 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Tumor Vaccines for Malignant Melanoma: Progress, Challenges, and Future Directions
1 Department of Dermatology, Jinzhou Medical University, The First Affiliated Hospital of Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou, 121001, China
2 Department of Urology, Jinzhou Medical University, The First Affiliated Hospital of Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou, 121001, China
3 Department of Clinical Lab, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University (Zhejiang Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine), Hangzhou, 310060, China
4 Department of Pharmacy, The First People’s Hospital of Lin’an District, Hangzhou, Lin’an People’s Hospital Affiliated to Hangzhou Medical College, Hangzhou, 311399, China
5 Department of Postpartum Rehabilitation, The First People’s Hospital of Lin’an District, Hangzhou, Lin’an People’s Hospital Affiliated to Hangzhou Medical College, Hangzhou, 311399, China
* Corresponding Authors: Judong Song. Email: ; Yunzhen Ding. Email:
# These two authors contributed equally to this work
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: New Insights in Drug Resistance of Cancer Therapy: A New Wine in an Old Bottle)
Oncology Research 2025, 33(8), 1875-1893. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2025.063843
Received 25 January 2025; Accepted 16 April 2025; Issue published 18 July 2025
Abstract
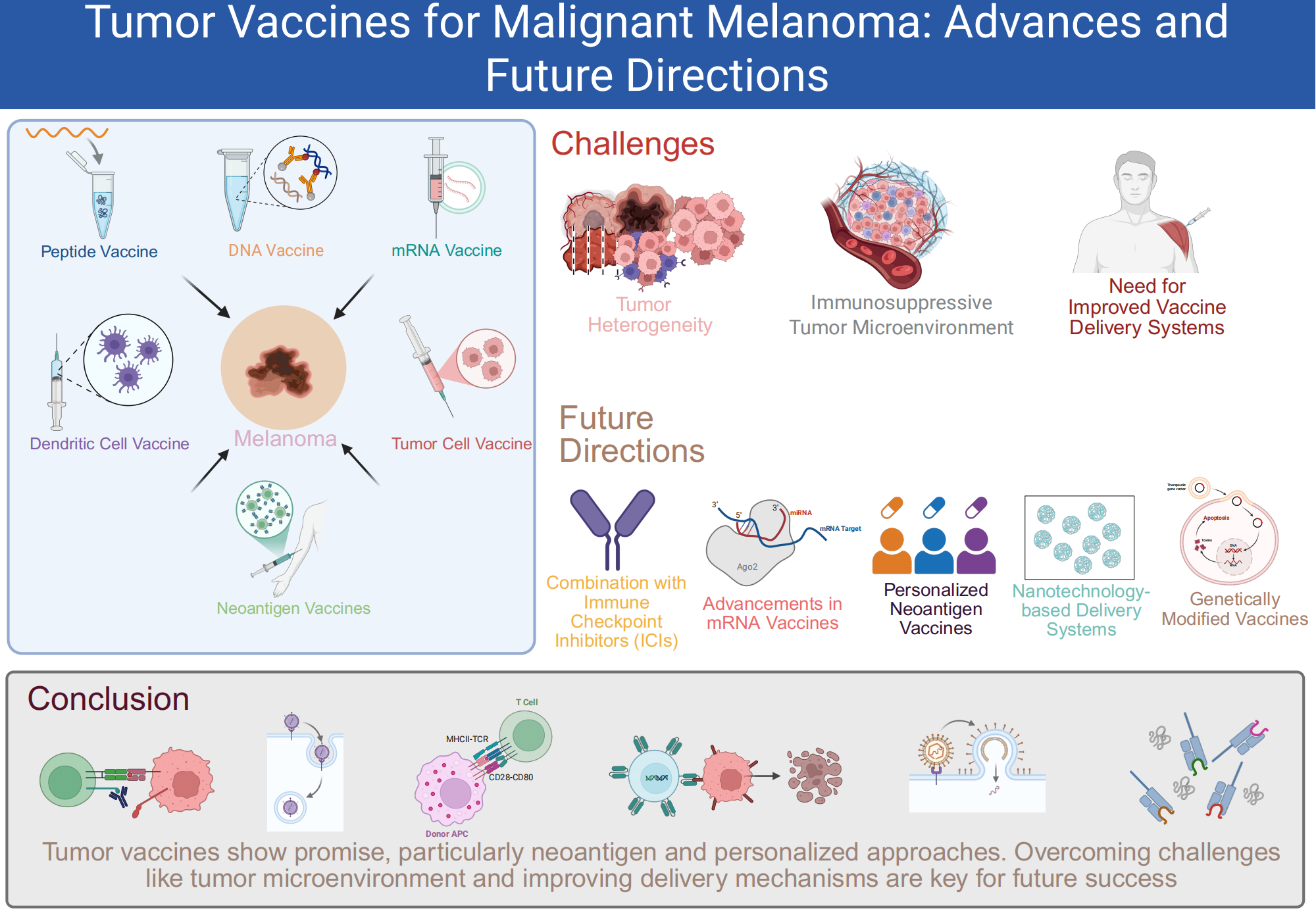
Malignant melanoma, characterized by its high metastatic potential and resistance to conventional therapies, presents a major challenge in oncology. This review explores the current status and advancements in tumor vaccines for melanoma, focusing on peptide, DNA/RNA, dendritic cell, tumor cell, and neoantigen-based vaccines. Despite promising results, significant challenges remain, including the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, patient heterogeneity, and the need for more effective antigen presentation. Recent strategies, such as combining vaccines with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), aim to counteract immune evasion and enhance T cell responses. Emerging approaches, including personalized neoantigen vaccines and the use of self-amplifying RNA platforms, hold promise for overcoming tumor heterogeneity and improving vaccine efficacy. Additionally, optimizing vaccine delivery systems through nanotechnology and genetic modifications is essential for increasing stability and scalability. This review highlights the potential of these innovative strategies to address current limitations, with a focus on how future research can refine and combine these approaches to improve melanoma treatment outcomes.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools