 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Bio-Based Trivalent Phytate: A Novel Strategy for Enhancing Fire Performance of Rigid Polyurethane Foam Composites
1 School of Architecture and Civil Engineering, Anhui University of Technology, Ma’anshan, 243002, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Fire Science, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026, China
3 School of Mechanical Engineering, Anhui University of Technology, Ma’anshan, 243002, China
4 University of Belgrade, Belgrade, 11120, Serbia
* Corresponding Authors: Gang Tang. Email: ; Xiangrong Xu. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Bio-based Halogen-free Flame Retardant Polymeric Materials)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2022, 10(5), 1201-1220. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2022.018047
Received 25 June 2021; Accepted 21 August 2021; Issue published 22 December 2021
Abstract
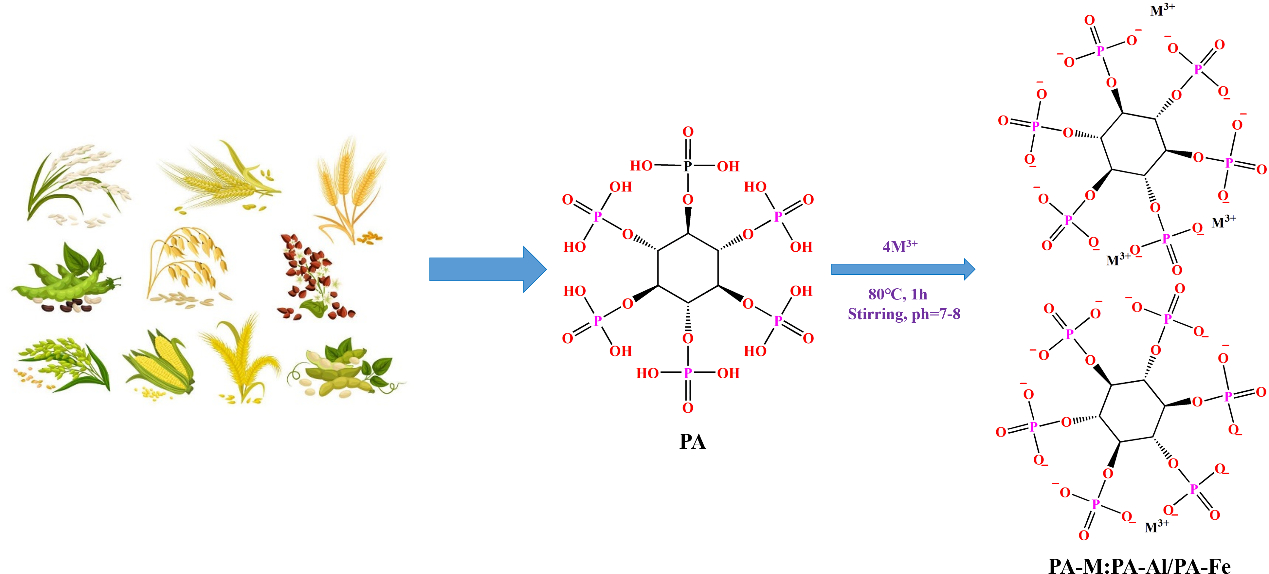
Biomass phytic acid has potential flame retardant value as the main form of phosphorus in plant seeds. In this study, phytate-based flame retardants aluminum phytate (PA-Al) and iron phytate (PA-Fe) were synthesized and characterized. Subsequently, they were introduced into rigid polyurethane foam (RPUF) as flame retardants by one-step water-blown method. The results indicated that RPUF/PA-Fe30 exhibited the highest char residue of 22.1 wt%, significantly higher than 12.4 wt% of RPUF. Cone calorimetry analysis showed that the total heat release (THR) of RPUF/PA-Al30 decreased by 17.0% and total smoke release (TSR) decreased by 22.0% compared with pure RPUF, which were the lowest, demonstrating a low fire risk and good smoke suppression. Thermogravimetric analysis-Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (TG-FTIR) implied the release intensity of flammable gases (hydrocarbons, esters) and toxic gases (isocyanate, CO, aromatic compounds, HCN) of composites was significantly reduced after the addition of PA-Fe. The analysis of char residue indicated that the RPUF composites formed a dense char layer with a high degree of graphitization after the addition of PA-Al/PA-Fe, endowing RPUF composites with excellent mass & heat transmission inhibition effect and fire resistance in the combustion process.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools