 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Traditional Uses, Polysaccharide Pharmacology, and Active Components Biosynthesis Regulation of Dendrobium officinale: A Review
1 Institute of Chinese Materia Medica, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, State Key Laboratory for Quality Ensurance and Sustainable Use of Dao-di Herbs, Beijing, 100700, China
2 Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin, 301617, China
3 Zhangzhou Pien Tze Huang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Zhangzhou, 363099, China
4 Zhejiang Provincial Station of Cultivated Land Quality and Fertilizer Management, Hangzhou, 310000, China
5 Yueqing Municipal Bureau of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Yueqing, 325600, China
* Corresponding Authors: Guozhuang Zhang. Email: ; Linlin Dong. Email:
Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany 2025, 94(11), 3721-3748. https://doi.org/10.32604/phyton.2025.072062
Received 18 August 2025; Accepted 15 October 2025; Issue published 01 December 2025
Abstract
Dendrobium officinale (DO) is a well-recognized medicinal and edible plant with a long history of application in traditional medicinal practices across China and Southeast Asia. Recent studies have demonstrated that DO is abundant in diverse bioactive compounds, including polysaccharides (DOP), flavonoids, alkaloids, and bibenzyls thought to exert a range of pharmacological effects, such as anti-tumor and immunomodulatory effects. However, our comprehensive understanding of two key aspects—pharmacological functions and biosynthetic mechanisms—of DO’s major constituents remains limited, especially when considered within the clinical contexts of traditional use. To address this gap, this study reviews DO’s historical applications, clinical effects, and related formulations through an analysis of ancient texts spanning nearly two millennia—with special attention to region-specific traditional medical texts. This provides a historical and empirical foundation for further exploration of its modern pharmacological potential. Given the central role of DOP in DO’s biological activities, this paper further summarizes its therapeutic applications across various diseases and the underlying mechanisms, with special emphasis on structure–activity relationships. This focus is particularly important because the structural characteristics of DOP are highly dependent on extraction and analytical methods, which have contributed to inconsistencies in pharmacological findings over the past two decades. Finally, the review highlights recent advances in the understanding of the in vivo biosynthesis and regulatory mechanisms of the major bioactive components in DO, with a particular focus on molecular regulation and responses to agricultural interventions. These factors are critical for the production of high-quality DO. Overall, this study develops a comprehensive knowledge framework that connects DO’s traditional applications of DO to its two key research areas: pharmacological functions and quality formation. We anticipate this framework will offer clear guidance for future research from a clinical perspective.Graphic Abstract
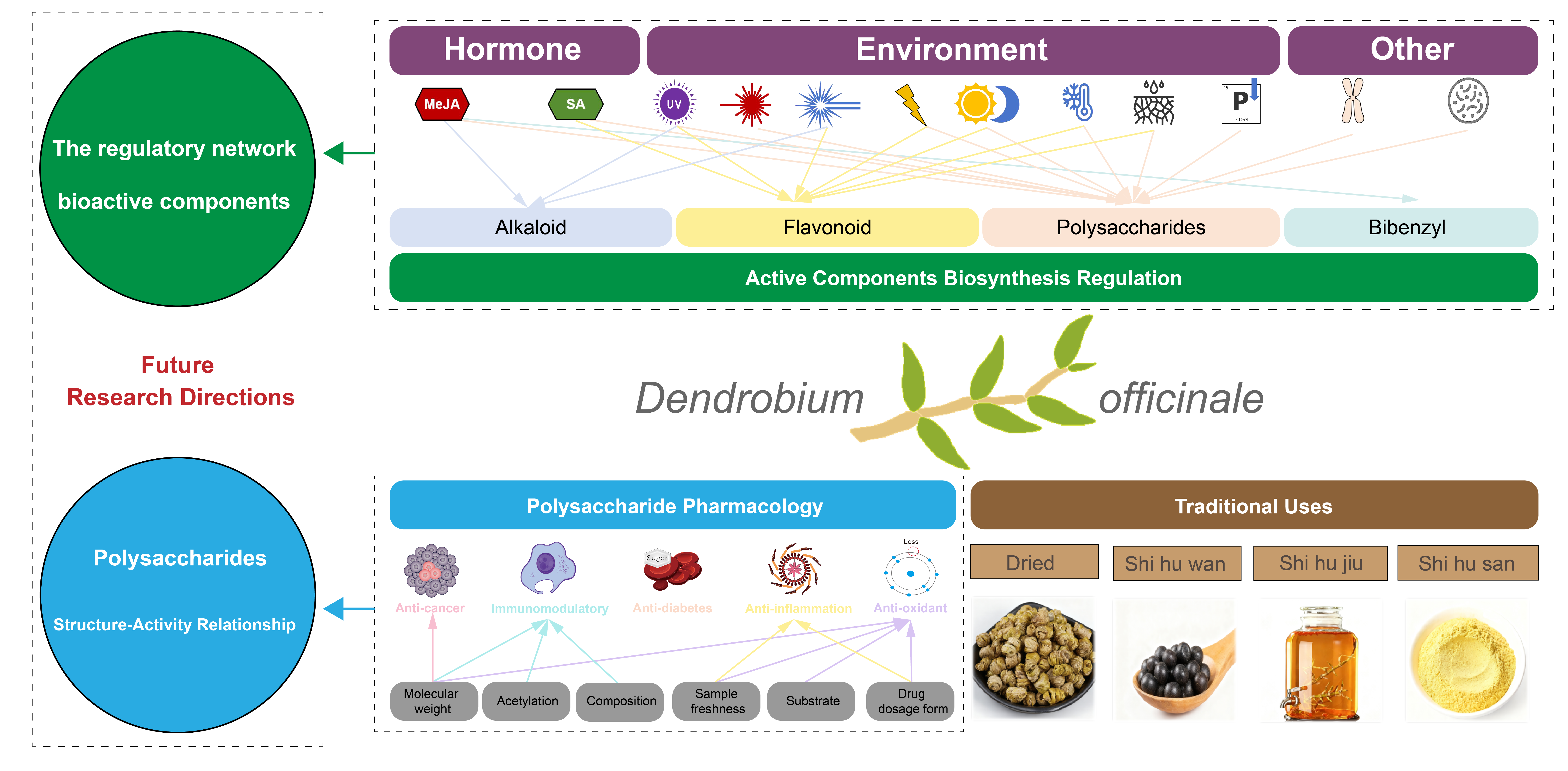
Keywords
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material FileCite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools