 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
AI-Driven Approaches to Utilization of Multi-Omics Data for Personalized Diagnosis and Treatment of Cancer: A Comprehensive Review
1 Department of Computer Science, Faculty of Computing and Information Technology, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, 21589, Saudi Arabia
2 Centre of Research Excellence in Artificial Intelligence and Data Science, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, 21589, Saudi Arabia
* Corresponding Author: Somayah Albaradei. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Computational Intelligence Techniques, Uncertain Knowledge Processing and Multi-Attribute Group Decision-Making Methods Applied in Modeling of Medical Diagnosis and Prognosis)
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2025, 145(3), 2937-2970. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2025.072584
Received 30 August 2025; Accepted 07 November 2025; Issue published 23 December 2025
Abstract
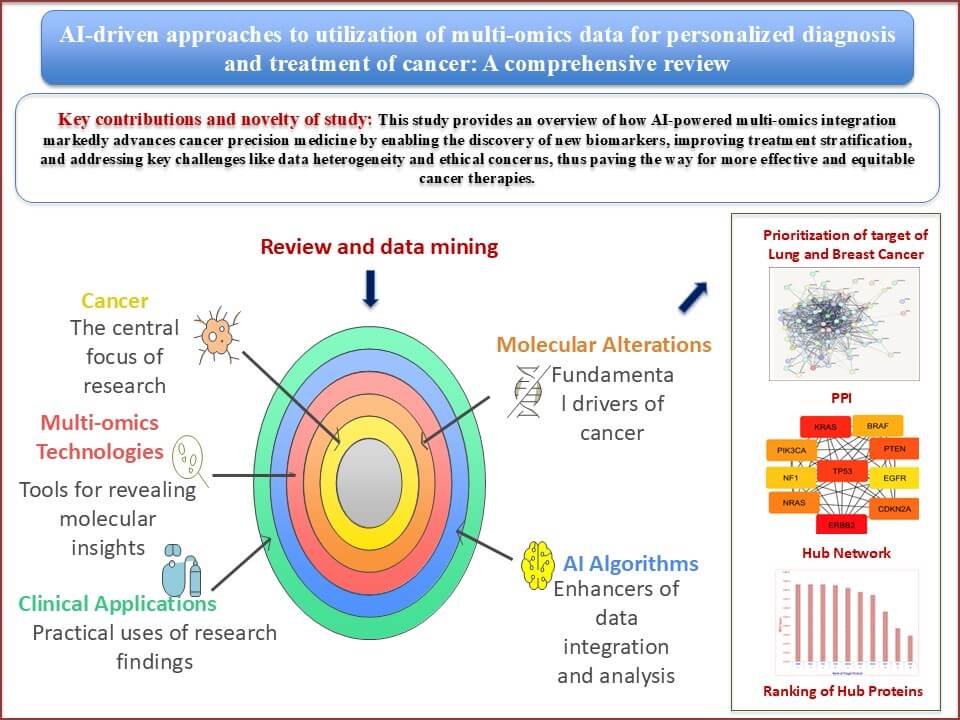
Cancer deaths and new cases worldwide are projected to rise by 47% by 2040, with transitioning countries experiencing an even higher increase of up to 95%. Tumor severity is profoundly influenced by the timing, accuracy, and stage of diagnosis, which directly impacts clinical decision-making. Various biological entities, including genes, proteins, mRNAs, miRNAs, and metabolites, contribute to cancer development. The emergence of multi-omics technologies has transformed cancer research by revealing molecular alterations across multiple biological layers. This integrative approach supports the notion that cancer is fundamentally driven by such alterations, enabling the discovery of molecular signatures for precision oncology. This review explores the role of AI-driven multi-omics analyses in cancer medicine, emphasizing their potential to identify novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets, enhance understanding of Tumor biology, and address integration challenges in clinical workflows. Network biology analyzes identified ERBB2, KRAS, and TP53 as top hub genes in lung cancer based on Maximal Clique Centrality (MCC) scores. In contrast, TP53, ERBB2, ESR1, MYC, and BRCA1 emerged as central regulators in breast cancer, linked to cell proliferation, hormonal signaling, and genomic stability. The review also discusses how specific Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms can streamline the integration of heterogeneous datasets, facilitate the interpretation of the tumor microenvironment, and support data-driven clinical strategies.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools