 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
A Review: Functionalized Renewable Natural Fibers as Substrates for Photo-Driven Desalination, Photocatalysis, and Photothermal Biomedical Applications in Sustainable Photothermal Materials
1 Jiangsu Province Key Laboratory of Fine Petrochemical Engineering, Changzhou University, Changzhou, 213164, China
2 School of Materials Science and Engineering, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Nanjing, 210023, China
3 Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Catalytic Materials and Technology, School of Petrochemical Engineering, Changzhou University, Changzhou, 213164, China
* Corresponding Authors: Man Zhou. Email: ; Zhongyu Li. Email:
Journal of Renewable Materials 2025, 13(10), 1993-2041. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0065
Received 18 March 2025; Accepted 25 June 2025; Issue published 22 October 2025
Abstract
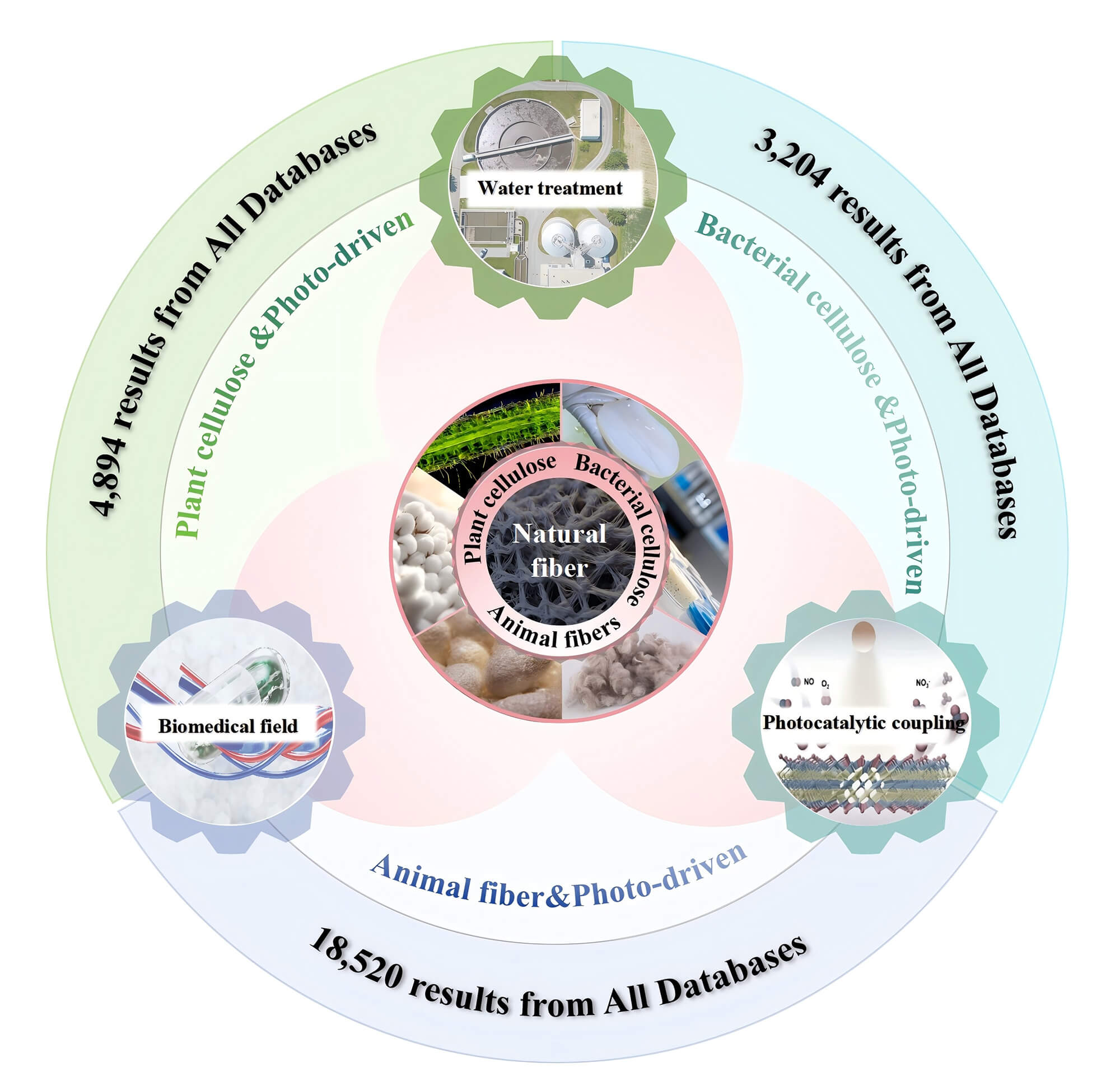
Natural fibers, as a typical renewable and biodegradable material, have shown great potential for many applications (e.g., catalysis, hydrogel, biomedicine) in recent years. Recently, the growing importance of natural fibers in these photo-driven applications is reflected by the increasing number of publications. The utilization of renewable materials in photo-driven applications not only contributes to mitigating the energy crisis but also facilitates the transition of society toward a low-carbon economy, thus enabling harmonious coexistence between humans and the environment within the context of sustainable development. This paper provides an overview of the recent advances of natural fibers which acted as substrates or precursors to construct an efficient system of light utilization. The different chemical properties and pretreatment methods of cellulose affect its performance in final photo-driven applications, including solar-driven water purification, photocatalysis, and photothermal biomedical applications. Nevertheless, current research rarely conducts a comprehensive comparison of them from a broad perspective. As a whole, this review first reveals the different structural advantages as well as the matching degree between natural fibers (bacterial cellulose, plant cellulose, and animal fiber) and three typical photo-driven applications. Besides, new strategies for optimizing the utilization of natural fibers are an important subject under the background of low-carbon and circular economy. Finally, some suggestions and prospects are put forward for the limitations and research prospects of natural fibers in photo-driven applications, which provides a new idea for the synthesis of renewable functional materials.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools