 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Targeting HER2-Positive HCC1954 Breast Cancer Cells by Novel Thiazole-Dihydrobenzisoxazoles: In-Depth Design, Synthesis and Initial In Vitro Study
1 Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry, National Academy of Sciences of Belarus, Minsk, 220084, Belarus
2 Department of Experimental Tumor Biology, Blokhin N.N. National Medical Research Center of Oncology, Moscow, 115522, Russia
3 Health Institution “National Anti-Doping Laboratory”, Minsk, 223040, Belarus
4 Gause Institute of New Antibiotics, Moscow, 119021, Russia
* Corresponding Author: Alexander M. Scherbakov. Email:
Oncology Research 2025, 33(12), 4049-4072. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2025.067832
Received 13 May 2025; Accepted 22 August 2025; Issue published 27 November 2025
Abstract
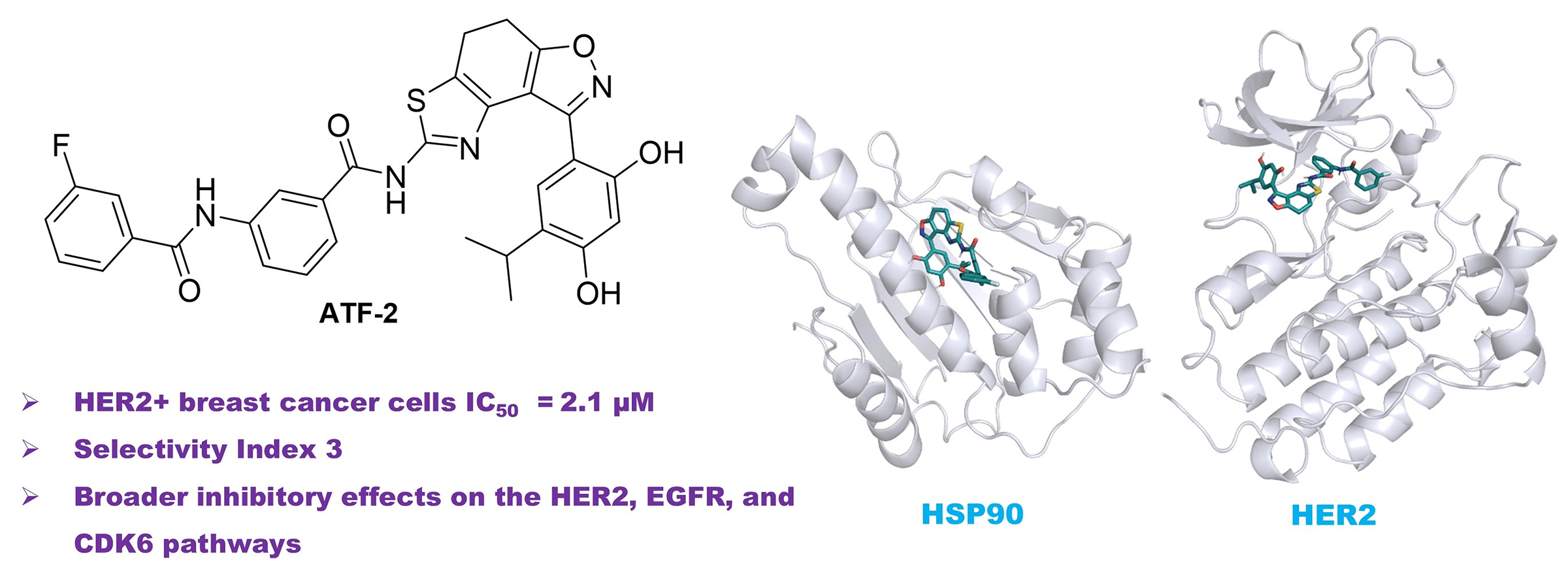
Background: The most aggressive forms of breast cancer are characterized by independence from steroid hormones but a strong dependence on growth factors. In such cancer cells, oncogenic receptors, including human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), are activated, and their targeted inhibition represents an attractive therapeutic strategy. The study aimed to develop small-molecule potential dual heat shock protein 90 (HSP90)-HER2 inhibitors and evaluate them as anticancer agents in HER2-positive cells. Methods: The research project involved obtaining a series of compounds with potential dual inhibitory activity against HSP90 and HER2 by targeted organic synthesis, which was preliminarily assessed using molecular modelling and calculation of key parameters of molecular dynamics. The potential therapeutic benefit of the obtained molecules was studied using basic molecular biological methods, including assessment of cytotoxic activity in vitro using the MTT test, as well as determination of a possible mechanism of action based on the expression of key participants in intracellular signaling (western blotting). Additionally, therapeutic combinations were developed and tested on a cellular model of the disease, including a lead compound and chemotherapeutic drugs used in clinical practice, in order to find synergistic pairs and improve the effectiveness of the treatment. Results: In this work, novel dual HSP90-HER2 inhibitors, based on the fused thiazole-dihydrobenzisoxazole polycyclic scaffold, were designed and synthesized. The resulting compounds exhibited strong antiproliferative activity against HER2-positive breast cancer cells with high selectivity. Among them, ATF-2 demonstrated antiproliferative activity comparable to HER2 inhibitor lapatinib and significantly suppressed HER2 expression and activity, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) activity, and cyclin-dependent kinase 6 (CDK6) expression in HCC1954 breast cancer cells. Conclusion: These findings highlight ATF-2 as a promising dual HSP90-HER2 inhibitor with broader inhibitory effects on the HER2, EGFR, and CDK6 pathways.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material FileCite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools