 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
ERRγ Promotes Multiple Myeloma Survival by Coordinating NF-κB Signaling and Mitochondrial Apoptosis Regulation
1 Department of Hematology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, 400016, China
2 Department of Hematology, University-Town Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, 400016, China
* Corresponding Author: Jianbin Chen. Email:
# These two authors contributed equally to this work
Oncology Research 2025, 33(9), 2399-2420. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2025.063700
Received 21 January 2025; Accepted 14 May 2025; Issue published 28 August 2025
Abstract
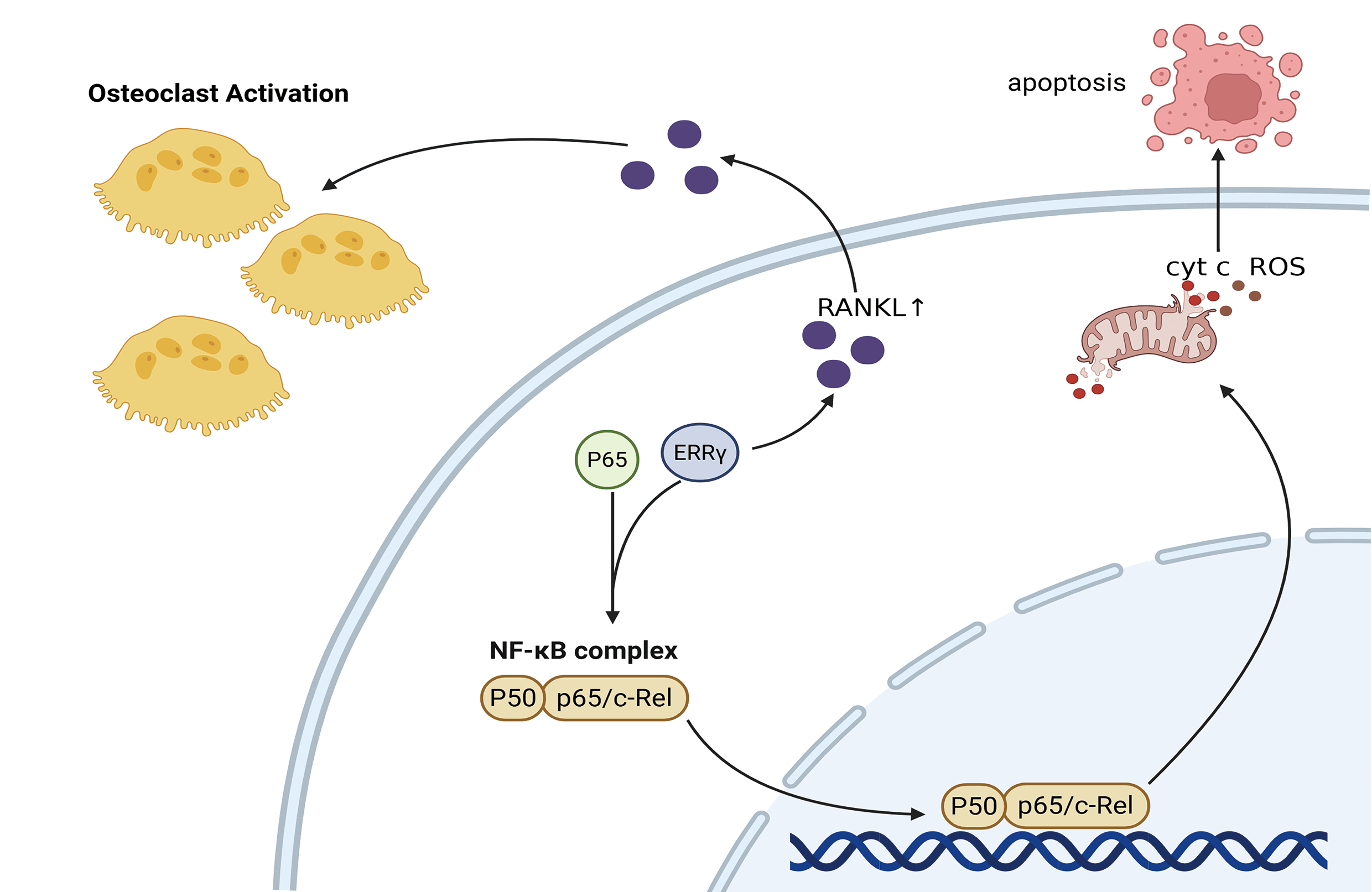
Background: Multiple myeloma (MM) remains a formidable clinical challenge due to its high relapse rate and resistance to existing therapies. Estrogen-related receptor gamma (ERRγ), a nuclear receptor critical for cellular energy metabolism, has been implicated in various cancers. but its role in MM remains unclear. Methods: ERRγ expression was assessed using bioinformatics and RT-qPCR. Functional studies were conducted through siRNA-mediated ERRγ knockdown and treatment with the inverse agonist GSK5182 to examine their effects on MM cell proliferation and apoptosis. Results: ERRγ was significantly upregulated in the bone marrow of MM patients, correlating with advanced clinical stages and pathological fractures. Inhibition of ERRγ reduced MM cell expansion both in vitro and in vivo, while promoting mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis. Co-immunoprecipitation assays demonstrated a physical association between ERRγ and P65. Inhibition of ERRγ attenuated canonical nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling by blocking the nuclear translocation of its key effector p65. Additionally, modulation of ERRγ altered receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL) levels, implying a potential role in bone degradation observed in MM cases. Conclusion: Collectively, the data broaden understanding of ERRγ’s contribution to MM development and propose it as a viable target for therapeutic intervention.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools