 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Influence of Sulfonated Chitosan on Conductivity of Sulfonated Polyether Ether Ketone (SPEEK) at Room Temperature
1 Faculty of Applied Sciences, Universiti Teknologi MARA, Shah Alam, 40450, Selangor, Malaysia
2 Ionic Materials and Devices (iMADE) Research Laboratory, Institute of Sciences, Universiti Teknologi MARA, Shah Alam, 40450, Selangor, Malaysia
3 Faculty of Applied Sciences, Universiti Teknologi MARA, Sabah Branch, Locked Bag 71, Kota Kinabalu, 88997, Sabah, Malaysia
* Corresponding Authors: Mohd Tajudin Mohd Ali. Email: ; Nazli Ahmad Aini. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Renewable Energy and Storage: Harnessing Hydrocarbon Prediction and Polymetric Materials for Enhanced Efficiency and Sustainability)
Energy Engineering 2026, 123(1), 22 https://doi.org/10.32604/ee.2025.071726
Received 11 August 2025; Accepted 27 October 2025; Issue published 27 December 2025
Abstract
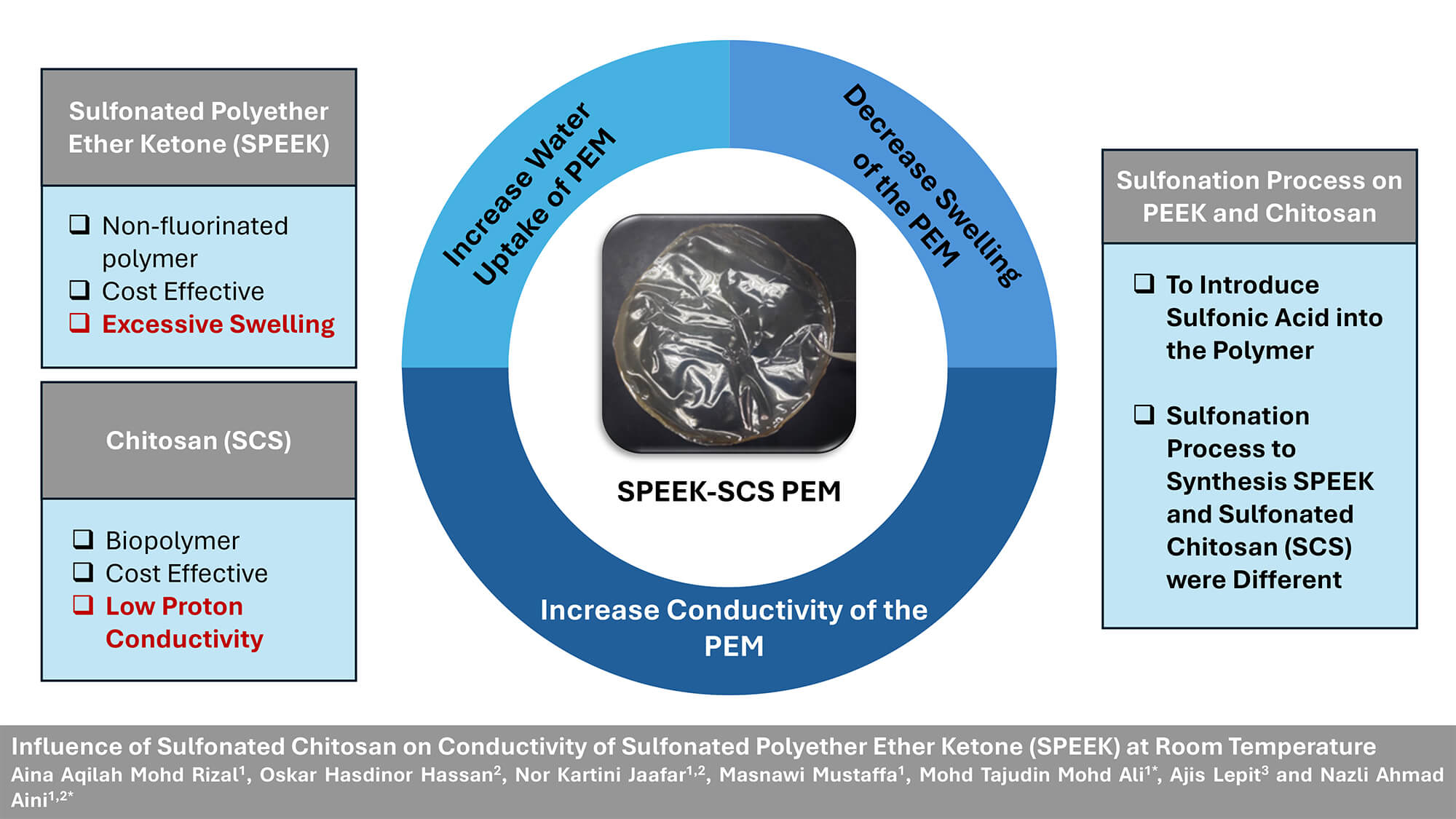
Proton exchange membrane (PEM) is an integral component in fuel cells which enables proton transport for efficient energy conversion. Sulfonated Polyether Ether Ketone (SPEEK) has emerged as a cost-effective option with non-fluorinated aromatic backbones for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC) applications, even though it exhibits lower proton conductivity compared to Nafion. This work aims to study the influence of Sulfonated Chitosan (SCS) concentrations on proton conductivity of SPEEK-based PEM at room temperature. SPEEK was synthesized using a sulfonation process with concentrated sulfuric acid at room temperature. SCS was synthesized via reflux of CS and 1.2 M H2SO4 with a ratio of 1:35 (w/v) at 90°C for 30 min. The composite membranes of SPEEK-SCS were formed with four different SCS concentrations, using the solution casting method, and Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO) was used as a solvent. The composite membranes synthesized include pure SPEEK (S0), SPEEK with 1% SCS (S1), SPEEK with 2% SCS (S2), and SPEEK with 3% SCS (S3). Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), water uptake, degree of swelling, Ionic exchange capacity (IEC) with Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) were used to characterize the composite membranes in terms of composition, crystallinity, water absorption, dimensional changes, number of exchangeable ions in membranes, and proton conductivity, respectively. Notably, S3 had the highest water uptake and the lowest degree of swelling. S2 had the highest proton conductivity among the SPEEK-SCS composite membranes at room temperature withGraphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2026 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2026 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools