 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
The SMAD2/miR-4256/HDAC5/p16INK4a signaling axis contributes to gastric cancer progression
1 Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Jinan University, Guangzhou, 510632, China
2 Department of Gastroenterology, Affiliated Hospital of Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities, Baise, 533000, China
3 Department of Gastroenterology, The First People’s Hospital of Zunyi, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi, 563099, China
4 Department of Gastroenterology, Shenzhen Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Shenzhen, 518104, China
5 Department of Gastroenterology, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, 510799, China
* Corresponding Author: SHAOHUI TANG. Email:
# These authors contributed equally to this work
Oncology Research 2023, 31(4), 515-541. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2023.029101
Received 06 February 2023; Accepted 11 April 2023; Issue published 25 June 2023
Abstract
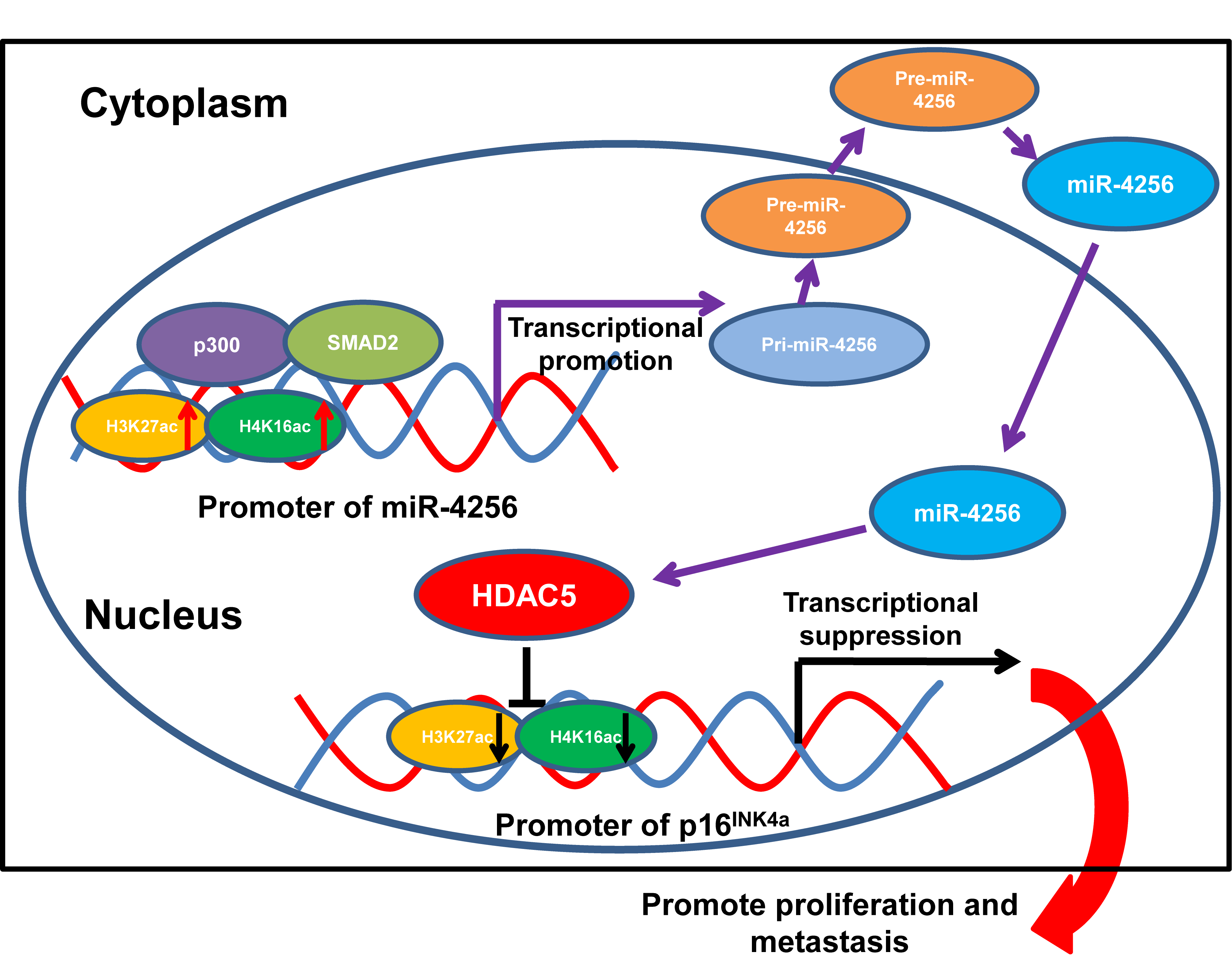
The dysregulation of exosomal microRNAs (miRNAs) plays a crucial role in the development and progression of cancer. This study investigated the role of a newly identified serum exosomal miRNA miR-4256 in gastric cancer (GC) and the underlying mechanisms. The differentially expressed miRNAs were firstly identified in serum exosomes of GC patients and healthy individuals using next-generation sequencing and bioinformatics. Next, the expression of serum exosomal miR-4256 was analyzed in GC cells and GC tissues, and the role of miR-4256 in GC was investigated by in vitro and in vivo experiments. Then, the effect of miR-4256 on its downstream target genes HDAC5/p16INK4a was studied in GC cells, and the underlying mechanisms were evaluated using dual luciferase reporter assay and Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP). Additionally, the role of the miR-4256/HDAC5/p16INK4a axis in GC was studied using in vitro and in vivo experiments. Finally, the upstream regulators SMAD2/p300 that regulate miR-4256 expression and their role in GC were explored using in vitro experiments. miR-4256 was the most significantly upregulated miRNA and was overexpressed in GC cell lines and GC tissues; in vitro and in vivo results showed that miR-4256 promoted GC growth and progression. Mechanistically, miR-4256 enhanced HDAC5 expression by targeting the promoter of the HDAC5 gene in GC cells, and then restrained the expression of p16INK4a through the epigenetic modulation of HDAC5 at the p16INK4a promoter. Furthermore, miR-4256 overexpression was positively regulated by the SMAD2/p300 complex in GC cells. Our data indicate that miR-4256 functions as an oncogene in GC via the SMAD2/miR-4256/HDAC5/p16INK4a axis, which participates in GC progression and provides novel therapeutic and prognostic biomarkers for GC.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools