 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Low-Carbon Operation Optimization of Integrated Energy System Considering Multi-Equipment Coordination and Multi-Market Interaction
1 College of Electrical Engineering and New Energy, China Three Gorges University, Yichang, 443002, China
2 Hebei Electric Power Transmission Transformation Co., State Grid Hebei Electric Power Company, Shijiazhuang, 050000, China
* Corresponding Author: Cheng Peng. Email:
Energy Engineering 2025, 122(11), 4579-4602. https://doi.org/10.32604/ee.2025.067704
Received 10 May 2025; Accepted 07 July 2025; Issue published 27 October 2025
Abstract
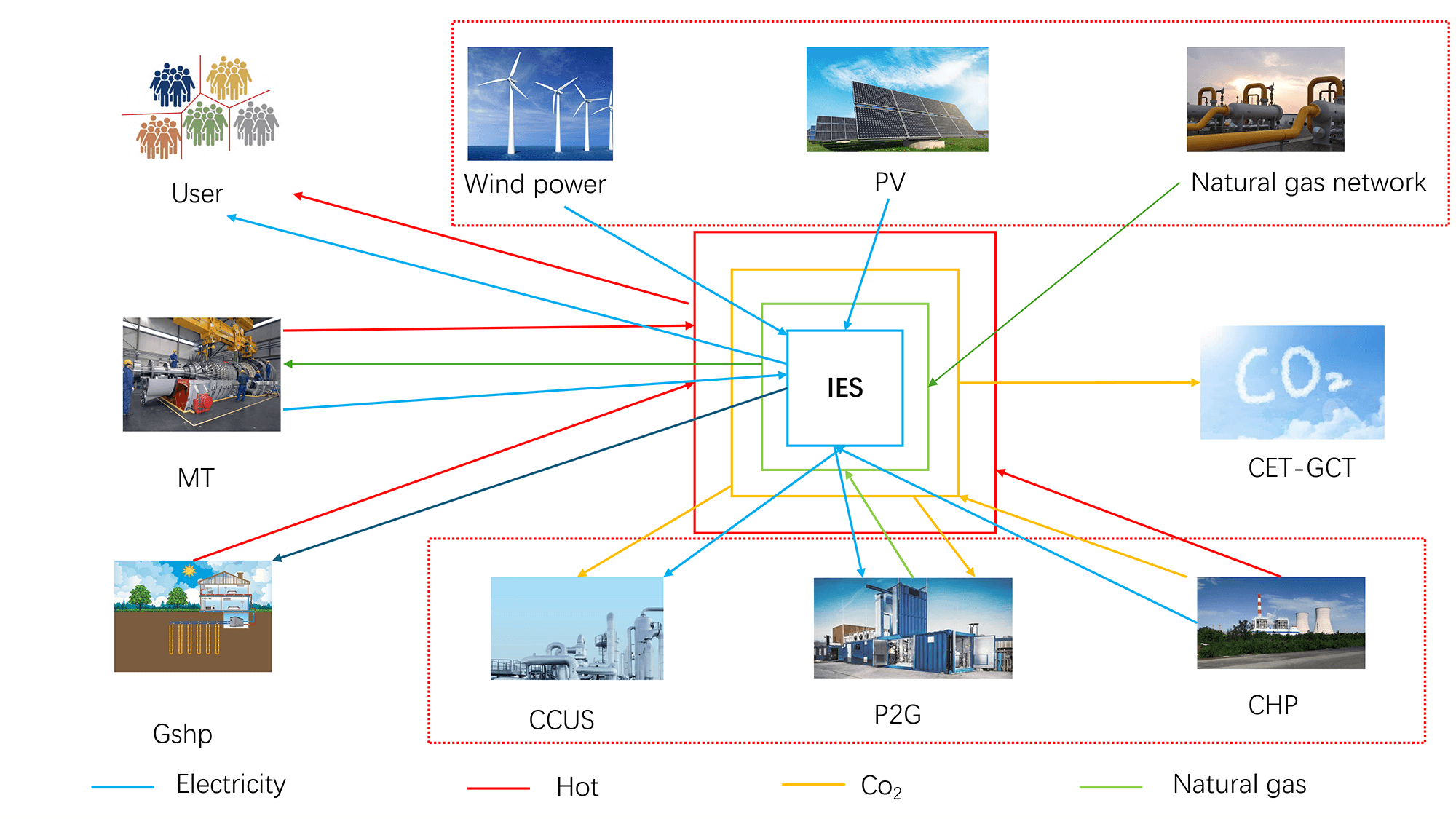
Integrated energy systems (IES) are widely regarded as a key enabler of carbon neutrality, enabling the coordinated use of electricity, heat, and gas to support large-scale renewable integration. Yet their practical deployment still faces major challenges, including rigid thermoelectric coupling, insufficient operational flexibility, and fragmented carbon and certificate market mechanisms. To address these issues, this study proposes a low-carbon economic dispatch model for integrated energy systems (IES) that reduces emissions and costs while improving renewable energy utilization. A coordinated framework integrating carbon capture, utilization, and storage, two-stage power-to-gas, combined heat and power, and ground-source heat pump technologies enhances multi-energy complementarity and overcomes the heat-led constraints of traditional combined heat and power systems. A unified carbon emission trading and green certificate trading mechanism is designed to balance economic and environmental goals through cross-market synergy. To address uncertainty, a distributionally robust chance-constrained model based on Kullback–Leibler divergence is introduced in Scenario 8. The model is solved using the GUROBI solver under multiple scenarios. Simulation results show a cost reduction from $56,166.66 to $25,840.32, carbon emission cuts from 801.38 to 440.90 t, and wind/photovoltaic utilization rates reaching 98%, which fully demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed framework in achieving cost-efficient low-carbon operation of IES.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools