 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
VPS37A Activates the Autophagy-Lysosomal Pathway for TNFR1 Degradation and Induces NF-κB-Regulated Cell Death under Metabolic Stress in Colorectal Cancer
1 Cheeloo College of Medicine, Shandong University, Jinan, 250012, China
2 Department of Pathology, Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University, Jining Medical University, Jining, 272029, China
* Corresponding Authors: Yukun Liu. Email: ; Ran Zhao. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Unraveling cell death in solid tumors: single-cell & spatial transcriptomics illuminate therapeutic target)
Oncology Research 2025, 33(8), 2085-2105. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2025.065739
Received 20 March 2025; Accepted 29 April 2025; Issue published 18 July 2025
Abstract
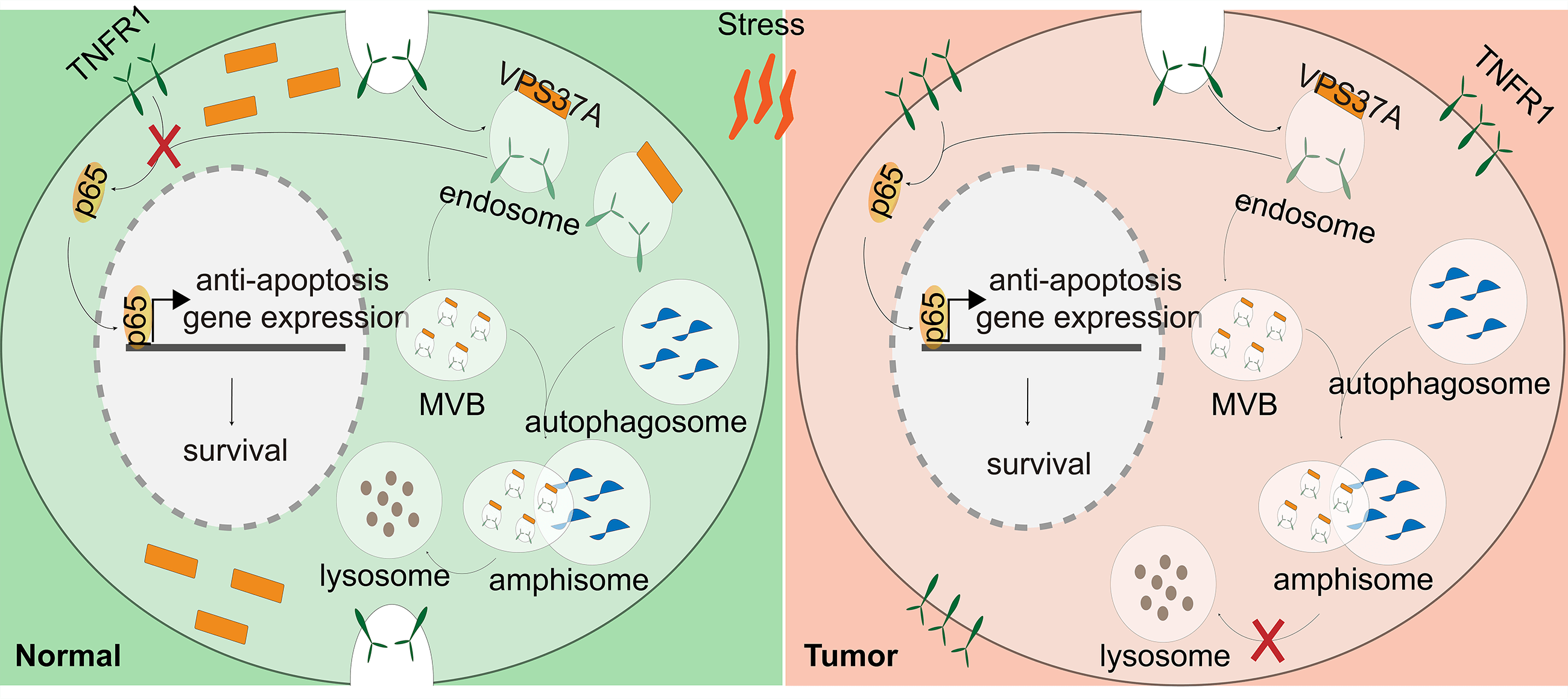
Background: VPS37A (VPS37A subunit of ESCRT-I), a component of the ESCRT-I (endosomal sorting complex required for transport I) complex, mediates vesicular trafficking through sorting endocytic ubiquitinated cargos into multivesicular bodies (MVBs). Although accumulating evidence indicates that VPS37A deficiency occurs in numerous malignancies and exerts tumor-suppressive effects during cancer progression, its functional significance in colorectal cancer (CRC) pathogenesis remains poorly characterized. Therefore, this study aims to further investigate the functional and molecular mechanisms by which VPS37A downregulation contributes to malignant biological phenotypes in CRC, with a specific focus on how its dysregulation affects cell death pathways. Methods: Multi-omics analysis of TCGA, GEO, and CPTAC cohorts identified VPS37A as a downregulated tumor suppressor gene in CRC. The prognostic relevance of VPS37A was validated in two clinical cohorts (Cohorts 1 and 2) using immunohistochemistry. Functional assays in VPS37A-overexpressing CRC cells and xenografts assessed proliferation, cell cycle progression, and stress-induced cell death. RNA sequencing, nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) luciferase reporter assays, and lysosomal inhibition experiments elucidated the mechanisms underlying tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNFR1) degradation. Results: VPS37A is significantly downregulated in advanced-stage CRC and independently predicts poor survival. Functionally, VPS37A overexpression suppresses proliferation and induces G2/M arrest in vitro, while reducing xenograft growth. Under metabolic stress (glucose deprivation/galactose adaptation), VPS37A triggers cell death via apoptosis, necroptosis, and ferroptosis. Mechanistically, VPS37A redirects TNFR1 to lysosomal degradation, suppressing NF-κB nuclear translocation and transcriptional activity. Conclusion: VPS37A deficiency drives CRC progression by sustaining TNFR1/NF-κB signaling under metabolic stress. Restoring VPS37A activity promotes TNFR1 degradation, offering a therapeutic strategy to counteract NF-κB-mediated treatment resistance in CRC.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material FileCite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools