 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Exergy Analysis of Organic Rankine Cycles with Zeotropic Working Fluids
Department of Engineering DI, Università della Campania “Luigi Vanvitelli” Aversa (CE), Caserta, 81031, Italy
* Corresponding Author: Biagio Morrone. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Materials and Energy an Updated Image for 2021)
Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2023, 19(3), 593-601. https://doi.org/10.32604/fdmp.2022.022524
Received 14 March 2022; Accepted 28 March 2022; Issue published 29 September 2022
Abstract
Waste heat recovery is one of the possible solutions to improve the efficiency of internal combustion engines. Instead of wasting the exhaust stream of an energy conversion system into the environment, its residual energy content can be usefully recovered, for example in Organic Rankine Cycles (ORC). This technology has been largely consolidated in stationary power plants but not yet for mobile applications, such as road transport, due to the limitations in the layout and to the constraints on the size and weight of the ORC system. An ORC system installed on the exhaust line of a bus powered by a natural gas spark ignition engine has been investigated. The thermal power available at engine exhaust has been evaluated by measuring gas temperature and mass flow rate during real driving operation. The waste thermal power has been considered as heat input for the ORC plant simulation. A detailed heat exchanger model has been developed because it is a crucial component for the ORC performance. The exergy analysis of the ORC was performed comparing different working fluids: R601, R1233zd(E) and two zeotropic blends of the two organic pure fluids. The model allowed the evaluation of the ORC produced energy over the driving cycle and the potential benefit on the engine efficiency.Graphic Abstract
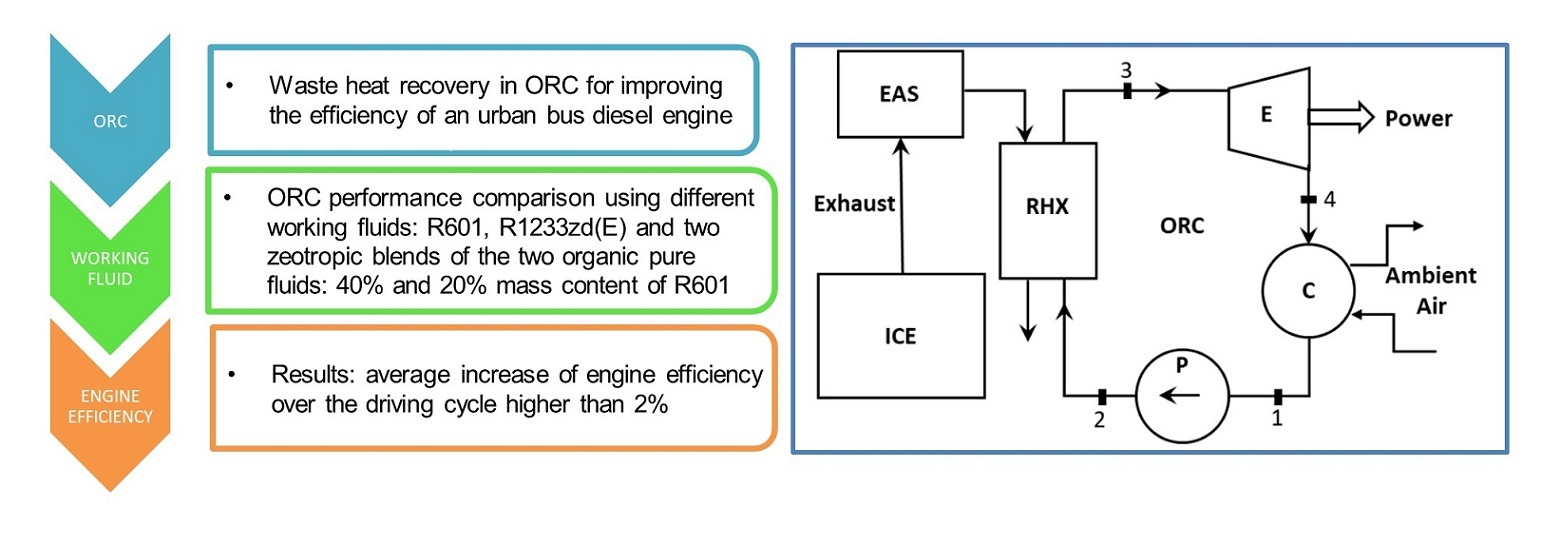
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools