 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Boiling Dynamics and Entropy Generation in Inclined Tubular Systems: Analysis and Optimization
1 National Joint Engineering Research Center of Energy Saving and Environmental Protection Technology in Metallurgy and Chemical Engineering Industry, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, 650093, China
2 Engineering Research Center of Metallurgical Energy Conservation and Emission Reduction, Ministry of Education, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, 650093, China
3 Faulty of Metallurgical and Energy Engineering, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, 650093, China
* Corresponding Author: Jianxin Xu. Email:
Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2025, 21(7), 1571-1600. https://doi.org/10.32604/fdmp.2025.063741
Received 22 January 2025; Accepted 29 April 2025; Issue published 31 July 2025
Abstract
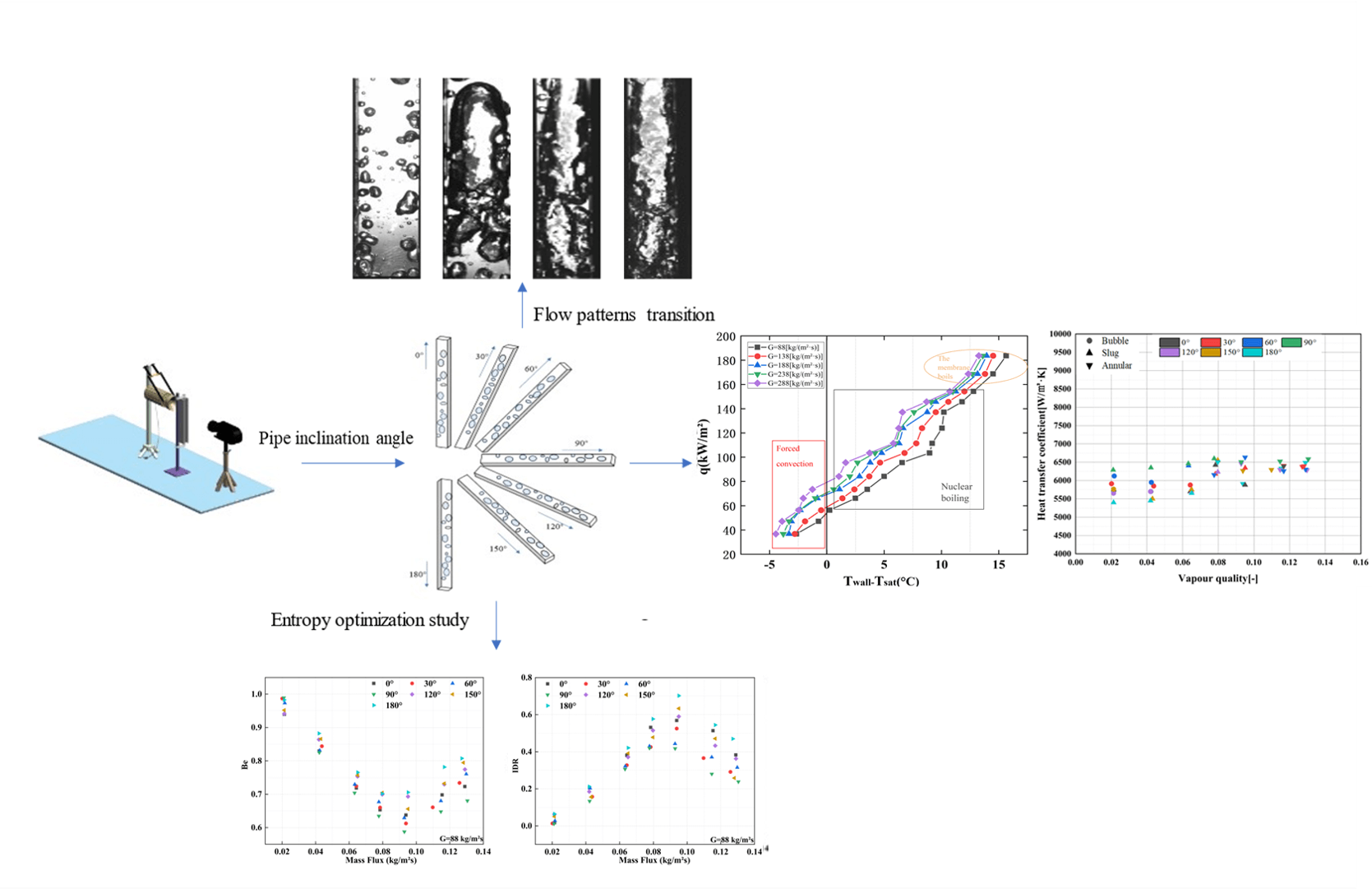
This research explores the characteristics of boiling in inclined pipes, a domain of great importance in engineering. Employing an experimental visualization technique, the boiling dynamics of deionized water are examined at varying inclination angles, paying special attention to the emerging flow patterns. The findings demonstrate that the inclination angle significantly impacts flow pattern transitions within the 0° to 90° range. As the heat flux rises, bubbles form in the liquid. The liquid’s inertia extends the bubble-wall contact time, thereby delaying the onset of bulk bubble flow. Beyond a 90° inclination, however, the patterning behavior is more influenced by the fluid velocity. At low speeds, incomplete pipe filling results in a large liquid plug hindering flow, while high speeds lead to full pipe filling. In general, gravity, inertia, buoyancy forces, and capillary forces are the main influential factors in the considered problem. However, an analysis of the heat transfer coefficient and boiling curve for different inclination angles reveals that the observed variations are essentially due to corresponding changes in the flow pattern. Finally, an optimal mass flux and inclination angle, able to minimize total entropy generation and improve heat transfer efficiency, are determined by means of an entropy generation analysis.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools