 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Effect of Libration on Fluid Flow and Granular Medium Dynamics in a Rotating Cylindrical Annulus
Laboratory of Vibrational Hydromechanics, Perm State Humanitarian Pedagogical University, Perm, 614990, Russia
* Corresponding Author: Denis Polezhaev. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Non-Equilibrium Processes in Continuous Media)
Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2025, 21(5), 1051-1061. https://doi.org/10.32604/fdmp.2025.062000
Received 08 December 2024; Accepted 22 January 2025; Issue published 30 May 2025
Abstract
The dynamics of fluid and non-buoyant particles in a librating horizontal annulus is studied experimentally. In the absence of librations, the granular material forms a cylindrical layer near the outer boundary of the annulus and undergoes rigid-body rotation with the fluid and the annulus. It is demonstrated that the librational liquefaction of the granular material results in pattern formation. This self-organization process stems from the excitation of inertial modes induced by the oscillatory motion of liquefied granular material under the influence of the gravitational force. The inertial wave induces vortical fluid flow which entrains particles from rest and forms eroded areas that are equidistant from each other along the axis of rotation. Theoretical analysis and experiments demonstrate that a liquefied layer of granular material oscillates with a radian frequency equal to the angular velocity of the annulus and interacts with the inertial wave it excites. The new phenomenon of libration-induced pattern formation is of practical interest as it can be used to control multiphase flows and mass transfer in rotating containers in a variety of industrial processes.Graphic Abstract
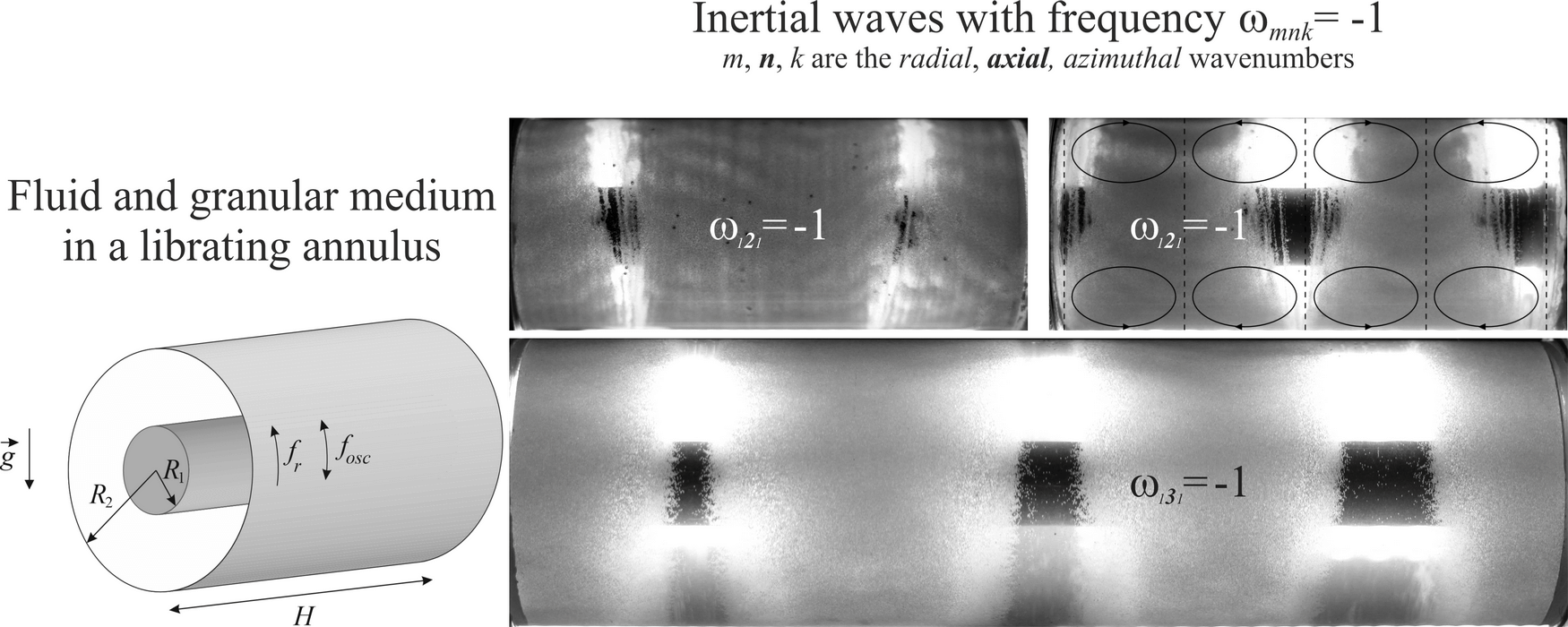
Keywords
Flows in a rotating cylinder have applications across a range of research areas, including the physics of granular matter, hydrodynamics of suspensions and pure liquid coating flows. A detailed examination of the phenomena associated with rotating cylinders has led to a better understanding related subjects, such as avalanches in granules, segregation in suspensions, and steady flow in pure liquids [1]. The diversity of observed effects in such a simple geometry can be attributed to the multitude of factors that influence phase motion, including rotational speed, surface tension, the density ratio of the media, and others.
One of the most intriguing phenomena is an axial segregation of non-neutrally buoyant particles in diluted suspensions (for example, [2]). This leads to the formation of bands of high particle concentration, which are spaced at regular intervals. The phenomenon occurs when the rotation rate of the cylinder is less than the critical rate at which the centrifugal force becomes dominant, resulting in the formation of a uniform layer of particles adjacent to the cylinder surface. The results of numerous experiments conducted with low-viscosity fluids and negatively buoyant particles indicate that the distance between bands of high particle concentration is dependent on both the radius of the cylinder and the size of the particles. At least two theoretical approaches have been proposed to explain the axial segregation of particles.
According to Lee et al. [3], axial segregation is caused by an attractive interaction between the suspended particles. Specifically, axial perturbations in the concentration field lead to faster settling where particles are closer together, which draws more particles toward the high-concentration regions.
In a second approach, the authors consider the collective action of moving particles on fluid dynamics, rather than the interaction between individual particles [4]. In a rotating cylinder, the combined action of gravitational force, buoyancy force, and viscous force causes particles to move in a circular trajectory with the centre of rotation displaced from the cylinder’s axis. The rotation rate of the suspended particle is found to be close to that of the cylinder. The collective effect of the suspended particles can be viewed as a persistently perturbing driving force acting on the fluid. Assuming that both the Rossby number and Ekman number are significantly smaller than one, the action of the driving force results in the excitation of inertial waves in the fluid [5]. The predictions of this theoretical approach are found to be in good agreement with observations under the assumption that inertial waves are excited with a frequency equal to the frequency of gravity-induced motion of the suspended particles [4].
This theoretical approach was applied to containers of varying geometries. For example, Borcia et al. [6] derived an equation to predict the excitation of inertial waves with varying wave numbers in an annulus. Inertial waves occur in a variety of natural systems related to bounded rotating fluids, ranging from the Earth’s interior to atmosphere waves. For this purpose, they are thoroughly examined from both theoretical and experimental perspectives (a review can be found in [7]). In particular, researchers investigate the propagation of inertial waves in rotating and librating containers of various geometries filled with isothermal [8–10] or non-isothermal fluids [11,12]. A further strand of research examines the effect of inertial waves on the stability of Couette flow in geometries that may be spherical [13] or cylindrical [14] in nature.
The objective of this paper is to examine the dynamics of fluid and negatively buoyant particles in a non-uniformly rotating (librating) annulus. We consider a rapidly rotating annulus in which particles of granular material are pressed against the outer wall of the annulus by centrifugal force of inertia. A significant difference between the present study and prior studies is a large amount of granular material which forms a layer of several particle diameters in thickness near the rotating wall.
Librations have an advantage over uniform rotation. The management of both the amplitude and frequency of oscillations allows for the control of both the frequency and amplitude of particle oscillations. This enables the excitation of inertial waves with various frequencies and wavenumbers while the gravity-induced motion of particles in a uniformly rotating container results in the excitation of inertial waves with a single frequency that is equal to the rotation rate.
The experiments are carried out with a liquid and a granular medium in a rotating cylindrical annulus (Fig. 1). Two cavities are used in the experiments. Their dimensions are given in Table 1. Each cavity is a horizontal cylindrical annulus, with a metal cylinder forming the inner boundary and a transparent Plexiglas tube forming the outer boundary.
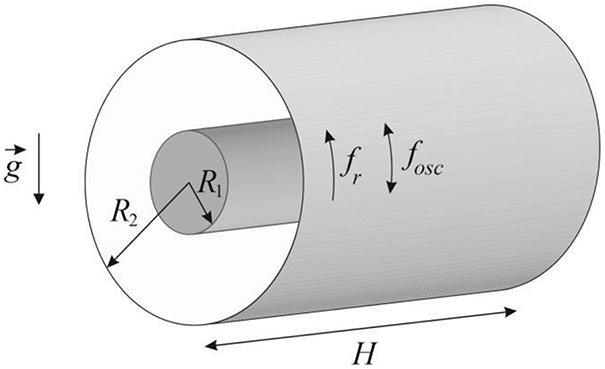
Figure 1: Scheme of the annulus

The experiments are conducted at a room temperature of 20°C, with temperature fluctuations of ±2°C. A typical experiment is conducted over a period of one to two hours, during which temperature fluctuations are negligible. The working fluid is water with a density of ρl = 1.0 g/cm3 and a viscosity of ν = 0.01 cm/s2.
The granular material is composed of glass spheres with a diameter of
The cavity is driven by a stepper motor. The rotation rate of the cavity varies with time according to the law
The granular material is observed through the cylindrical wall of the cavity. For this purpose, a digital camera Canon 600D with a lens EF 50 mm f/1.8 STM is positioned against the rotating cavity. An Light Emitting Diode (LED) is used to illuminate the layer. It is mounted opposite the photo camera, with the rotating cavity between them. The exposure time is selected to be no longer than 1/2000 s in order to achieve optimal image sharpness.
The protocol for the experiments is as follows. The cylindrical annulus is slowly accelerated from rest to seven revolutions per second. At this rotation rate, the granular material forms a layer of uniform thickness near the cylindrical surface. The two-phase system undergoes a rigid-body rotation: the rotation rate of the fluid and the granular material is equal to the rotation rate of the cavity. In the absence of rotation rate modulation, this state is maintained indefinitely. Once an axisymmetric interface is established between the granular layer and the fluid, the selected rotation rate fr is set and azimuthal oscillations with a frequency fosc are initiated. The modulation amplitude ε gradually increases in steps of 0.01–0.05. Each step takes 10–15 min, during which time photos and videos are taken.
When the cylindrical annulus is rotated at a high rate, the fluid and the granular material undergo a rigid-body rotation, with a uniform distribution of granules near the outer boundary of the annulus (Fig. 2a). When modulation is applied, the initially axisymmetric interface becomes unstable. It is demonstrated that as the amplitude of azimuthal oscillations increases, the banding pattern appears at the surface of the granular layer (Fig. 2b). The alternating light and dark stripes, with a width of a few millimeters, show changes in the thickness of the granular layer. A further increase in the oscillation amplitude results in the appearance of wavy patterns elongated along the rotation axis superimposed on a background of banding patterns (Fig. 2c). These patterns are regular in the azimuthal direction but not parallel. This may indicate azimuthal time-averaged flows with inhomogeneous velocity along the rotation axis.
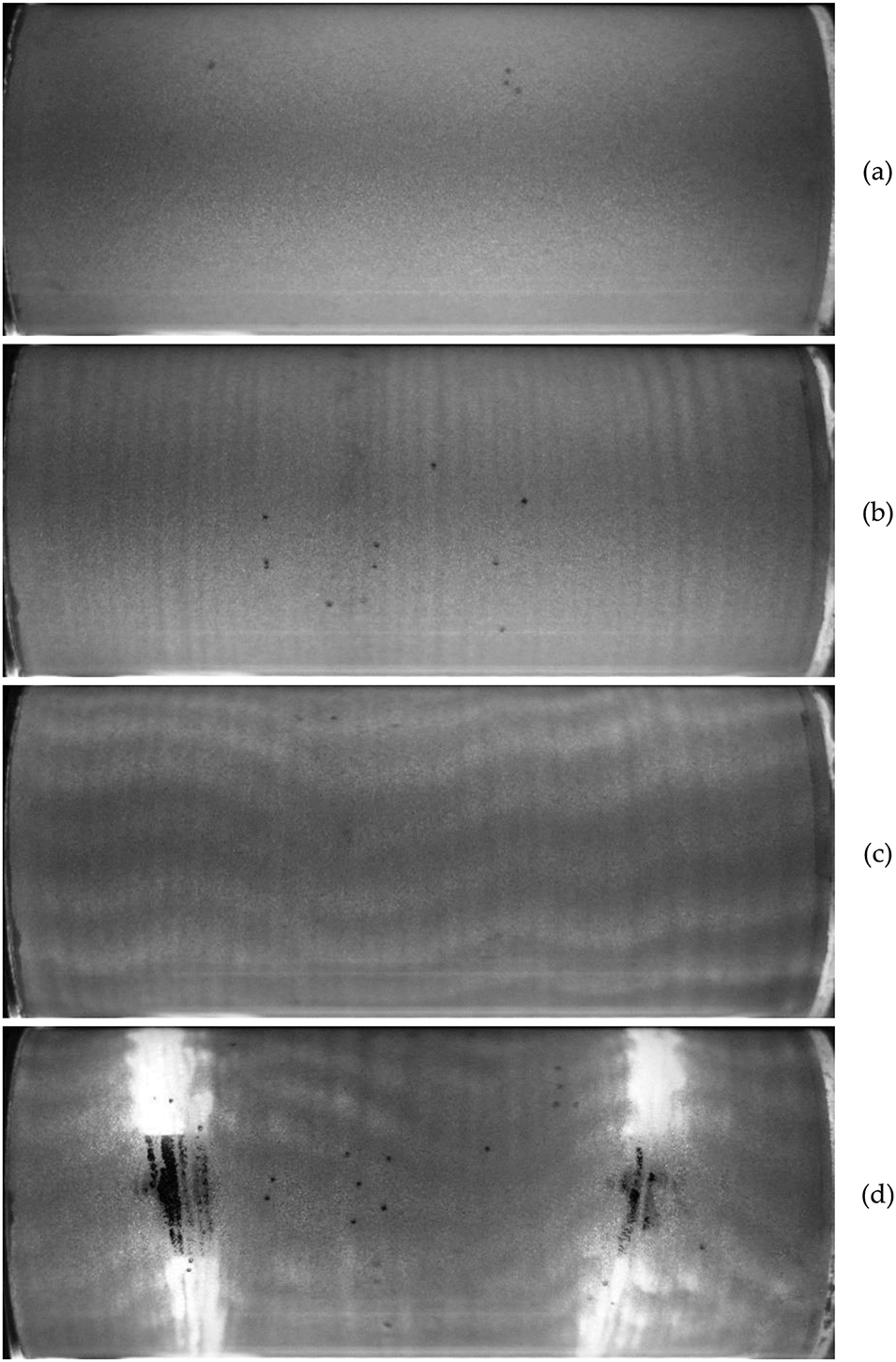
Figure 2: Photos of granular medium and liquid obtained at rotation rate fr = 5 rps and oscillation frequency fosc = 1 Hz in the cavity #1 (a–d): ε = 0, 0.17, 0.24, and 0.32. The black horizontal band in photo (d) is the inner boundary of the cylindrical annulus which is formed by a black-painted metal tube
As the amplitude of oscillation is further increased, the formation of azimuthal bands with a zero concentration of granular material is observed (Fig. 2d). These areas are hereafter referred to as eroded areas. Two eroded areas are located symmetrically relative to the centre of the rotating annulus. The distance between these areas is approximately twice the distance between the eroded areas and the end walls of the cavity. So, the spatial period (axial distance between neighboring eroded areas) is half the length of the annulus. Fig. 2d indicates that the eroded areas are about 1–2 cm wide and their edges are sloped in relation to the direction of the oscillatory motion of the fluid. The origin of the unique geometry of the eroded areas is yet to be determined.
Thus, in the experiments with a fixed rotation rate and oscillation frequency, and an increasing oscillation amplitude, three distinct patterns are observed: band patterns, azimuthally periodic distribution of granular material, and eroded areas. The present paper is devoted to an examination of eroded areas. Two other phenomena of scientific interest will be discussed in detail in subsequent papers.
Pattern formation in the layer of granular material in response to an increasing modulation amplitude has been observed at varying rotation rates and oscillation frequencies in cavities of different lengths. The development of patterns follows a process that is analogous to the aforementioned scenario. As illustrated in Figs. 2d and 3a, the location of eroded areas can vary in different experiments. In some instances, these areas are located in the middle of the cavity, while in others they are located near the end walls. It is noteworthy that in both instances, the length of the pattern formation remains unaltered, with the pattern extending to a length equal to half that of cavity #1. The different arrangement of the eroded areas (Figs. 2d and 3a) in cavity #1 clearly indicates that both the eroded areas and the granular material bands can be located in pressure antinodes. Thus, the wavelength of the patterns is twice the distance between adjacent pressure antinodes. Fig. 3b shows that there are three eroded areas in the cavity #2 instead of two as in the cavity #1. It is noteworthy that the ratio of the radii of the cylindrical boundaries in both cavities is approximately equal, and that the relative length of cavity #2 is approximately one and a half times the length of cavity #1. This demonstrates that the pattern formation observed in the two cavities is of a similar nature.
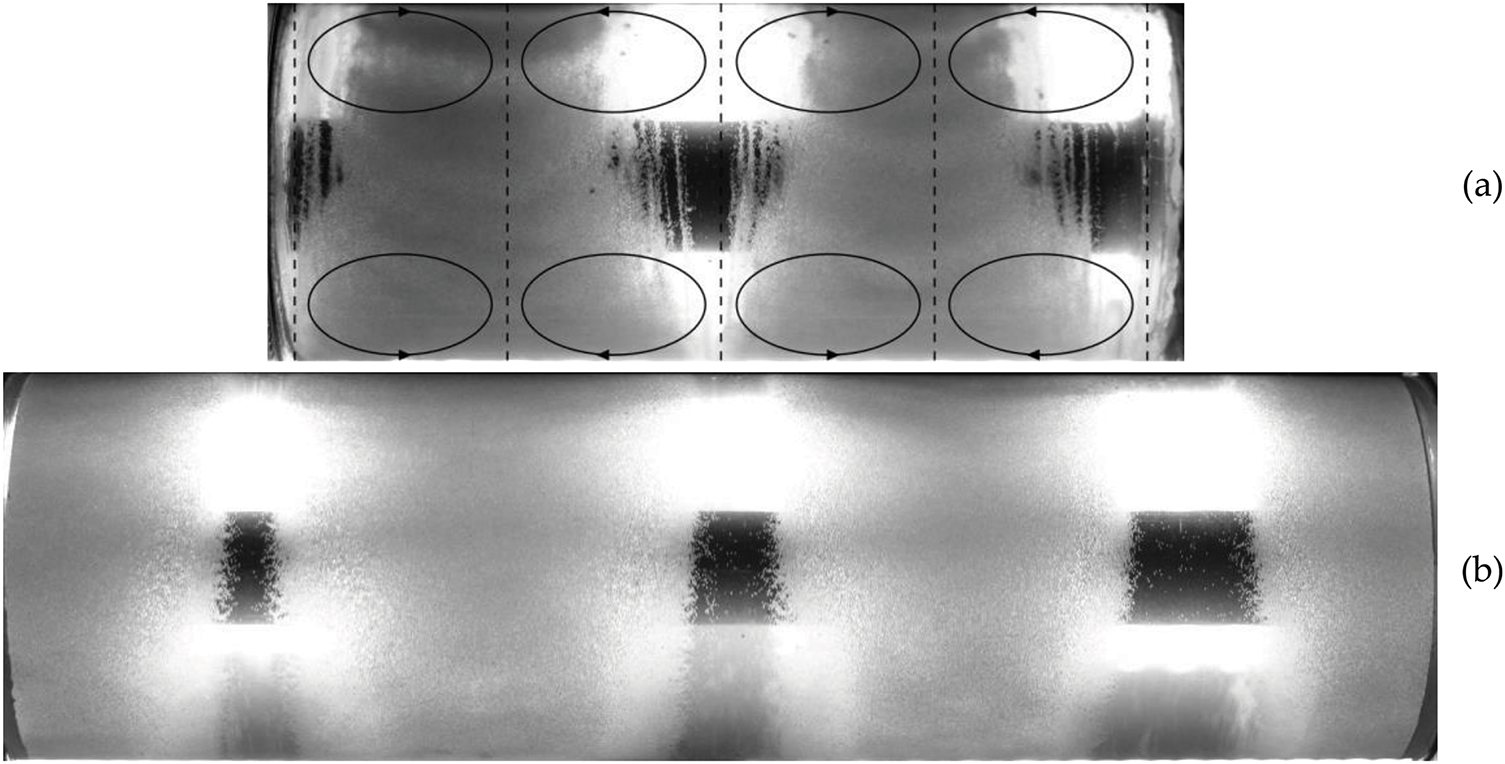
Figure 3: Photos of granular medium and liquid obtained (a) in the short cavity #1 (fr = 4 rps, fosc = 1 Hz, ε = 0.36) and (b) in the long cavity #2 (fr = 4 rps, fosc = 1.82 Hz, ε = 0.45). The dashed lines indicate the location of pressure antinodes. The vertical pairs of ellipses illustrate the cross-section of the vortices (arrows show the direction of steady rotation)
Here we consider the action of gravity on a two-phase system in a rapidly rotating annulus. The centrifugal force of inertia induces the distribution of the granular material in the form of a thin axisymmetric layer near the outer cylindrical wall of the cavity. The gravitational force rotates in the reference frame of the cavity with a velocity equal to the rotation rate, acting as a periodic external force. When the cavity rotates rapidly, the gravitational force is negligible in comparison to the centrifugal force of inertia. Consequently, the granular material is stationary in the rotating frame of reference in the absence of azimuthal oscillations. Once a critical level of azimuthal oscillations is reached, the granular medium undergoes liquefaction resulting in the formation of a quasi-liquid layer of high density and viscosity. The fluid and the liquefied granular material respond to the alternating action of gravitational force and tangential force caused by librations. It is known that oscillations with a frequency equal to the rotation rate or libration frequency can give rise to inertial waves in a rotating fluid. Let us now consider these waves.
Currently, research interest in inertial waves and inertial oscillations is largely driven by the need to understand the dynamics of liquid cores in rotating planets [15]. Experimental studies [16,17] of various wave modes in a rotating cylinder under vibrations confirmed the theoretical predictions concerning the dynamics of inertial modes in the limit of small Ekman and Rossby numbers.
Now we turn our attention to the problem of determining the natural frequencies of inertial oscillations of a fluid (inertial modes) in a rotating horizontal annulus of given aspect ratios
Here, the unit of distance measurement is the cavity length H. If the radial coordinate is expressed in the form
where
at
In the case under consideration, the wave is excited by the force of gravity, with a velocity equal to the rotation rate of the cavity. A wave with the frequency
Given that
If we take into account the thickness
It should be noted that the nodes of the axial velocity and the antinodes of the radial and azimuthal velocities, as well as the pressure antinodes, are located on the end walls of the cavity. Thus, the fluid flow within an inertial wave has the form of annular vortices located between pressure antinodes. The rotation of neighboring vortices occurs in opposite directions, with the velocity of rotation varying in accordance with a sinusoidal law along the azimuthal coordinate. The rotation of neighboring vortices is opposite, with the velocity of rotation varying in accordance with a sinusoidal law along the azimuth.
The analysis of the results indicates that the inertial wave (mode) may be responsible for the development of a series of eroded areas at the surface of the granular medium. The formation of each eroded area is attributed to the interaction of two neighboring vortices, which results in a wavelength twice the distance between the pressure antinodes. Although neighboring vortices rotate in a coordinated manner, the direction of their rotation can vary and is determined by random factors. This clearly demonstrates that the location of eroded areas in different experiments may differ while the essential feature remains unchanged: They are located in the pressure antinodes. What is the driving force for the excitation of the inertial wave and the axial segregation of granular material?
At a rotation rate of fr = 5 rps, the granular medium and the fluid undergo a rigid-body rotation resulting in the formation of a cylindrical interface between them. This is due to the fact that the effect of gravity is relatively insignificant in comparison to the centrifugal force, that is to say,
Let us check that the band formation occurs only after the granules become mobile. We can calculate the critical value of the Shields number
In the discussed experiment, band patterns are clearly visible at fr = 5 rps, fosc = 1 Hz, and
Now we can determine the experimental value of the Shields number. We will use the data obtained from the study of the pattern formation at the interface between fluid and the granular medium in a short cylinder under librations [19]:
Here,
We will now proceed to discuss the formation of eroded areas. They could appear if inertial toroidal vortices perform a steady rotation against the background of inertial oscillations. Steady flow is analogous to a Taylor-Couette vortical flow between independently rotating cylinders. What is the nature of the vortical flow?
One potential explanation for this phenomenon is that the granular medium is liquefied under the action of libration and gravity. Then, the degree of liquefaction, and thus the physical properties of the liquefied material (density, viscosity, and granular layer thickness), oscillate with a frequency equal to the rotation rate. This frequency coincides with the frequency
The solution of Eq. (1) for cavity #2 indicates that the mode with wavenumbers n = 6 and k = 1 is excited at a frequency
The effect of librations on the excitation of inertial modes remains unclear. Does the effect of librations solely result in the liquefaction of the granular material?
As mentioned above, librations can excite axisymmetric inertial modes with azimuthal wavenumber k = 0 in a rotating cylinder [16]. The solution of Eq. (1) indicates that there are no inertial modes with k = 0 within the investigated region of low libration frequencies (Fig. 4). Here, the solid line shows the results of calculating the axial wavenumber n at k = 0 and m = 1 using Eqs. (1)–(3) for cavity #1. The symbols illustrate data obtained in the experiments presented in Fig. 2d (circle) and Fig. 3a (square). This finding confirms that the phenomenon of eroded areas is caused by the interaction between liquefied granular material and the inertial wave with azimuthal wavenumber k = 1, which is excited by gravitational force. In this context, it is relevant to cite the work [4], which describes the excitation of the mode with azimuthal wavenumber k = 1 in a rotating horizontal cylinder filled with fluid and non-neutrally buoyant particles. The particles do not undergo rotation together with the cavity but rather descend from the rising cylindrical wall, thereby introducing perturbations with k = 1 and

Figure 4: Dependence of axial wavenumber on dimensionless frequency. The results of the calculations (solid line) and experiments (symbols) correspond to cavity #1
The dynamics of fluid and non-buoyant particles in a librating horizontal annulus is studied experimentally. It is found that at high rotation rates when the layer of granular material is axisymmetric, modulation of the rotation rate leads to the formation of eroded areas. Theoretical analysis indicates that the pattern formation occurs as a result of the excitation of inertial waves. The excitation of inertial waves is made possible by the liquefaction of the granular material. An inertial standing wave is generated by oscillatory motion of a liquefied granular material which is induced by the rotation of the gravitational force relative to the cavity frame of reference. In the rotating frame of reference, the inertial wave rotates with the angular velocity of the annulus rotation in a direction opposite to that of the annulus rotation. Thus, the wave is stationary in the laboratory frame of reference. It is demonstrated that the distance between the eroded areas is governed by the axial wavenumber of the inertial mode for a given size of an annulus. The experimental results are in accordance with the findings of the theoretical analysis performed under the approximation of low fluid viscosity and rapid rotation (in the limit of small values of Ekman and Rossby numbers).
Acknowledgement: The authors are grateful for the technical assistance of Alexander Selyanin.
Funding Statement: This research is funded by the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation within the framework of a state assignment, number 1023032300071-6-2.3.1.
Author Contributions: Study conception and design: Victor Kozlov; Data collection: Denis Polezhaev and Alexey Vjatkin; Analysis and interpretation of results: Victor Kozlov and Denis Polezhaev; draft manuscript preparation: Victor Kozlov and Denis Polezhaev. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Availability of Data and Materials: The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Ethics Approval: Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest to report regarding the present study.
Nomenclature
| d | Particle diameter, cm |
| f | Annulus rotation rate, rps |
| fr | Mean rotation rate of the annulus, rps |
| fosc | Oscillation frequency, Hz |
| fw | Frequency of wave oscillations, Hz |
| h | Granular layer thickness, cm |
| H | Annulus length, cm |
| k | Azimuthal wavenumber |
| L | Relative length of the annulus (ratio of H and R1) |
| m | Radial wavenumber |
| n | Axial wavenumber |
| R1 | Annulus inner radius, cm |
| R2 | Annulus outer radius, cm |
| Rs | Radius of the interface between the granular bed and the fluid, cm |
| R | Ratio of R1 and R2 |
| Re | Reynolds number |
| q | Relative volume of granular material |
| uosc | Velocity amplitude of the fluid oscillatory motion, cm/s |
| Va | Annulus volume |
| Vs | Granular material volume |
| Γ | Ratio of gravitational acceleration and centrifugal acceleration |
| ε | Libration amplitude |
| δ | Thickness of the Stokes boundary layer, cm |
| ν | Fluid kinematic viscosity, cm2/s |
| ρl | Fluid density, g/cm3 |
| ρs | Particle density, g/cm3 |
| τ | Shields number |
| τc | Critical value of the Shields number |
| φ0 | Angular amplitude of the fluid oscillations, rad |
| ω | Dimensionless frequency |
References
1. Seiden G, Thomas PJ. Complexity, segregation, and pattern formation in rotating-drum flows. Rev Mod Phys. 2011;83(4):1323–65. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.83.1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
2. Breu APJ, Kruelle CA, Rehberg I. Pattern formation in a rotating aqueous suspension. Europhys Lett. 2003;62(4):491–7. doi:10.1209/epl/i2003-00379-x. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
3. Lee J, Ladd AJC. Particle dynamics and pattern formation in a rotating suspension. J Fluid Mech. 2007;577:183–209. doi:10.1017/S002211200700465X. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
4. Seiden G, Ungarish M, Lipson SG. Banding of suspended particles in a rotating fluid-filled horizontal cylinder. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2005;72(2 Pt 1):021407. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.72.021407. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
5. Greenspan HP. Theory of rotating fluids. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1969. [Google Scholar]
6. Borcia ID, Harlander U. Inertial waves in a rotating annulus with inclined inner cylinder: comparing the spectrum of wave attractor frequency bands and the eigenspectrum in the limit of zero inclination. Theor Comput Fluid Dyn. 2013;27(3):397–413. doi:10.1007/s00162-012-0278-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
7. Sibgatullin IN, Ermanyuk EV. Internal and inertial wave attractors: a review. J Appl Mech Tech Phy. 2019;60(2):284–302. doi:10.1134/S002189441902010X. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
8. Lin Y, Noir J. Libration-driven inertial waves and mean zonal flows in spherical shells. Geophys Astrophys Fluid Dyn. 2021;115(3):258–79. doi:10.1080/03091929.2020.1761350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
9. Wu K, Welfert BD, Lopez JM. Reflections and focusing of inertial waves in a tilted librating cube. J Fluid Mech. 2022;947:A10. doi:10.1017/jfm.2022.639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
10. Shiryaeva M, Subbotina M, Subbotin S. Linear and non-linear dynamics of inertial waves in a rotating cylinder with antiparallel inclined ends. Fluid Dyn Mater Process. 2024;20(4):787–802. doi:10.32604/fdmp.2024.048165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
11. Rysin K. Libration-generated average convection in a rotating flat layer with horizontal axis. Fluid Dyn Mater Process. 2024;20(10):2235–49. doi:10.32604/fdmp.2024.052324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
12. Vjatkin A, Petukhov S, Kozlov V. Experimental study of thermal convection and heat transfer in rotating horizontal annulus. Fluid Dyn Mater Process. 2024;20(11):2475–88. doi:10.32604/fdmp.2024.052377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
13. Barik A, Triana SA, Hoff M, Wicht J. Transition to turbulence in the wide-gap spherical Couette system. J Fluid Mech. 2024;1001(401):A1. doi:10.1017/jfm.2024.650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
14. Riahi M, Hayani Choujaa M, Aniss S. Instabilities and inertial waves generated in a Rayleigh stable Taylor-Couette flow by slowly oscillating the outer cylinder: Floquet analysis and two quasi-steady approaches. Phys Lett A. 2024;513(5):129604. doi:10.1016/j.physleta.2024.129604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
15. Le Bars M, Barik A, Burmann F, Lathrop DP, Noir J, Schaeffer N, et al. Fluid dynamics experiments for planetary interiors. Surv Geophys. 2022;43(1):229–61. doi:10.1007/s10712-021-09681-1. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
16. Stanislav S. Steady circulation induced by inertial modes in a librating cylinder. Phys Rev Fluids. 2020;5(1):014804. doi:10.1103/PhysRevFluids.5.014804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
17. Subbotin S, Shiryaeva M, Shmakova N, Ermanyuk E. Zonal flow instability induced by nonlinear inertial waves in a librating cylinder with sloping ends. Phys Fluids. 2024;36(12):124121. doi:10.1063/5.0239827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
18. Yang Y, Gao S, Wang YP, Jia J, Xiong J, Zhou L. Revisiting the problem of sediment motion threshold. Cont Shelf Res. 2019;187(7):103960. doi:10.1016/j.csr.2019.103960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
19. Dyakova V, Kozlov V, Polezhaev D. Oscillation-induced sand dunes in a liquid-filled rotating cylinder. Phys Rev E. 2016;94(6–1):063109. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.94.063109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
20. Gershuni GZ, Lyubimov AV. Thermal vibrational convection. New York, NY, USA: Wiley; 1998. [Google Scholar]
21. Seiden G, Ungarish M, Lipson SG. Formation and stability of band patterns in a rotating suspension-filled cylinder. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2007;76(2 Pt 2):026221. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.76.026221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools