 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Alleviates the Inhibition of Dendrobium huoshanense Photosynthesis by Cadmium through Enhancing Antioxidant Enzyme System
1 College of Biological and Pharmaceutical Engineering, Anhui Engineering Research Center for Eco-Agriculture of Traditional Chinese Medicine, West Anhui University, Luan, 237012, China
2 Department of Plant Science, School of Agriculture and Biology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 201109, China
3 Low Dimensional Materials Research Center, Khazar University, Baku, AZ1096, Azerbaijan
4 Department of Plant Protection, Faculty of Agriculture, Sakarya University of Applied Sciences, Arifiye, 54580, Türkiye
5 National Key Laboratory for Tropical Crop Breeding, School of Breeding and Multiplication (Sanya Institute of Breeding and Multiplication), Hainan University, Sanya, 572025, China
* Corresponding Authors: Cheng Song. Email: ; Muhammad Aamir Manzoor. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Application of Nanomaterials in Plants)
Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany 2025, 94(11), 3427-3451. https://doi.org/10.32604/phyton.2025.070778
Received 23 July 2025; Accepted 11 September 2025; Issue published 01 December 2025
Abstract
Heavy metal pollution has become a pervasive environmental issue affecting numerous regions worldwide. Recently, there has been significant attention given to the application of nano-enabled technologies with the purpose of enhancing plant development and alleviating heavy metal stress. This study aimed to illustrate the potential of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) to enhance the morphological traits of D. huoshenense exposed to cadmium (Cd) stress. The chemical structure and elemental composition of the ZnO-NPs were characterised by a series of analytical methods, including X-ray diffraction, UV-Vis spectrometry, XPS, and TEM. Plant samples used were collected at 0, 5, and 15 days in order to assess physiological and biochemical parameters under different Cd treatments. ZnO-NPs administered in pot experiments have been shown to enhance plant proliferation through the modulation of Cd enrichment levels. The results revealed that ZnO-NPs enhanced plant growth by increasing soluble sugars and proline levels, enhancing activities of antioxidant enzymes (SOD, POD, CAT, APX) and reducing electrolyte leakage (EL) and malondialdehyde (MDA) content. Furthermore, ZnO-NPs enhanced the net photosynthetic rate, transpiration, stomatal conductance, and chlorophyll content in leaves subjected to Cd stress at the 10-day sampling stage. Exogenous ZnO-NPs significantly elevated the expression of genes associated with flavonoid biosynthesis, potentially facilitating the accumulation of medicinal compounds to mitigate Cd stress. Taken together, these findings provide a novel perspective on the strategies employed by medicinal plants in response to Cd.Graphic Abstract
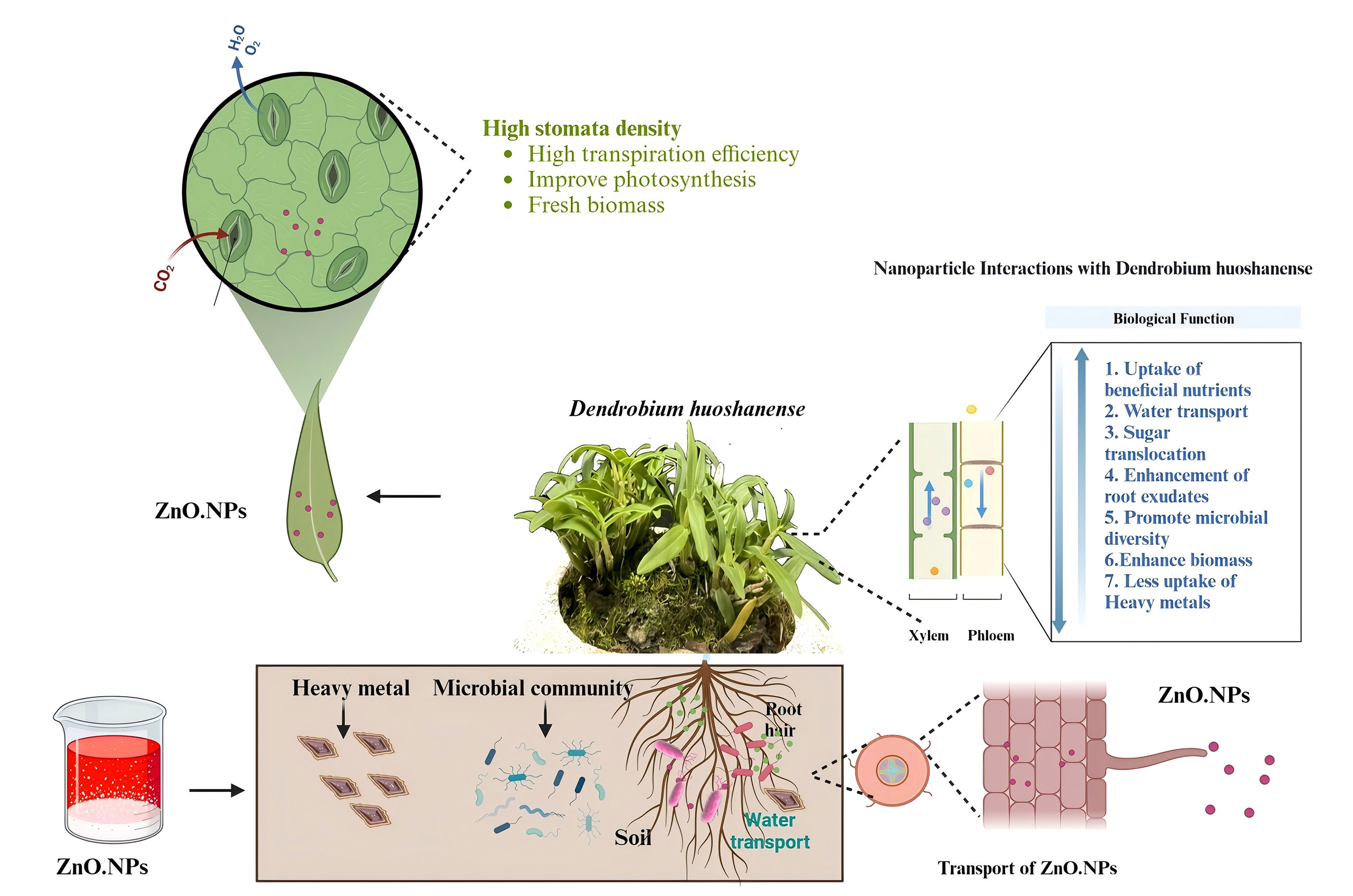
Keywords
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material FileCite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools