 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Effect of Libration on Fluid Flow and Granular Medium Dynamics in a Rotating Cylindrical Annulus
Laboratory of Vibrational Hydromechanics, Perm State Humanitarian Pedagogical University, Perm, 614990, Russia
* Corresponding Author: Denis Polezhaev. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Non-Equilibrium Processes in Continuous Media)
Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2025, 21(5), 1051-1061. https://doi.org/10.32604/fdmp.2025.062000
Received 08 December 2024; Accepted 22 January 2025; Issue published 30 May 2025
Abstract
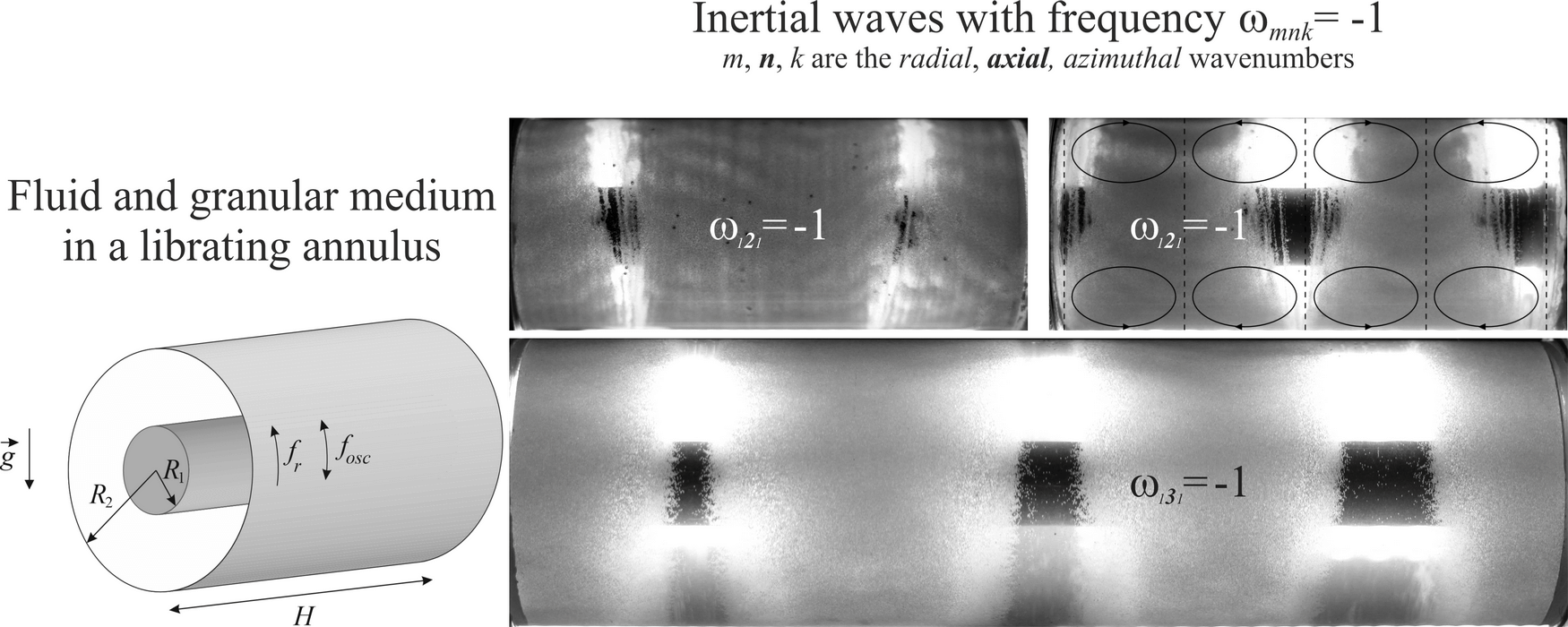
The dynamics of fluid and non-buoyant particles in a librating horizontal annulus is studied experimentally. In the absence of librations, the granular material forms a cylindrical layer near the outer boundary of the annulus and undergoes rigid-body rotation with the fluid and the annulus. It is demonstrated that the librational liquefaction of the granular material results in pattern formation. This self-organization process stems from the excitation of inertial modes induced by the oscillatory motion of liquefied granular material under the influence of the gravitational force. The inertial wave induces vortical fluid flow which entrains particles from rest and forms eroded areas that are equidistant from each other along the axis of rotation. Theoretical analysis and experiments demonstrate that a liquefied layer of granular material oscillates with a radian frequency equal to the angular velocity of the annulus and interacts with the inertial wave it excites. The new phenomenon of libration-induced pattern formation is of practical interest as it can be used to control multiphase flows and mass transfer in rotating containers in a variety of industrial processes.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools