 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
N-Doped rGO-Like Carbon Prepared from Coconut Shell: Structure and Specific Capacitance
1
Department of Physics, Faculty of Science and Data Analytics, Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember, Surabaya, 60111, Indonesia
2
Department of Electrical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University of Muhammadiyah Malang, Malang, 65144, Indonesia
3
Geopolymer & Green Technology Centre of Excellence, Universiti Malaysia Perlis, Arau, Perlis, 02600, Malaysia
4
Applied Electromagnetic Laboratory 1, Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Selangor, 43400,
Malaysia
5
Synchrotron Light Research Institute (SLRI), Nakhon Ratchasima, 3000, Thailand
* Corresponding Authors: Imam Khambali. Email: ; Darminto. Email:
Journal of Renewable Materials 2023, 11(4), 1823-1833. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2023.025026
Received 18 June 2022; Accepted 25 August 2022; Issue published 01 December 2022
Abstract
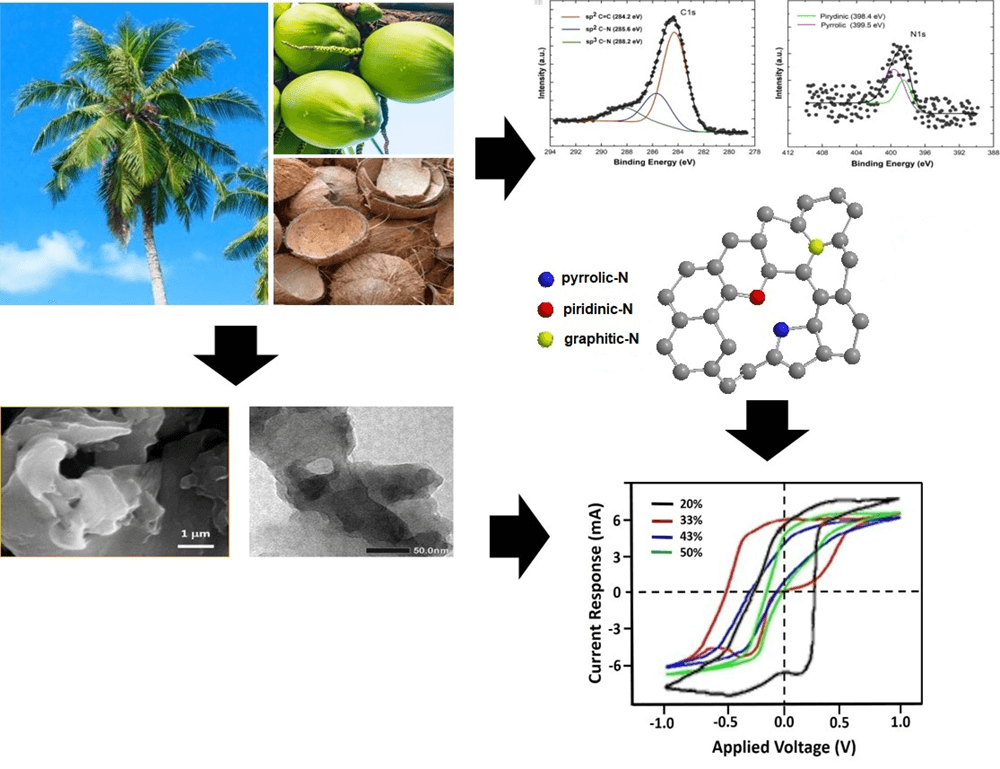
An rGO−like carbon compound has been synthesized from biomass, i.e., old coconut shell, by a carbonization process followed by heating at 400°C for 5 h. The nitrogen doping was achieved by adding the urea (CH4N2O) and stirring at 70°C for 14 h. The morphology and structure of the rGO-like carbon were investigated by electron microscopies and Raman spectroscopy. The presence of C-N functional groups was analyzed by Fourier transform infrared and synchrotron X-ray photoemission spectroscopy, while the particle and the specific capacitance were measured by particle sizer and cyclic voltammetry. The highest specific capacitance of 72.78 F/g is achieved by the sample with 20% urea, having the smallest particles size and the largest surface area. The corresponding sample has shown to be constituted by the appropriate amount of C–N pyrrolic and pyridinic defects.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools