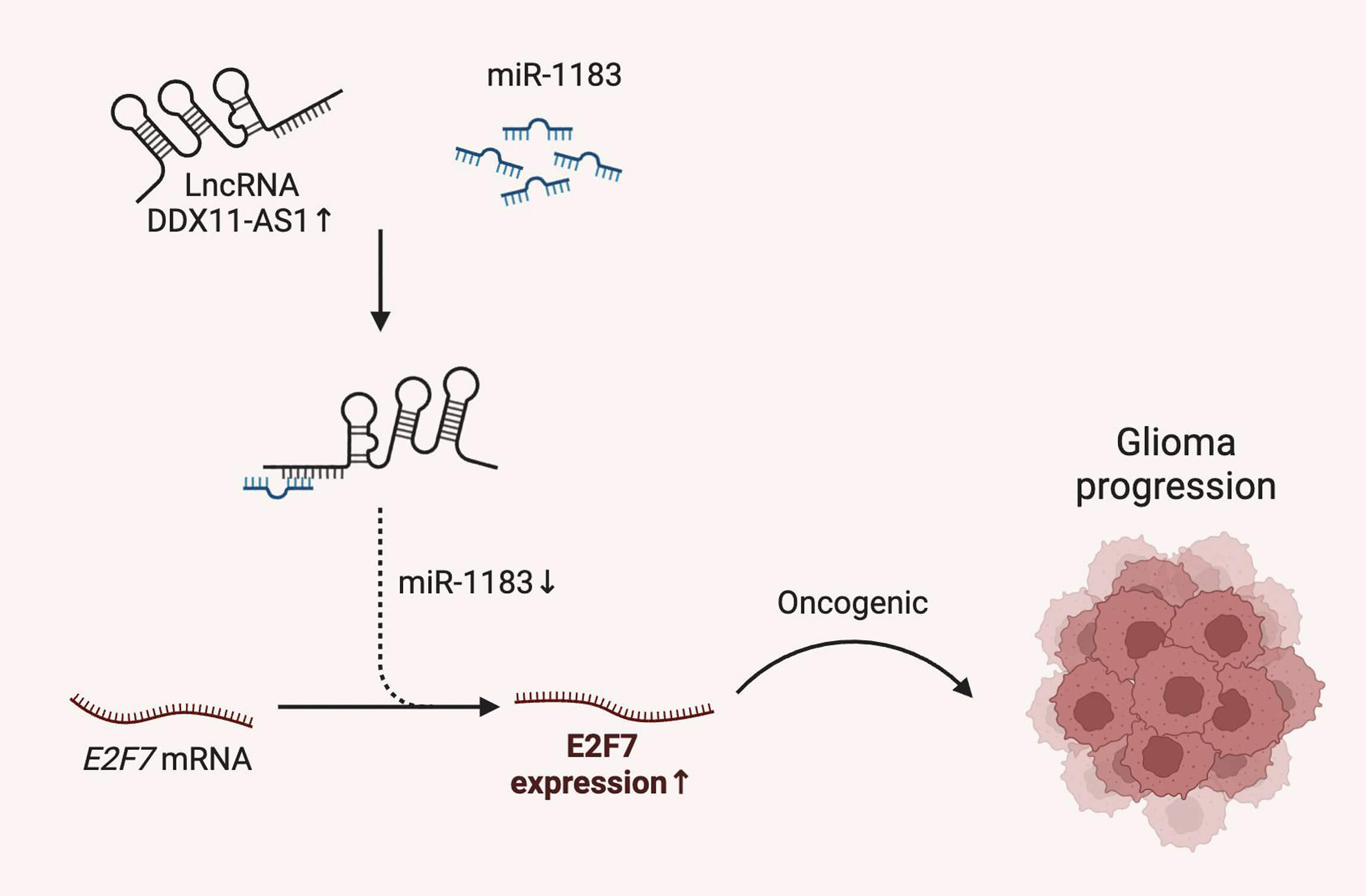
Objectives: Glioma, as the most lethal primary brain malignancy with poor prognosis, requires further elucidation on the functional role of long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) DDX11 antisense RNA 1 (DDX11-AS1) in its pathogenesis, despite its established oncogenic functions in other cancers. Therefore, this study sought to characterize the oncogenic role and molecular mechanism of DDX11-AS1 in glioma. Methods: DDX11-AS1 expression levels were analyzed in clinical surgical glioma specimens and publicly available datasets. The functional roles of DDX11-AS1 on glioma cell proliferation and migration were investigated using in vitro knockdown and overexpression assays. In vivo tumor growth was assessed using orthotopic glioma-bearing mouse models. To elucidate the regulatory axis involving DDX11-AS1, miR-1183, and E2F transcription factor 7 (E2F7), we performed competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) analysis and conducted functional rescue experiments via miR-1183 inhibition. Results: DDX11-AS1 expression was markedly upregulated in clinical glioma specimens. Functionally, DDX11-AS1 knockdown significantly suppressed glioma cell proliferation and migration in vitro, while its overexpression exacerbated these malignant phenotypes. Orthotopic glioma-bearing mouse models confirmed that DDX11-AS1 drives in vivo glioma tumor growth. Mechanistically, DDX11-AS1 functions as a ceRNA by competitively interacting with miR-1183. Critically, inhibition of miR-1183 rescued the suppressive effects of DDX11-AS1 knockdown on glioma tumorigenic phenotypes and restored E2F7 expression levels. Conclusions: This study demonstrates that lncRNA DDX11-AS1 promotes glioma progression by regulating the miR-1183/E2F7 axis, indicating a potential therapeutic target for glioma.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material FileCite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools