 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Investigation of the Thermal Decomposition Behavior of Oleuropein with Many Pharmacological Activities from Olive by Thermogravimetry
1 School of Business and Trade, Dongguan Polytechnic, Dongguan, 523808, China
2 School of Chemical Engineering and Energy Technology, Dongguan University of Technology, Dongguan, 523808, China
* Corresponding Author: Junling Tu. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Renewable Biomass as a Platform for Preparing Green Chemistry)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2023, 11(8), 3371-3385. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2023.028046
Received 28 November 2022; Accepted 30 January 2023; Issue published 26 June 2023
Abstract
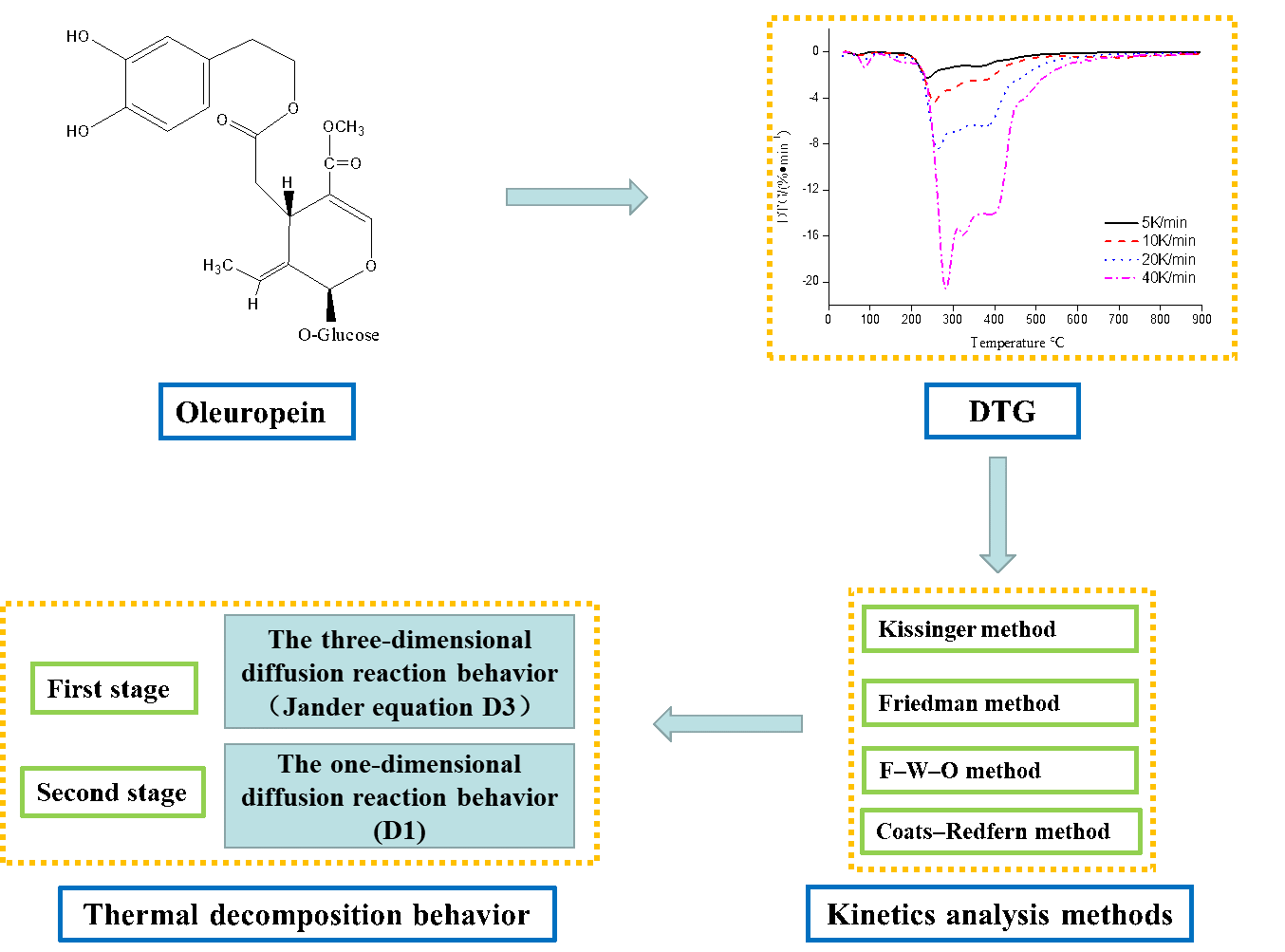
Due to the existence of poly-hydroxyl structures, the temperature may have an effect on the thermal stability of oleuropein for its applications. In the current study, the thermal decomposition process and kinetics behavior of oleuropein from the olive resource were researched by thermogravimetric theoretical analysis methods and non-isothermal kinetics simulation. The results of thermogravimetry analysis showed the whole thermal decomposition process of oleuropein involved two stages, with 21.22% of residue. It was also revealed that high heating rates of more than 20 K min−1 led to significant thermal hysteresis and inhibited the whole thermal decomposition behavior of oleuropein. Moreover, an investigation of the thermal decomposition kinetics indicated that the non-isothermal decomposition behavior followed a D3 model during the first stage (three-dimensional diffusion, Jander equation) and a D1 model in the second stage (one-dimensional diffusion). For the first and second thermal decomposition stages, the Kissinger, Friedman, Flynn-Wall-Ozawa, and Coats–Redfern four methods were applied to determine the activation energy (E = 143.72 and 247.01 kJ mol−1) and Arrhenius preexponential factor (ln A = 26.34 and 42.45 min−1), respectively. Therefore, the study will provide good theoretical guidance for thermal stability and thermal transformation application of oleuropein. It will be suitable for low-temperature applications in the cosmetic, food supplement and pharmaceutical industries.
Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools