 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Research on the Hydrophobic Performance of Bamboo Surface Treated via Coordinated Plasma and PDMS Solution Treatments
1 College of Furnishings and Industrial Design, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, 210037, China
2 Bamboo Research Institute of Zhejiang Academy of Forestry, Hangzhou, 310023, China
* Corresponding Author: Hongyan Wang. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Modification and Functionalization of Wood)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2025, 13(5), 931-955. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2025.02024-0040
Received 17 November 2024; Accepted 17 February 2025; Issue published 20 May 2025
Abstract
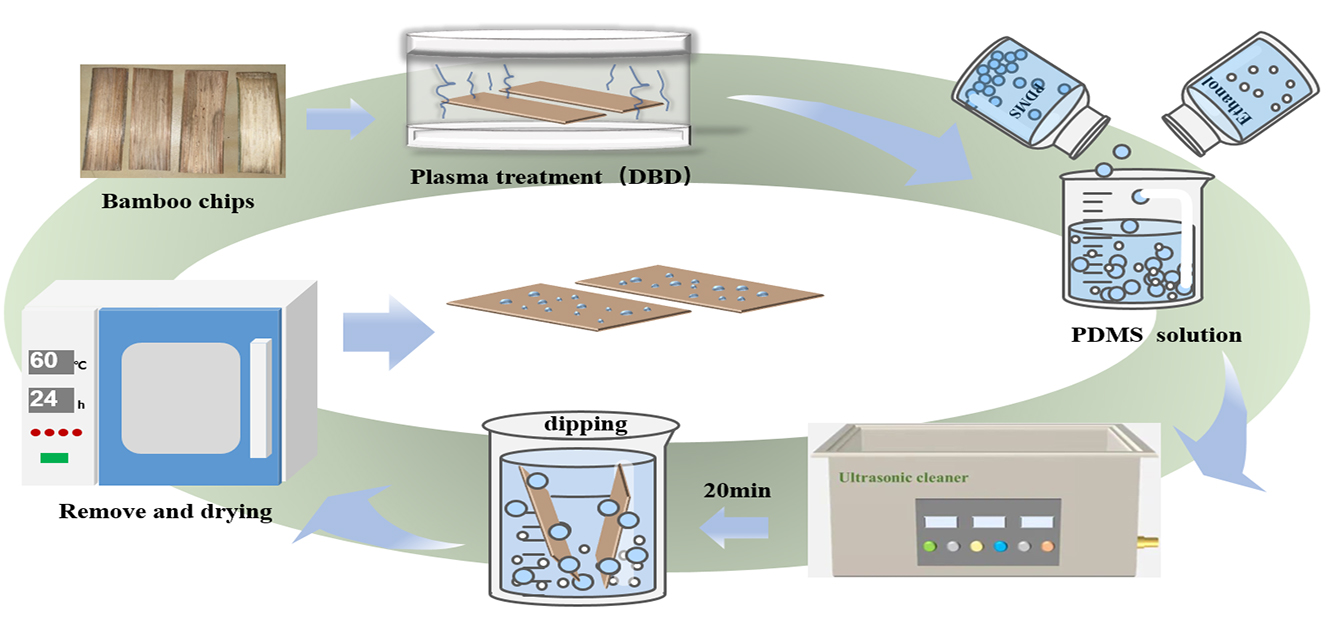
Herein, the surface of Moso bamboo was hydrophobically modified by combining O2/N2 plasma treatments with polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) solution treatment as the hydrophobic solution. The effects of plasma treatment process (power and time), PDMS solution concentration, and maceration time on the hydrophobic performance of bamboo specimens were studied, and the optimal treatment conditions for improving the hydrophobicity were determined. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), fourier transform infrared (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) were used to analyze the surface morphology, chemical structure, and functional groups in the specimens before and after the plasma and PDMS solution treatments under optimal conditions. Response surface analysis was also performed to determine the optimal treatment conditions. Results show that the hydrophobic performance of the Moso bamboo surface is effectively improved and the surface energy is reduced after the coordinated treatment. The optimal conditions for improving the hydrophobic performance of Moso bamboo surface are a treatment power of 800 W, treatment time of 15 s, O2 flow rate of 1.5 L/min, PDMS solution concentration of 5%, and maceration time of 60 min for O2 plasma treatment and a treatment power of 1000 W, treatment time of 15 s, N2 flow rate of 1.5 L/min, PDMS solution concentration of 5%, and maceration time of 60 min for N2 plasma treatment. After treatment, silicone oil particles and plasma etching traces are observed on the bamboo surface. Moreover, Si-O bonds in the PDMS solution are grafted to the bamboo surface via covalent bonds, thereby increasing the contact angle and decreasing the surface energy to achieve the hydrophobic effect.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools